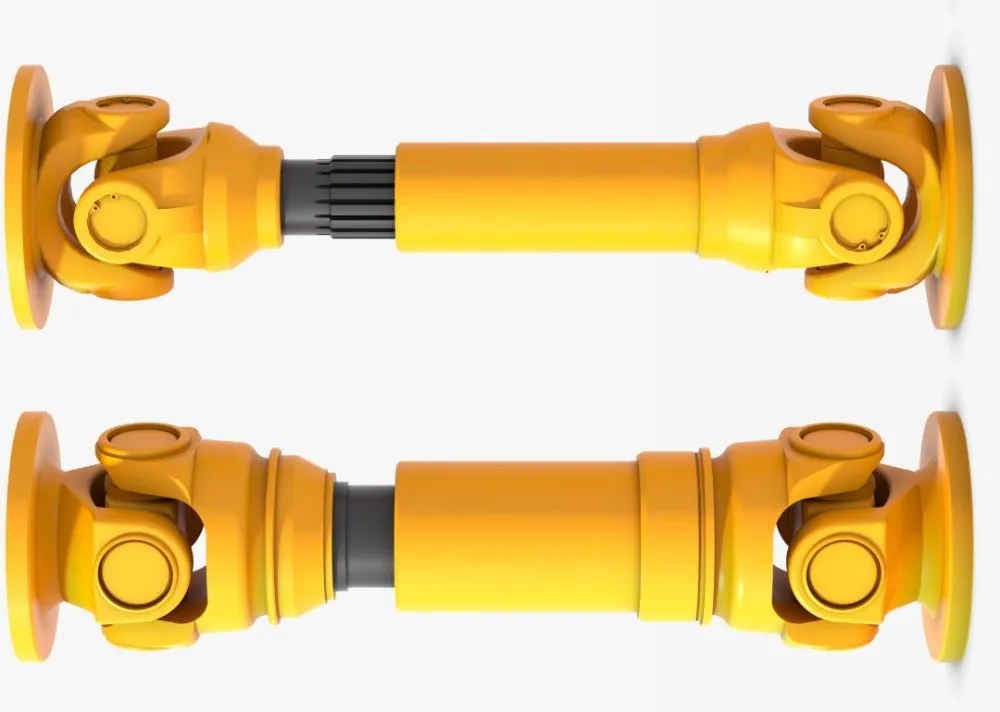
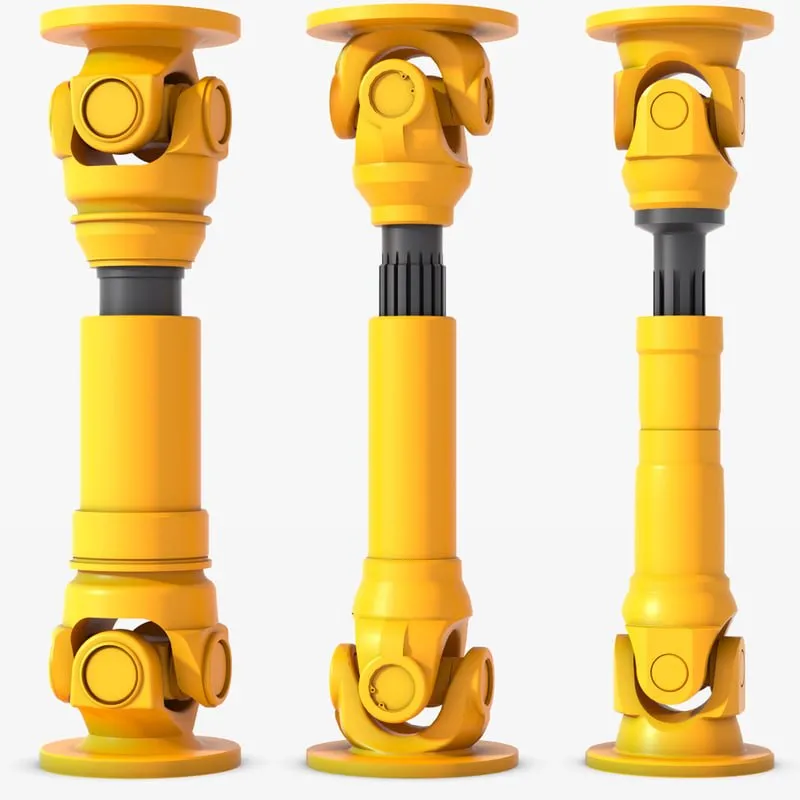
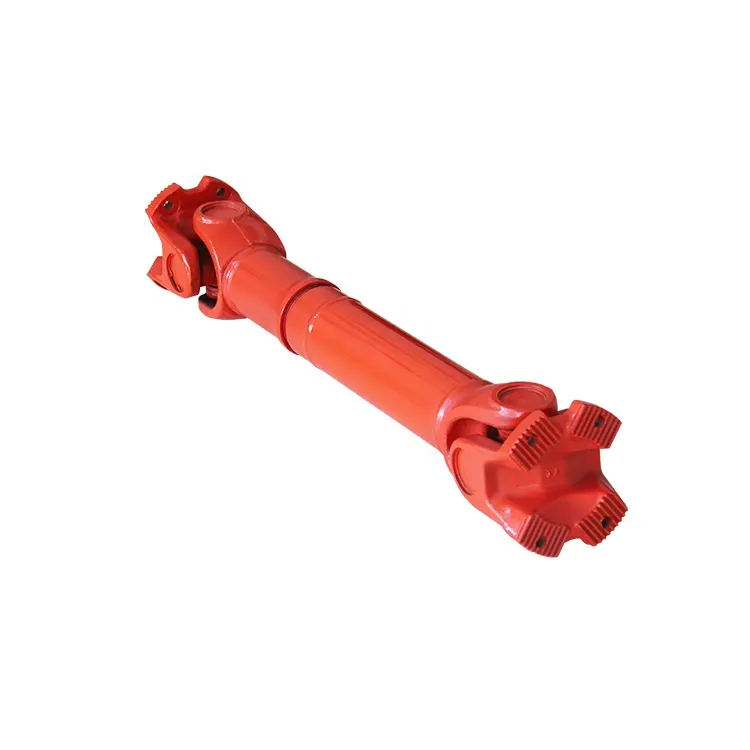
Product Description
WS Type Universal Joint Shaft
Features:
1. It is suitable for transmission coupling space on the same plane of 2 axis angle beta β≤45°, the nominal torque transmission 11.2-1120N.
2.The WSD type is a single cross universal coupling, and the WS type is a double cross universal coupling.
3.Each section between the largest axis angle 45º.
4.The finished hole H7, according to the requirements of keyseating, 6 square hole and square hole.
5.The angle between the 2 axes is allowed in a limited range as the work requirements change.
|
NO |
Tn/N·m |
d(H7) |
D |
L0 |
L |
L1 |
m/kg |
I/kg·m2 |
||||||||||
|
WSD |
WS |
WSD |
WS |
WSD |
WS |
|||||||||||||
|
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
|||||
|
WS1 WSD1 |
11.2 |
8 |
16 |
60 |
– |
80 |
– |
20 |
– |
20 |
0.23 |
– |
0.32 |
– |
0.06 |
– |
0.08 |
– |
|
9 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
10 |
66 |
60 |
86 |
80 |
25 |
22 |
0.2 |
0.29 |
0.05 |
0.07 |
||||||||
|
WS2 WSD2 |
22.4 |
10 |
20 |
70 |
64 |
96 |
90 |
26 |
0.64 |
0.57 |
0.93 |
0.88 |
0.1 |
0.09 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
||
|
11 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
12 |
84 |
74 |
110 |
100 |
32 |
27 |
||||||||||||
|
WS3 WSD3 |
45 |
12 |
25 |
90 |
80 |
122 |
112 |
32 |
1.45 |
1.3 |
2.1 |
1.95 |
0.17 |
0.15 |
0.24 |
0.22 |
||
|
14 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS4 WSD4 |
71 |
16 |
32 |
116 |
82 |
154 |
130 |
42 |
30 |
38 |
5.92 |
4.86 |
8.56 |
0.48 |
0.39 |
0.32 |
0.56 |
0.49 |
|
18 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS5 WSD5 |
140 |
19 |
40 |
144 |
116 |
192 |
164 |
48 |
16.3 |
12.9 |
24 |
20.6 |
0.72 |
0.59 |
1.04 |
0.91 |
||
|
20 |
52 |
38 |
||||||||||||||||
|
22 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS6 WSD6 |
280 |
24 |
50 |
152 |
124 |
210 |
182 |
52 |
38 |
58 |
45.7 |
36.7 |
68.9 |
59.7 |
1.28 |
1.03 |
1.89 |
1.64 |
|
25 |
172 |
136 |
330 |
194 |
62 |
44 |
||||||||||||
|
28 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS7 WSD7 |
560 |
30 |
60 |
226 |
182 |
296 |
252 |
82 |
60 |
70 |
148 |
117 |
207 |
177 |
2.82 |
2.31 |
3.9 |
3.38 |
|
32 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
35 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS8 WSD8 |
1120 |
38 |
75 |
240 |
196 |
332 |
288 |
92 |
396 |
338 |
585 |
525 |
5.03 |
4.41 |
7.25 |
6.63 |
||
|
40 |
300 |
244 |
392 |
336 |
112 |
84 |
||||||||||||
|
42 |
||||||||||||||||||
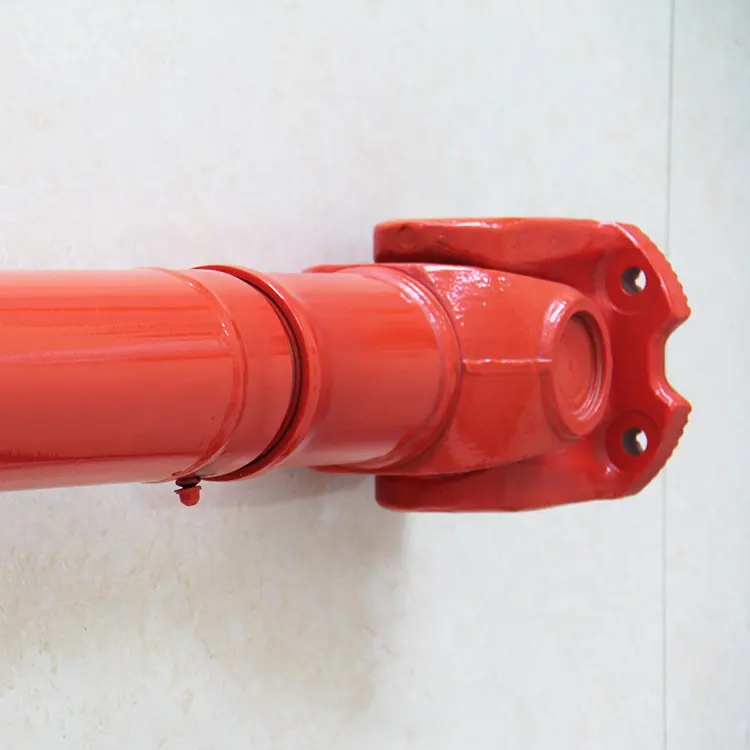
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
HangZhou CHINAMFG Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the design and manufacture of various types of coupling. There are 86 employees in our company, including 2 senior engineers and no fewer than 20 mechanical design and manufacture, heat treatment, welding, and other professionals.
Advanced and reasonable process, complete detection means. Our company actively introduces foreign advanced technology and equipment, on the basis of the condition, we make full use of the advantage and do more research and innovation. Strict to high quality and operate strictly in accordance with the ISO9000 quality certification system standard mode.
Our company supplies different kinds of products. High quality and reasonable price. We stick to the principle of “quality first, service first, continuous improvement and innovation to meet the customers” for the management and “zero defect, zero complaints” as the quality objective.
Our Services
1. Design Services
Our design team has experience in Cardan shafts relating to product design and development. If you have any needs for your new product or wish to make further improvements, we are here to offer our support.
2. Product Services
raw materials → Cutting → Forging →Rough machining →Shot blasting →Heat treatment →Testing →Fashioning →Cleaning→ Assembly→Packing→Shipping
3. Samples Procedure
We could develop the sample according to your requirement and amend the sample constantly to meet your need.
4. Research & Development
We usually research the new needs of the market and develop new models when there are new cars in the market.
5. Quality Control
Every step should be a particular test by Professional Staff according to the standard of ISO9001 and TS16949.
FAQ
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing
various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all customers with customized PDF or AI format artwork.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: Do you provide samples? Is it free or extra?
Yes, we could offer the sample but not for free. Actually, we have an excellent price principle, when you make the bulk order the cost of the sample will be deducted.
Q 5: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 6: What is the MOQ?
A: Usually our MOQ is 1pcs.
Q 7: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 8: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory.
Q 9: What’s your payment?
A:1) T/T.
♦Contact Us
Web: huadingcoupling
Add: No.11 HangZhou Road,Chengnan park,HangZhou City,ZheJiang Province,China
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 14mm |
| Speed: | 9000r/M |
| Structure: | Flexible |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
Can cardan joints be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment. Cardan joints, also known as universal joints, are versatile mechanical couplings that transmit torque between misaligned shafts. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of why cardan joints can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment:
- Torque Transmission: Cardan joints are capable of transmitting high levels of torque between misaligned shafts. This makes them well-suited for heavy-duty applications that require the transfer of substantial power. The design of the joint allows for smooth torque transmission, even in cases where the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
- Misalignment Compensation: In heavy-duty machinery and equipment, misalignments between shafts can occur due to factors such as thermal expansion, vibration, or structural flexing. Cardan joints excel at compensating for such misalignments. Their flexible design accommodates angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, allowing for reliable operation in challenging industrial environments.
- Durability and Strength: Heavy-duty machinery and equipment often operate under demanding conditions, subjecting components to high loads and harsh environments. Cardan joints are typically constructed from durable materials such as alloy steels, which provide excellent strength and resistance to fatigue and wear. This durability enables them to withstand the heavy loads and prolonged operation associated with heavy-duty applications.
- Compact Design: Cardan joints have a compact design, which is advantageous in heavy-duty machinery and equipment where space constraints may be present. Their compactness allows for efficient installation and integration within the system, making them suitable for applications where minimizing size and weight is important.
- Versatility: Cardan joints are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different heavy-duty applications. They can be customized to meet specific torque and speed requirements, making them versatile for use in a wide range of machinery and equipment, including industrial machinery, construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and more.
While cardan joints are generally suitable for heavy-duty applications, it is important to consider certain factors to ensure optimal performance. These factors include proper selection of the joint size and type based on the application requirements, adherence to specified torque and speed limits, regular maintenance to prevent wear and ensure proper lubrication, and consideration of any environmental factors that may affect the joint’s performance.
In summary, cardan joints can indeed be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment due to their excellent torque transmission capabilities, ability to compensate for misalignments, durability, compact design, and versatility. By considering the specific requirements of the application and following appropriate maintenance practices, cardan joints can provide reliable and efficient operation in heavy-duty industrial settings.

Can cardan joints be used in industrial machinery and manufacturing?
Yes, cardan joints are commonly used in industrial machinery and manufacturing applications due to their versatility, durability, and ability to transmit torque at various angles. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Torque Transmission: Industrial machinery often requires the transmission of torque between different components or shafts that may not be in a perfectly aligned position. Cardan joints excel at transmitting torque even at significant angles and misalignments, allowing for flexible power transmission in industrial applications. They can efficiently transfer high torque loads and handle varying operating conditions.
2. Misalignment Compensation: Cardan joints are designed to accommodate misalignments and angular variations, making them ideal for industrial machinery. They can compensate for misalignments caused by structural deflection, thermal expansion, or other factors, ensuring smooth and reliable power transmission. This capability helps to minimize stress and wear on connected components and extends the life of the machinery.
3. Flexibility and Articulation: Industrial machinery often requires flexibility and articulation to adapt to different production processes or accommodate dynamic movements. Cardan joints provide rotational freedom and allow for angular movement, enabling the machinery to adjust to changing requirements. Their universal joint design allows for smooth rotation and accommodates the required range of motion.
4. Compact Design: Cardan joints have a relatively compact design, making them suitable for integration into industrial machinery where space is often limited. Their compact size allows for efficient packaging within the machinery, optimizing overall design and minimizing footprint. This is especially beneficial in applications where multiple joints are required within a confined space.
5. Durability and Strength: Industrial machinery operates under demanding conditions, including heavy loads, high speeds, and harsh environments. Cardan joints are often constructed using durable materials such as alloy steels or high-strength alloys, providing the necessary strength and resilience to withstand industrial applications. They are designed to handle the demanding loads and forces encountered in manufacturing processes.
6. Easy Maintenance and Serviceability: Cardan joints are generally low-maintenance components. They require periodic inspection, lubrication, and replacement of worn parts, but their design often allows for easy access and replacement if needed. This facilitates maintenance activities and minimizes downtime in industrial machinery.
7. Versatility: Cardan joints are available in various configurations, sizes, and load capacities, allowing them to be tailored to specific industrial machinery requirements. They can be customized to accommodate different shaft sizes, torque ratings, and mounting arrangements, making them adaptable to a wide range of manufacturing applications.
8. Cost-Effectiveness: Cardan joints offer a cost-effective solution for torque transmission in industrial machinery. Their durability, reliability, and long service life contribute to reduced maintenance and replacement costs. Additionally, their ability to compensate for misalignments can help minimize wear on other machinery components, further reducing overall maintenance expenses.
When integrating cardan joints into industrial machinery and manufacturing systems, it is important to consider the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and load characteristics. Proper design, selection, and installation practices should be followed to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Consulting with engineers or experts specializing in drivetrain systems and industrial machinery design can provide valuable insights and guidance on the selection, integration, and maintenance of cardan joints for specific industrial applications.

What are the applications of a cardan joint?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, has a wide range of applications across various industries. Its ability to transmit rotational motion and accommodate misalignment between shafts makes it suitable for different systems and machines. Here’s a detailed explanation of the applications of a cardan joint:
- Automotive Drivetrains: One of the primary applications of cardan joints is in automotive drivetrains. They are used in vehicles with rear-wheel drive, all-wheel drive, and four-wheel drive systems. Cardan joints help transmit power from the engine to the driveshaft, allowing the rotational motion to be transferred to the rear axle or all four wheels. They provide flexibility and compensation for misalignment between the engine, transmission, and rear differential.
- Industrial Machinery: Cardan joints find extensive use in various industrial machinery applications. They are commonly employed in power transmission systems, especially when there is a need to transmit rotational motion between non-collinear shafts. Cardan joints are used in conveyor systems, printing presses, machine tools, pumps, mixers, and many other industrial machines that require efficient transmission of rotational power.
- Aerospace and Aviation: Cardan joints have applications in the aerospace and aviation industries. They are used in aircraft control systems, such as the control linkages between the control surfaces (elevator, rudder, ailerons) and the cockpit controls. Cardan joints allow for the transmission of pilot input to the control surfaces while accommodating any misalignment or changes in angles during flight.
- Marine Propulsion: In marine applications, cardan joints are utilized in propulsion systems. They are commonly used in boat drivetrains to transfer rotational motion from the engine to the propeller shaft. Cardan joints enable the engine to be mounted at an angle or in a different position from the propeller shaft, compensating for the misalignment that can arise due to the boat’s hull shape and design.
- Railway Systems: Cardan joints play a role in railway systems, particularly in drivetrains and couplings. They are used in locomotives and train cars to transfer rotational motion between different components, such as the engine, gearbox, and wheel axle. Cardan joints provide flexibility and accommodate misalignment that may occur due to the movement and articulation of train cars on curved tracks.
- Mining and Construction Equipment: Cardan joints are employed in heavy-duty mining and construction equipment. They are used in applications such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and off-highway trucks. Cardan joints help transmit power and motion between different components of these machines, allowing them to operate efficiently and withstand the demanding conditions of mining and construction environments.
- Industrial Robotics: Cardan joints find applications in industrial robotics and automation. They are used in robotic arms and manipulators to transmit rotational motion between different segments or joints of the robotic system. Cardan joints enable precise and flexible movement, allowing robots to perform complex tasks in manufacturing, assembly, and other industrial processes.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of cardan joints. Their ability to handle misalignment, transmit rotational motion at varying angles, and provide flexibility make them a fundamental component in numerous systems and machines across industries.


editor by CX 2024-05-07
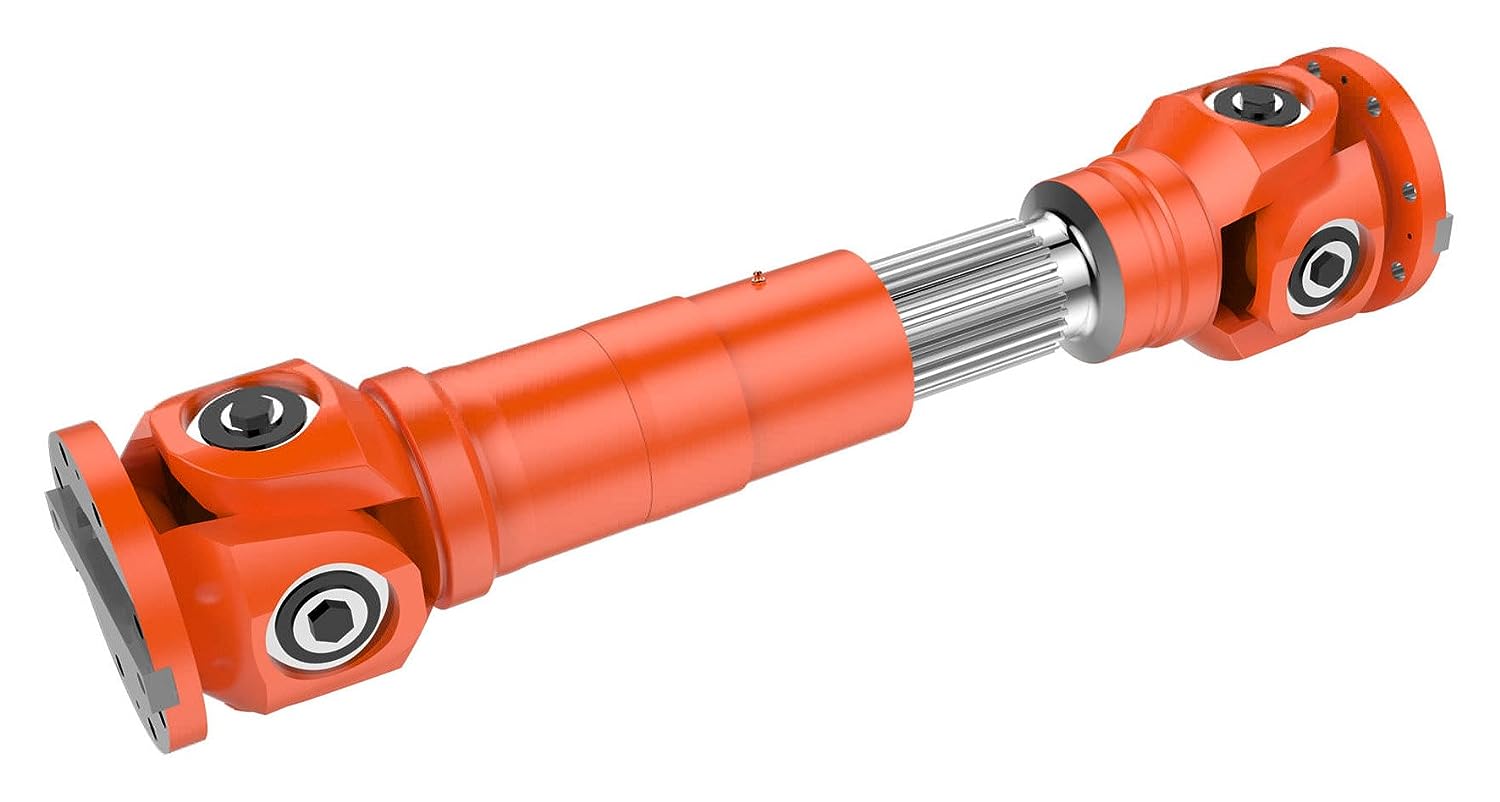
China supplier SWC-Wd Type Coupling Nontelescopic Shorten Cardan Shaft Coupling Universal Joint
Product Description
SWC-WD type coupling Nontelescopic Shorten Cardan Shaft Coupling
Product Description
SWC-WD-type cross shaft universal coupling is 1 of the most common coupling. With its characteristic structure enables not on the same axis or the axis angle greater or axial movement of a larger two-axis continuous constant angular velocity rotation, and reliably transmit torque and motion. Can be widely used in metallurgy, lifting, engineering, transportation, mining, oil, shipbuilding, coal, rubber, paper machinery and other heavy machinery industry, mechanical shafting transmitting torque.
Product Parameters
Advantages
1. The ability to have a large angle compensation.
2. The structure is compact and reasonable. SWC-WD type with integral fork, so carrying more reliable.
3. The carrying capacity. Compared with other types of the same diameter rotary joint axis, it delivers more torque, the turning diameter of restricted mechanical equipment, the complete range is more advantageous.
4. High transmission efficiency. Its transmission efficiency of 98-99.8% for high-power transmission, energy-saving effect.
5. carrying smooth, low noise, easy maintenance, assembly and disassembly.
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing
various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks in PDF or AI format.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 5: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 6: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 19mm |
| Speed: | 4000r/M |
| Structure: | Rigid |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the potential limitations or drawbacks of using cardan joints?
While cardan joints offer numerous advantages in transmitting rotational motion between misaligned shafts, they also have certain limitations and drawbacks to consider. Here are some potential limitations associated with the use of cardan joints:
- Angular Limitations: Cardan joints have limited angularity or operating angles. They are designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and exceeding these angles can cause accelerated wear, increased vibration, and potential joint failure. Extreme operating angles can lead to binding, decreased efficiency, and reduced power transmission capacity. In applications where large operating angles are required, alternative flexible coupling mechanisms or constant velocity joints may be more suitable.
- Backlash and Torsional Stiffness: Cardan joints inherently exhibit some degree of backlash, which is the clearance or free play between the mating components. This can result in a slight delay in power transmission and can affect the precision of motion in certain applications. Additionally, cardan joints may have higher torsional stiffness compared to other coupling mechanisms, which can transmit higher vibrations and shocks to the connected components.
- Maintenance Requirements: Cardan joints require regular maintenance to ensure proper lubrication, alignment, and performance. The lubricant needs to be regularly replenished or replaced, and the joint should be inspected for wear, misalignment, or other issues. Failure to perform adequate maintenance can result in premature wear, reduced efficiency, and potential joint failure. Maintenance procedures may require specialized tools and expertise.
- Space and Weight: Cardan joints can occupy a significant amount of space due to their design and the need for perpendicular shafts. In applications with limited space constraints, finding suitable locations for cardan joints can be challenging. Additionally, the weight of cardan joints, especially in heavy-duty applications, can add to the overall weight of the system, which may have implications for fuel efficiency, payload capacity, or overall performance.
- Cost: Cardan joints, particularly high-quality and precision-engineered ones, can be relatively expensive compared to other coupling mechanisms. The complex design, manufacturing tolerances, and specialized materials involved contribute to their higher cost. In cost-sensitive applications, alternative coupling solutions may be considered if the angular limitations and other drawbacks of cardan joints are not critical.
- High-Speed Limitations: At high rotational speeds, cardan joints can experience increased vibration, imbalance, and potential for fatigue failure. The rotating components of the joint can generate centrifugal forces that impact the balance and stability of the system. In high-speed applications, careful design considerations, including balancing and vibration analysis, may be necessary to mitigate these issues.
It is important to evaluate the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and limitations when considering the use of cardan joints. While they offer versatility and flexibility in many scenarios, alternative coupling mechanisms may be more suitable in cases where the limitations and drawbacks of cardan joints pose significant challenges.

How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint?
When retrofitting an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint, careful planning and consideration of various factors are necessary to ensure a successful integration. The retrofitting process involves modifying the system to accommodate the cardan joint’s requirements for torque transmission and misalignment compensation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to retrofit an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint:
- Evaluate the Existing System: Begin by thoroughly evaluating the existing mechanical system to understand its design, components, and operational requirements. Identify the areas where a cardan joint can be integrated effectively and assess the feasibility of retrofitting.
- Identify the Integration Points: Determine the specific locations within the system where the cardan joint will be installed. This could include areas where torque transmission or misalignment compensation is required, such as connections between shafts, pulleys, or other rotating components.
- Measurements and Compatibility: Take accurate measurements of the existing components and spaces where the cardan joint will be installed. Ensure that the dimensions and specifications of the cardan joint are compatible with the available space and the system’s requirements. Consider factors such as shaft sizes, torque ratings, misalignment angles, and operating conditions.
- Design Modifications: Based on the evaluation and measurements, make necessary design modifications to accommodate the cardan joint. This may involve modifying shaft ends, adding or removing components, or adjusting mounting positions. Ensure that the modifications do not compromise the structural integrity or functionality of the system.
- Installation and Alignment: Install the cardan joint at the identified integration points according to the manufacturer’s guidelines and engineering best practices. Pay attention to proper alignment, ensuring that the joint aligns with the shafts and other connected components. Precise alignment is crucial for efficient torque transmission and to prevent excessive wear or failure.
- Secure Mounting: Properly secure the cardan joint to the system, ensuring that it is firmly and securely mounted. Use appropriate fasteners, couplings, or brackets to hold the joint in place and prevent any movement or vibration that could affect its performance.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication and maintenance of the cardan joint. Proper lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the joint. Establish a maintenance schedule to regularly inspect and maintain the retrofit components to prevent any potential issues.
- Testing and Validation: After the retrofitting is complete, perform thorough testing to validate the functionality and performance of the retrofitted system. Test for torque transmission, misalignment compensation, and overall system operation. Monitor the system during operation to ensure that the cardan joint performs as expected and does not introduce any adverse effects.
It is essential to consult with experienced engineers or professionals specializing in retrofitting and cardan joint applications during the process. They can provide valuable guidance, expertise, and assistance in selecting the appropriate cardan joint, making design modifications, and ensuring a successful retrofit of the existing mechanical system.

How is a cardan joint different from other types of universal joints?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, is a specific type of universal joint design. While there are different variations of universal joints, the cardan joint has distinct characteristics that set it apart from other types. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a cardan joint differs from other universal joints:
1. Design and Structure: The cardan joint consists of two yokes and a cross-shaped member called the cross or spider. The yokes are typically fork-shaped and attached to the shafts, while the cross sits in the center, connecting the yokes. In contrast, other types of universal joints, such as the constant-velocity (CV) joint or Rzeppa joint, have different designs and structures. CV joints often use a combination of bearings and balls to transmit motion and maintain constant velocity, making them suitable for applications requiring smooth rotation without speed fluctuations.
2. Misalignment Compensation: One of the primary functions of a cardan joint is to accommodate misalignment between shafts. It can handle angular misalignment, axial misalignment, or a combination of both. The design of the cardan joint allows for the tilting of the cross as the input and output shafts rotate at different speeds. This tilting action compensates for misalignment and allows the joint to transmit motion. Other types of universal joints, such as the Oldham coupling or Hooke’s joint, have different mechanisms for compensating misalignment. For example, the Oldham coupling uses sliding slots and intermediate disks to accommodate misalignment, while Hooke’s joint uses a combination of rotating links and flexible connections.
3. Operating Range: Cardan joints are commonly used in applications where a wide range of operating angles is required. They can effectively transmit motion and torque at various angles, making them suitable for applications with non-collinear shafts. Other types of universal joints may have specific limitations or operating ranges. For instance, some types of CV joints are designed for constant velocity applications and are optimized for specific operating angles or speed ranges.
4. Applications: Cardan joints find applications in various industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, and more. They are commonly used in drivetrain systems, power transmission systems, and applications that require flexibility, misalignment compensation, and reliable motion transmission. Other types of universal joints have their own specific applications. For example, CV joints are commonly used in automotive applications, particularly in front-wheel drive systems, where they provide smooth and constant power transmission while accommodating suspension movements.
5. Limitations: While cardan joints offer flexibility and misalignment compensation, they also have certain limitations. At extreme operating angles, cardan joints can introduce non-uniform motion, increased vibration, backlash, and potential loss of efficiency. Other types of universal joints may have their own limitations and considerations depending on their specific design and application requirements.
In summary, a cardan joint, or universal joint, is a specific type of universal joint design that can accommodate misalignment between shafts and transmit motion at various angles. Its structure, misalignment compensation mechanism, operating range, and applications differentiate it from other types of universal joints. Understanding these distinctions is crucial when selecting the appropriate joint for a specific application.


editor by CX 2024-04-25
China supplier 38X83mm SWC100 Cross Joint for Medium-Duty Cardan Shaft
Product Description
Specification OF Universal Joint —Speedway:
Product Description
Drive Shaft Description:
| Item | 38X83mm SWC100 Cross Joint For Medium-Duty Cardan Shaft |
| OEM | SWC100 |
| Material | 20Cr or 20CrMnTi |
| Use | After market |
| MOQ | 10 cps |
| Similar recomanded | ( 5-345X 5-303X 5-356X 5-328X 5-329X 5-330X 5-331X 5-347X 5-348X 5-5154X 5-2031X) |
We provide propeller shaft OEM service and we can also produce propeller shaft according to your samples and drawings.
Package and Delivery:
Neutral Packing Or Customerized Packing.
We accept customerized brand packing if the quantity is good.
Neutral Packing means each propeller shaft is packed with foam polybags, then it will be put into box, and all propeller shafts are packed in cartons finally.
All of the products are well packed.
Delivery time is 35-45 days as normal.
Packing show
Company Profile
Certifications
FAQ
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Condition: | New |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you address noise issues in a cardan joint?
Noise issues in a cardan joint can arise due to various factors such as misalignment, improper lubrication, wear, or imbalance. Addressing these noise issues requires a systematic approach to identify and rectify the underlying causes. Here’s a detailed explanation of the steps involved in addressing noise issues in a cardan joint:
- Inspection and Diagnosis: The first step is to visually inspect the cardan joint and surrounding components to identify any visible signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Additionally, examining the joint during operation can help pinpoint the source of the noise. Noise can originate from the joint itself, the connected components, or the supporting structure.
- Misalignment Correction: Misalignment is a common cause of noise in cardan joints. If misalignment is detected, it is essential to correct it by adjusting the alignment of the joint and the connected components. This may involve realigning the shafts or adjusting the mounting positions to ensure proper alignment. Precision alignment techniques should be employed to minimize misalignment and reduce noise.
- Lubrication Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction and noise in a cardan joint. Inadequate lubrication or using incorrect lubricants can lead to increased friction, wear, and noise. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding lubrication intervals and use lubricants specifically designed for cardan joints. Regular lubrication maintenance should be carried out to ensure optimal lubrication and minimize noise generation.
- Wear Assessment and Replacement: Wear of the joint components, such as bearings or bushings, can contribute to noise issues. If wear is detected during the inspection, it is necessary to assess the extent of wear and determine if component replacement is required. Worn-out components should be replaced with new ones of appropriate quality and specifications to restore proper functionality and reduce noise.
- Balancing: Imbalance in the rotating components of the cardan joint, such as the driveshaft, can result in noise and vibrations. Balancing the rotating parts can help minimize these issues. Dynamic balancing techniques, either during manufacturing or through precision balancing procedures, can be employed to achieve smoother operation and reduce noise levels.
- Noise Dampening Measures: In some cases, additional noise dampening measures may be necessary to address persistent noise issues. This can involve the use of vibration-dampening materials, such as rubber bushings or vibration isolators, at the connection points of the joint. These measures help absorb and dampen vibrations, reducing noise transmission to the surrounding structure.
By systematically addressing these factors, it is possible to mitigate noise issues in a cardan joint. It is important to consider the specific conditions and requirements of the application and consult with experts or the manufacturer if needed to ensure appropriate corrective actions are taken.

Can cardan joints be used in off-road vehicles and equipment?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in off-road vehicles and equipment, and they are commonly employed in various drivetrain and power transmission applications. Cardan joints offer several characteristics that make them suitable for off-road environments. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Misalignment Compensation: Off-road vehicles and equipment often encounter uneven terrain, which can result in misalignments between the drivetrain components. Cardan joints are designed to accommodate misalignments and angular variations, allowing for smooth power transmission even in challenging off-road conditions. They can compensate for misalignments caused by suspension articulation, vehicle flexing, and uneven ground surfaces.
2. High Torque Transmission: Off-road vehicles and equipment typically require the transfer of high torque from the engine to the wheels or other driven components. Cardan joints are capable of efficiently transmitting torque even at significant angles, enabling robust power delivery in off-road applications. They can handle the torque demands associated with climbing steep inclines, traversing obstacles, and powering heavy equipment.
3. Durability and Strength: Off-road environments can be harsh, subjecting drivetrain components to extreme conditions such as impacts, vibrations, and debris. Cardan joints are often constructed using durable materials such as alloy steels or high-strength alloys, which provide the necessary strength and resilience to withstand the rigors of off-road use. They are designed to handle the demanding loads and forces encountered in rough terrains.
4. Articulation and Flexibility: Off-road vehicles and equipment require articulation and flexibility to navigate uneven surfaces and challenging obstacles. Cardan joints offer rotational freedom and allow for angular movement, enabling the drivetrain to adapt to varying terrains and maintain consistent power transmission. Their universal joint design allows for smooth rotation and accommodates the required range of motion.
5. Compact Design: Cardan joints have a relatively compact design, making them suitable for integration into the limited space available in off-road vehicles and equipment. Their compact size allows for efficient packaging within the drivetrain system, maximizing ground clearance, and optimizing vehicle or equipment design.
6. Maintenance and Serviceability: Cardan joints are generally robust and require minimal maintenance. However, regular inspection and lubrication are necessary to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Their design often allows for easy access and replacement if needed, facilitating maintenance and minimizing downtime in off-road applications.
It’s important to note that while cardan joints offer advantages for off-road vehicles and equipment, their performance and suitability depend on specific application requirements, loads, operating conditions, and other factors. Careful consideration should be given to selecting the appropriate cardan joint size, material, and design based on the anticipated demands of the off-road application.
When incorporating cardan joints into off-road vehicles and equipment, it is advisable to consult with engineers or experts specializing in drivetrain systems and off-road vehicle design. They can provide valuable insights and guidance on the selection, integration, and maintenance of cardan joints for specific off-road applications.

Are there different types of cardan joints available?
Yes, there are different types of cardan joints available to suit various applications and requirements. The design and configuration of a cardan joint can vary based on factors such as load capacity, torque transmission, operating conditions, and installation constraints. Here’s a detailed explanation of some commonly used types of cardan joints:
- Single Universal Joint: The single universal joint is the most basic and commonly used type of cardan joint. It consists of two yokes connected by a cross, forming a single joint. This type of cardan joint allows for angular misalignment between the input and output shafts. It is often used in applications where misalignment angles are relatively small, and flexibility is required.
- Double Cardan Joint: The double cardan joint, also known as a constant velocity joint (CV joint), is an enhanced version of the single universal joint. It consists of two single universal joints connected by an intermediate shaft. This configuration helps to cancel out the velocity fluctuations and torque variations that can occur with a single joint. Double cardan joints are commonly used in applications where smooth and constant power transmission is required, such as in front-wheel drive vehicles.
- Tractor Joint: A tractor joint is a specialized type of cardan joint used in agricultural machinery, particularly in power take-off (PTO) systems. It consists of three yokes connected by two crosses. The tractor joint allows for higher torque transmission and can accommodate larger misalignment angles. It is designed to handle the demanding conditions and heavy loads often encountered in agricultural applications.
- Ball-and-Socket Joint: The ball-and-socket joint, also known as a Hooke’s joint, is another variant of the cardan joint. It consists of a cross with a spherical ball at each end, which fits into a corresponding socket in the yokes. The ball-and-socket joint provides greater flexibility and can accommodate larger angles of misalignment. It is commonly used in applications where significant angular movement is required, such as steering systems in vehicles.
- Flexible Coupling: While not strictly a cardan joint, flexible couplings serve a similar purpose in accommodating misalignment. Flexible couplings are often used in applications where the misalignment is minimal and torque transmission is a primary concern. They utilize elastomeric or flexible elements to provide flexibility and compensate for small misalignments between shafts.
These are some of the commonly used types of cardan joints. Each type offers specific advantages and is suitable for different applications based on factors such as misalignment requirements, torque transmission, and operating conditions. The selection of the appropriate cardan joint type depends on the specific needs of the application and the desired performance characteristics.


editor by CX 2024-04-12
China supplier Standard Steel Ccr or Private Label Cardan Shaft Constant Velocity Joint
Product Description
ABS Ring Included : No
Axle Nut Locking Type: Self Lock
Axle Nut Supplied: Yes
Compressed Length: 21 1/4″
CV Axles Inboard Spline Count: 26
Emission Code : 1
Inboard Joint Type: Female
Input Shaft Connection Style: Spline
Input Shaft Spline Count: 26
Interchange Part Number: , GM-8047, 179047, GM-6120, GM6120, 9456N
Label Description – 80: New Constant Velocity Drive Axle
Length Measurement Method: Compressed
Life Cycle Status Code: 2
Life Cycle Status Description: Available to Order
Maximum Cases per Pallet Layer: 10
MSDS Required Flag: N
National Popularity Code : B
National Popularity Description: Next 20% of Product Group Sales Value
New or Remanufactured: New
Nut Head Size: 36mm Hex Head
Nut Length: OAH 20.8mm
Nut Locking Type: Self Lock
Nut Thread Size: M24 x 2.0
Other Part Number: 815-5270, GM-8232, 80-1507, , 80571
Outboard Joint Type: Male
Outboard Spline Count: 27
Output Shaft Connection Style: Spline
Output Shaft Spline Count: 27
Overall Length: 21 1/4″
Pallet Layer Maximum: 6
Product Condition: New
Product Description – Invoice – 40: CV Drive Axle New
Product Description – Long – 80: CV Drive Axle – Domestic New
Product Description – Short – 20: CV Drive Axle
Remanufactured Part: N
Spindle Nut Hex Head Size: 36mm
Spindle Nut Included: Yes
Spindle Nut Thread Size: M24 x 2.0
Drive Shaft | PATRON : PDS1507
- Fitting Position: Front Axle Right
REF NO.
FactoryNumber
GSP208050
OE Number
MakeNumber
GMC93720063
MakeNumber
GMC
MakeNumber
CHINAMFG
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Available |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Certification: | DIN, ISO, ISO, DIN |
| Type: | C.V. Joint |
| Application Brand: | GM |
| Material: | Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What is the lifespan of a typical cardan joint?
The lifespan of a typical cardan joint can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the joint, the operating conditions, maintenance practices, and the specific application. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors that can influence the lifespan of a cardan joint:
- Quality and Materials: The quality of the cardan joint and the materials used in its construction play a significant role in determining its lifespan. High-quality joints manufactured from durable materials, such as alloy steels or other suitable alloys, tend to have longer lifespans compared to lower-quality or poorly constructed joints. The joint’s ability to withstand the applied loads, resist fatigue, and maintain its structural integrity over time contributes to its overall lifespan.
- Operating Conditions: The operating conditions in which the cardan joint is used can impact its lifespan. Factors such as torque levels, rotational speeds, operating temperatures, and environmental conditions (e.g., presence of corrosive substances or contaminants) can affect the joint’s performance and durability. Operating the joint within its specified limits, avoiding excessive loads or speeds, and providing suitable environmental protection can help prolong its lifespan.
- Maintenance and Lubrication: Regular maintenance and proper lubrication are essential for maximizing the lifespan of a cardan joint. Adequate lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and the potential for damage due to inadequate lubricant film. Regular maintenance practices, including inspection for wear, alignment checks, and timely replacement of worn or damaged components, can help identify and address issues before they lead to premature joint failure.
- Application-Specific Factors: The specific application in which the cardan joint is used can influence its lifespan. Factors such as the type of machinery or equipment, the magnitude and frequency of applied loads, and the duty cycle of the joint can affect its longevity. Heavy-duty applications with high loads, frequent use, or harsh operating conditions may experience more significant wear and fatigue, potentially shortening the joint’s lifespan.
- Proper Installation: Correct installation practices are important for ensuring the longevity of a cardan joint. Improper installation, including misalignment, inadequate torqueing of fasteners, or incorrect assembly procedures, can lead to premature wear, increased stress on the joint, and reduced lifespan. Following the manufacturer’s installation guidelines and consulting with experts if needed can help ensure proper installation and maximize the joint’s lifespan.
Considering these factors, it is challenging to provide a precise lifespan value for a typical cardan joint as it can vary widely. However, with proper selection, installation, maintenance, and adherence to operational limits, a well-designed and well-maintained cardan joint can have a lifespan of several years to several decades in many applications.
It is important to consult with the manufacturer or engineering experts familiar with the specific application and operating conditions to determine the expected lifespan and implement appropriate maintenance practices to optimize the joint’s longevity.

How do you address thermal expansion and contraction in a cardan joint?
Addressing thermal expansion and contraction in a cardan joint requires careful consideration of the materials used, proper design techniques, and appropriate installation practices. By implementing strategies to accommodate thermal variations, the integrity and performance of the cardan joint can be maintained. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Material Selection: Choose materials for the cardan joint components that have compatible coefficients of thermal expansion. This helps to minimize the differential expansion and contraction rates between the connected parts. Selecting materials with similar thermal expansion characteristics reduces the potential for excessive stress, deformation, or binding of the joint during temperature fluctuations.
2. Clearance and Tolerance Design: Incorporate appropriate clearances and tolerances in the design of the cardan joint. Allow for slight axial or radial movement between the joint components to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction. The clearances should be designed to prevent binding or interference while maintaining proper functionality and torque transmission.
3. Lubrication: Apply suitable lubrication to the cardan joint components to minimize friction and wear. Lubrication helps to reduce the effects of thermal expansion by providing a thin film between the moving parts. The lubricant should have a high operating temperature range and maintain its properties under thermal stress.
4. Temperature Monitoring: Implement temperature monitoring systems to track the operating temperatures of the cardan joint. This allows for real-time monitoring of temperature variations and helps identify potential issues related to thermal expansion or contraction. Monitoring can be done using temperature sensors or thermal imaging techniques.
5. Installation and Preload: Pay attention to the installation process of the cardan joint. Ensure that the joint is installed with appropriate preload or axial play to allow for thermal expansion and contraction without causing excessive stress or binding. Preload should be adjusted to accommodate the expected temperature range and thermal expansion coefficients of the materials used.
6. Heat Dissipation: Consider heat dissipation mechanisms in the vicinity of the cardan joint. Proper cooling or ventilation systems can help dissipate excess heat generated during operation, minimizing temperature differentials and reducing the impact of thermal expansion and contraction on the joint.
7. Thermal Shields or Insulation: In applications where extreme temperature differentials are anticipated, thermal shields or insulation materials can be employed to limit heat transfer to the cardan joint. By reducing direct exposure to high temperatures or rapid temperature changes, the effects of thermal expansion and contraction can be mitigated.
8. System Testing and Analysis: Conduct thorough testing and analysis to assess the performance of the cardan joint under varying temperature conditions. This includes evaluating the joint’s response to thermal expansion and contraction, measuring clearances, torque transmission efficiency, and any potential issues related to temperature differentials. Testing can be done through simulation, laboratory experiments, or field trials.
By considering these strategies, thermal expansion and contraction can be addressed in a cardan joint, minimizing the risk of damage, binding, or compromised performance. It is important to evaluate the specific operating conditions, temperature ranges, and materials used in the cardan joint to determine the most appropriate approaches for addressing thermal variations.

Are there different types of cardan joints available?
Yes, there are different types of cardan joints available to suit various applications and requirements. The design and configuration of a cardan joint can vary based on factors such as load capacity, torque transmission, operating conditions, and installation constraints. Here’s a detailed explanation of some commonly used types of cardan joints:
- Single Universal Joint: The single universal joint is the most basic and commonly used type of cardan joint. It consists of two yokes connected by a cross, forming a single joint. This type of cardan joint allows for angular misalignment between the input and output shafts. It is often used in applications where misalignment angles are relatively small, and flexibility is required.
- Double Cardan Joint: The double cardan joint, also known as a constant velocity joint (CV joint), is an enhanced version of the single universal joint. It consists of two single universal joints connected by an intermediate shaft. This configuration helps to cancel out the velocity fluctuations and torque variations that can occur with a single joint. Double cardan joints are commonly used in applications where smooth and constant power transmission is required, such as in front-wheel drive vehicles.
- Tractor Joint: A tractor joint is a specialized type of cardan joint used in agricultural machinery, particularly in power take-off (PTO) systems. It consists of three yokes connected by two crosses. The tractor joint allows for higher torque transmission and can accommodate larger misalignment angles. It is designed to handle the demanding conditions and heavy loads often encountered in agricultural applications.
- Ball-and-Socket Joint: The ball-and-socket joint, also known as a Hooke’s joint, is another variant of the cardan joint. It consists of a cross with a spherical ball at each end, which fits into a corresponding socket in the yokes. The ball-and-socket joint provides greater flexibility and can accommodate larger angles of misalignment. It is commonly used in applications where significant angular movement is required, such as steering systems in vehicles.
- Flexible Coupling: While not strictly a cardan joint, flexible couplings serve a similar purpose in accommodating misalignment. Flexible couplings are often used in applications where the misalignment is minimal and torque transmission is a primary concern. They utilize elastomeric or flexible elements to provide flexibility and compensate for small misalignments between shafts.
These are some of the commonly used types of cardan joints. Each type offers specific advantages and is suitable for different applications based on factors such as misalignment requirements, torque transmission, and operating conditions. The selection of the appropriate cardan joint type depends on the specific needs of the application and the desired performance characteristics.


editor by CX 2024-03-28
China supplier Front Right ISO, DIN Ccr or Private Label Cardan Shaft Universal Joint
Product Description
ABS Ring Included : No
Axle Nut Locking Type: Self Lock
Axle Nut Supplied: Yes
Compressed Length: 21 1/4″
CV Axles Inboard Spline Count: 26
Emission Code : 1
Inboard Joint Type: Female
Input Shaft Connection Style: Spline
Input Shaft Spline Count: 26
Interchange Part Number: , GM-8047, 179047, GM-6120, GM6120, 9456N
Label Description – 80: New Constant Velocity Drive Axle
Length Measurement Method: Compressed
Life Cycle Status Code: 2
Life Cycle Status Description: Available to Order
Maximum Cases per Pallet Layer: 10
MSDS Required Flag: N
National Popularity Code : B
National Popularity Description: Next 20% of Product Group Sales Value
New or Remanufactured: New
Nut Head Size: 36mm Hex Head
Nut Length: OAH 20.8mm
Nut Locking Type: Self Lock
Nut Thread Size: M24 x 2.0
Other Part Number: 815-5270, GM-8232, 80-1507, , 80571
Outboard Joint Type: Male
Outboard Spline Count: 27
Output Shaft Connection Style: Spline
Output Shaft Spline Count: 27
Overall Length: 21 1/4″
Pallet Layer Maximum: 6
Product Condition: New
Product Description – Invoice – 40: CV Drive Axle New
Product Description – Long – 80: CV Drive Axle – Domestic New
Product Description – Short – 20: CV Drive Axle
Remanufactured Part: N
Spindle Nut Hex Head Size: 36mm
Spindle Nut Included: Yes
Spindle Nut Thread Size: M24 x 2.0
Drive Shaft | PATRON : PDS1507
- Fitting Position: Front Axle Right
REF NO.
FactoryNumber
GSP208050
OE Number
MakeNumber
GMC93720063
MakeNumber
GMC
MakeNumber
CHINAMFG
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Available |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Certification: | DIN, ISO, ISO, DIN |
| Type: | C.V. Joint |
| Application Brand: | GM |
| Material: | Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are cardan joints suitable for both high-torque and high-speed applications?
Cardan joints can be used in a variety of applications, but their suitability for high-torque and high-speed applications depends on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation of the considerations regarding the use of cardan joints in such scenarios:
1. High-Torque Applications: Cardan joints are generally well-suited for high-torque applications. The design of the joint allows for the transmission of significant torque between misaligned shafts. However, it is important to consider the specific torque requirements and operating conditions. Factors such as the size and type of the joint, the material used, and the application’s torque demands should be taken into account. In extremely high-torque applications, alternative coupling mechanisms such as gear couplings or universal joints may be more appropriate.
2. High-Speed Applications: While cardan joints can operate at relatively high speeds, there are some limitations to consider. At high rotational speeds, cardan joints can experience increased vibration, imbalance, and potential for fatigue failure. The rotating components of the joint can generate centrifugal forces, which can impact the balance and stability of the system. To mitigate these issues, careful design considerations, including balancing and vibration analysis, may be necessary. In some cases, alternative coupling mechanisms like flexible couplings or constant velocity joints may be better suited for high-speed applications.
3. Balancing and Vibration Control: Balancing the rotating components, such as the driveshaft and the joint itself, is essential for minimizing vibration issues in high-torque and high-speed applications. Imbalance can lead to increased vibrations, reduced efficiency, and potential damage to the joint and other system components. Proper balancing techniques, including dynamic balancing during manufacturing or precision balancing during installation, can help achieve smoother operation and minimize vibration problems.
4. Material Selection: The material used in the construction of the cardan joint plays a crucial role in its suitability for high-torque and high-speed applications. High-strength materials, such as alloy steels, are often preferred for their ability to handle increased torque loads. Additionally, materials with good fatigue resistance and high-speed capabilities can help ensure the durability and reliability of the joint in demanding applications.
5. Application-Specific Factors: The suitability of cardan joints for high-torque and high-speed applications also depends on the specific requirements and operating conditions of the application. Factors such as load characteristics, duty cycles, temperature, and environmental conditions should be considered. It is important to consult with the manufacturer or engineering experts to determine the appropriate size, type, and configuration of the cardan joint for a particular high-torque or high-speed application.
In summary, cardan joints can be suitable for both high-torque and high-speed applications, but careful consideration of factors such as torque requirements, speed limitations, balancing, material selection, and application-specific conditions is necessary. Evaluating these factors and consulting with experts can help determine the optimal coupling solution for a given high-torque or high-speed application.

Can cardan joints be used in robotics and automation?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in robotics and automation applications, depending on the specific requirements and constraints of the system. Cardan joints offer certain advantages and considerations that make them suitable for certain robotic and automation tasks. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Flexibility and Misalignment Compensation: Cardan joints are designed to accommodate misalignment between rotating shafts. In robotics and automation, where multiple axes of movement are often involved, cardan joints can provide the necessary flexibility to handle misalignments and angular variations. They can compensate for misalignments resulting from assembly tolerances, thermal expansion, or mechanical deflections, allowing smooth and continuous motion.
2. Torque Transmission: Cardan joints are capable of transmitting torque between shafts at various angles. In robotics and automation, where power needs to be transferred between different components or joints, cardan joints can efficiently transmit torque, even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned. This enables the robot or automated system to perform complex tasks involving multi-axis motion and power transmission.
3. Rotational Freedom: Cardan joints provide rotational freedom and allow for angular movement. This is advantageous in robotics and automation applications where the system requires articulation and maneuverability. The universal joint design of cardan joints allows for smooth rotation and enables the robot or automated system to reach different orientations and perform tasks in various configurations.
4. Compact Design: Cardan joints have a relatively compact design, which can be beneficial in space-constrained robotics and automation setups. The compact size allows for efficient integration into robotic arms, end-effectors, or other automated mechanisms, minimizing the overall footprint and maximizing the utilization of available space.
5. Considerations for Precision and Backlash: When considering the use of cardan joints in robotics and automation, it’s important to account for precision requirements. Cardan joints have inherent clearances or play, which can introduce backlash and affect the system’s accuracy. In applications where high precision is crucial, additional measures such as backlash compensation mechanisms or precision-aligned cardan joints may be necessary.
It’s important to note that the suitability of cardan joints in robotics and automation depends on the specific application requirements, load conditions, precision needs, and other factors. Careful evaluation, system design, and integration are necessary to ensure that the cardan joints function optimally and meet the desired performance criteria.
When considering the use of cardan joints in robotics and automation, it is advisable to consult with engineers or experts specializing in robotics, automation, and power transmission systems. They can provide valuable insights and guidance on the selection, integration, and maintenance of cardan joints for specific robotic and automation applications.

How do you choose the right size cardan joint for your application?
Choosing the right size cardan joint for your application is crucial to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. Several factors need to be considered when selecting the appropriate size of a cardan joint. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key considerations:
- Load Capacity: Determine the maximum load that the cardan joint will need to transmit. Consider both the torque (rotational force) and the axial load (thrust) that will be applied to the joint. The load capacity of the cardan joint should exceed the maximum expected loads in your application to ensure safe and reliable operation.
- Operating Speed: Consider the rotational speed at which the cardan joint will be operating. Higher speeds may require specific design considerations, such as balancing, lubrication, and material selection, to ensure smooth operation and avoid premature wear or failure. Verify that the selected cardan joint is rated for the intended operating speed range.
- Shaft Diameter: Measure the diameter of the input and output shafts that will be connected by the cardan joint. The cardan joint should have yokes and bearings that match the shaft diameter to ensure a proper fit and reliable power transmission. It is essential to consider both shaft diameters when selecting a cardan joint.
- Misalignment Angle: Determine the maximum expected misalignment angle between the input and output shafts. Different types of cardan joints have different capabilities to accommodate misalignment. Consider the angular misalignment and choose a cardan joint that can handle the required range of misalignment angles in your application.
- Environmental Factors: Evaluate the operating environment of the cardan joint. Consider factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, chemicals, and vibration. Choose a cardan joint that is suitable for the specific environmental conditions to ensure proper functioning and longevity.
- Service Life and Maintenance: Consider the expected service life of the cardan joint and the maintenance requirements. Some applications may require frequent maintenance or periodic lubrication of the joint. Evaluate the ease of maintenance and factor it into your selection process.
- Standards and Regulations: Depending on your industry or application, there may be specific standards or regulations that dictate the requirements for cardan joints. Ensure that the selected cardan joint complies with the relevant standards and regulations for your application.
It is advisable to consult with a knowledgeable supplier or engineer specializing in power transmission components to assist you in selecting the right size cardan joint for your specific application. They can consider all the relevant factors and provide guidance to ensure optimal performance and reliability of the cardan joint in your application.


editor by CX 2024-03-03
China supplier Made in China OEM Custom Stainless Steel Adjustable Shaft Coupling Double Cardan Universal Joint
Product Description
Product Description
|
Company Profile
HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Machinery Manufacture Co., Ltd., located in HangZhou, “China’s ancient copper capital”, is a “national high-tech enterprise”. At the beginning of its establishment, the company adhering to the “to provide clients with high quality products, to provide timely service” concept, adhere to the “everything for the customer, make customer excellent supplier” for the mission.
Certifications
Q: Where is your company located ?
A: HangZhou ZheJiang .
Q: How could l get a sample?
A: Before we received the first order, please afford the sample cost and express fee. we will return the sample cost back
to you within your first order.
Q: Sample time?
A: Existing items: within 20-60 days.
Q: Whether you could make our brand on your products?
A: Yes. We can print your Logo on both the products and the packages if you can meet our MOQ.
Q: How to guarantee the quality of your products?
A: 1) stict detection during production. 2) Strict completely inspecion on products before shipment and intact product
packaging ensured.
Q: lf my drawings are safe?
A: Yes ,we can CHINAMFG NDA.
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Nonstandard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 8-24 |
| Torque: | OEM/ODM/Customized |
| Bore Diameter: | OEM/ODM/Customized |
| Speed: | OEM/ODM/Customized |
| Structure: | Flexible |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the potential limitations or drawbacks of using cardan joints?
While cardan joints offer numerous advantages in transmitting rotational motion between misaligned shafts, they also have certain limitations and drawbacks to consider. Here are some potential limitations associated with the use of cardan joints:
- Angular Limitations: Cardan joints have limited angularity or operating angles. They are designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and exceeding these angles can cause accelerated wear, increased vibration, and potential joint failure. Extreme operating angles can lead to binding, decreased efficiency, and reduced power transmission capacity. In applications where large operating angles are required, alternative flexible coupling mechanisms or constant velocity joints may be more suitable.
- Backlash and Torsional Stiffness: Cardan joints inherently exhibit some degree of backlash, which is the clearance or free play between the mating components. This can result in a slight delay in power transmission and can affect the precision of motion in certain applications. Additionally, cardan joints may have higher torsional stiffness compared to other coupling mechanisms, which can transmit higher vibrations and shocks to the connected components.
- Maintenance Requirements: Cardan joints require regular maintenance to ensure proper lubrication, alignment, and performance. The lubricant needs to be regularly replenished or replaced, and the joint should be inspected for wear, misalignment, or other issues. Failure to perform adequate maintenance can result in premature wear, reduced efficiency, and potential joint failure. Maintenance procedures may require specialized tools and expertise.
- Space and Weight: Cardan joints can occupy a significant amount of space due to their design and the need for perpendicular shafts. In applications with limited space constraints, finding suitable locations for cardan joints can be challenging. Additionally, the weight of cardan joints, especially in heavy-duty applications, can add to the overall weight of the system, which may have implications for fuel efficiency, payload capacity, or overall performance.
- Cost: Cardan joints, particularly high-quality and precision-engineered ones, can be relatively expensive compared to other coupling mechanisms. The complex design, manufacturing tolerances, and specialized materials involved contribute to their higher cost. In cost-sensitive applications, alternative coupling solutions may be considered if the angular limitations and other drawbacks of cardan joints are not critical.
- High-Speed Limitations: At high rotational speeds, cardan joints can experience increased vibration, imbalance, and potential for fatigue failure. The rotating components of the joint can generate centrifugal forces that impact the balance and stability of the system. In high-speed applications, careful design considerations, including balancing and vibration analysis, may be necessary to mitigate these issues.
It is important to evaluate the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and limitations when considering the use of cardan joints. While they offer versatility and flexibility in many scenarios, alternative coupling mechanisms may be more suitable in cases where the limitations and drawbacks of cardan joints pose significant challenges.
Can cardan joints be used in pumps and compressors?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in pumps and compressors to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between the driving and driven shafts. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for these applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Torque Transmission: Pumps and compressors often require the transmission of torque from the driving motor or engine to the rotating shaft that operates the pump or compressor. Cardan joints excel at transmitting torque efficiently, even at significant angles and misalignments. They can handle the high torque loads typically encountered in pump and compressor applications.
2. Misalignment Compensation: Cardan joints are designed to accommodate misalignments between the driving and driven shafts. In pumps and compressors, misalignments can occur due to factors such as thermal expansion, structural deflection, or assembly tolerances. Cardan joints can compensate for these misalignments, ensuring smooth and reliable torque transmission without excessive stress or wear on the connected components.
3. Angular Flexibility: Pumps and compressors often require flexibility in their drivetrain to adapt to different installation configurations or accommodate dynamic movements. Cardan joints provide rotational freedom and allow for angular movement, enabling the pump or compressor to adjust to changing requirements. Their universal joint design allows for smooth rotation and accommodates the required range of motion.
4. Shock and Vibration Absorption: Pumps and compressors can generate significant vibrations and shocks during operation. Cardan joints help absorb these vibrations and shocks, reducing their transmission to the rest of the drivetrain. This feature helps protect other components, such as bearings and seals, from excessive stress and wear, enhancing the overall reliability and lifespan of the pump or compressor.
5. Compact Design: Cardan joints have a relatively compact design, making them suitable for integration into pump and compressor systems where space is often limited. Their compact size allows for efficient packaging within the equipment, optimizing overall design and minimizing footprint. This is especially beneficial in applications where multiple joints are required within a confined space.
6. Durability and Strength: Pumps and compressors operate under demanding conditions, including high pressures, heavy loads, and continuous operation. Cardan joints are often constructed using durable materials such as alloy steels or high-strength alloys, providing the necessary strength and resilience to withstand these conditions. They are designed to handle the demanding loads and forces encountered in pump and compressor applications.
7. Easy Maintenance and Serviceability: Cardan joints are generally low-maintenance components. They require periodic inspection, lubrication, and replacement of worn parts, but their design often allows for easy access and replacement if needed. This facilitates maintenance activities and minimizes downtime in pump and compressor systems.
8. Cost-Effectiveness: Cardan joints offer a cost-effective solution for torque transmission in pump and compressor applications. Their durability, reliability, and long service life contribute to reduced maintenance and replacement costs. Additionally, their ability to accommodate misalignments helps minimize wear on other drivetrain components, further reducing overall maintenance expenses.
When integrating cardan joints into pump and compressor systems, it is important to consider the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and load characteristics. Proper design, selection, and installation practices should be followed to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Consulting with engineers or experts specializing in drivetrain systems and pump/compressor design can provide valuable insights and guidance on the selection, integration, and maintenance of cardan joints for these applications.

What are the benefits of using a cardan joint in a mechanical system?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, offers several benefits when used in a mechanical system. These benefits contribute to efficient power transmission, flexibility, and the ability to accommodate misalignment. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using a cardan joint:
- Misalignment Compensation: One of the primary advantages of a cardan joint is its ability to accommodate misalignment between the input and output shafts. The flexible design of the joint allows for angular misalignment, axial misalignment, or a combination of both. This capability is particularly useful in applications where the shafts are not perfectly aligned, or where movement and flexibility are required.
- Power Transmission: Cardan joints are efficient in transmitting rotational motion and torque between non-collinear shafts. They maintain a constant velocity ratio between the input and output shafts, ensuring smooth power transmission. This feature is especially beneficial in applications where a consistent and uninterrupted transfer of power is essential, such as drivetrain systems in vehicles and industrial machinery.
- Flexibility and Articulation: The flexible nature of a cardan joint allows for articulation and movement between the connected shafts. It enables the mechanical system to adapt to changing angles, positions, or misalignment during operation. This flexibility is particularly advantageous in applications that involve variable operating conditions, such as vehicles navigating uneven terrain or machinery with moving components.
- Torsional Vibration Damping: Cardan joints can help dampen torsional vibrations that may occur in a mechanical system. The cross-shaped design of the joint, combined with the flexibility of the bearings, can absorb and mitigate torsional vibrations, reducing stress on the components and improving overall system performance and durability.
- Compact Design: Cardan joints have a relatively compact design, allowing them to be easily integrated into various mechanical systems. They occupy less space compared to other types of power transmission components, making them suitable for applications with limited installation space or where weight reduction is a concern.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cardan joints are generally cost-effective compared to alternative power transmission solutions. Their simple design, ease of manufacturing, and wide availability contribute to their affordability. Additionally, their durability and ability to handle misalignment can reduce the need for frequent maintenance or replacement, leading to cost savings in the long run.
These benefits make cardan joints a versatile and valuable component in numerous mechanical systems across industries such as automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, marine, and more. Their ability to transmit power efficiently, accommodate misalignment, and provide flexibility contribute to improved performance, reliability, and operational efficiency of the overall mechanical system.


editor by CX 2023-12-01
China Custom Car Parts Engine A2213306400 Drive Shaft for Mercedes-Benz near me supplier
Product Description
Car Parts Engine Adrive shaft for Mercedes-Benz
Product Specification
| Item Name | drive shaft for Mercedes-benz |
| Part Number | A2213306400 |
| size | Standard |
| Brand | FENGMING |
| MOQ | 1PCS |
| Warranty | 1 Year |
| Packing | 1.Original Packing 2. Neutral Packing 3. CZPT brand Packing 4.Customized |
| Payment | L/C, T/T, Western Union, Cash,Paypal,Alipay |
| Delivery | Within 2-3 days after payment |
| Shipment | by DHL/ FEDEX/ TNT, by sea,by air |
Contact information
Fengming Auto Parts CO., Ltd main products line:
1.Auto ignition system: Spark Plug, Ignition Coil
2.Suspension Parts: shock absorber, control arm, ball joint,stabilizer link, tie rod end, steering rack
3.Brake parts: brake pads, brake disc, brake master cylinder, wheel cylinder
4.Fuel pump, water pump, radiator, full gasket kit, engine belt
Customer Reviews:
95% positive testmonials from customers around the world. Fengming brand products’ quality, packing and Fengming service get excellent approval among customers. Seeing is believing!
What we can promise you?
1. Manufacturing & Selling Integration
2. Our companies located in HangZhou China which are in charge of different markets
3. 1 Year warranty for Fengming brand products under normal use
4. Unique Fengming brand packing: one Fengming poly bag plus one Fengming red box
5. Competitive price with high & stable quality products
6. Total 2,000 square meters warehouse to make sure fast delivery
7. 10 years’ experience in researching, developing and supplying auto parts for Japanese cars since 2009
What is a drive shaft?
If you notice a clicking noise while driving, it is most likely the driveshaft. An experienced auto mechanic will be able to tell you if the noise is coming from both sides or from 1 side. If it only happens on 1 side, you should check it. If you notice noise on both sides, you should contact a mechanic. In either case, a replacement driveshaft should be easy to find.
The drive shaft is a mechanical part
A driveshaft is a mechanical device that transmits rotation and torque from the engine to the wheels of the vehicle. This component is essential to the operation of any driveline, as the mechanical power from the engine is transmitted to the PTO (power take-off) shaft, which hydraulically transmits that power to connected equipment. Different drive shafts contain different combinations of joints to compensate for changes in shaft length and angle. Some types of drive shafts include connecting shafts, internal constant velocity joints, and external fixed joints. They also contain anti-lock system rings and torsional dampers to prevent overloading the axle or causing the wheels to lock.
Although driveshafts are relatively light, they need to handle a lot of torque. Torque applied to the drive shaft produces torsional and shear stresses. Because they have to withstand torque, these shafts are designed to be lightweight and have little inertia or weight. Therefore, they usually have a joint, coupling or rod between the 2 parts. Components can also be bent to accommodate changes in the distance between them.
The drive shaft can be made from a variety of materials. The most common material for these components is steel, although alloy steels are often used for high-strength applications. Alloy steel, chromium or vanadium are other materials that can be used. The type of material used depends on the application and size of the component. In many cases, metal driveshafts are the most durable and cheapest option. Plastic shafts are used for light duty applications and have different torque levels than metal shafts.
It transfers power from the engine to the wheels
A car’s powertrain consists of an electric motor, transmission, and differential. Each section performs a specific job. In a rear-wheel drive vehicle, the power generated by the engine is transmitted to the rear tires. This arrangement improves braking and handling. The differential controls how much power each wheel receives. The torque of the engine is transferred to the wheels according to its speed.
The transmission transfers power from the engine to the wheels. It is also called “transgender”. Its job is to ensure power is delivered to the wheels. Electric cars cannot drive themselves and require a gearbox to drive forward. It also controls how much power reaches the wheels at any given moment. The transmission is the last part of the power transmission chain. Despite its many names, the transmission is the most complex component of a car’s powertrain.
The driveshaft is a long steel tube that transmits mechanical power from the transmission to the wheels. Cardan joints connect to the drive shaft and provide flexible pivot points. The differential assembly is mounted on the drive shaft, allowing the wheels to turn at different speeds. The differential allows the wheels to turn at different speeds and is very important when cornering. Axles are also important to the performance of the car.
It has a rubber boot that protects it from dust and moisture
To keep this boot in good condition, you should clean it with cold water and a rag. Never place it in the dryer or in direct sunlight. Heat can deteriorate the rubber and cause it to shrink or crack. To prolong the life of your rubber boots, apply rubber conditioner to them regularly. Indigenous peoples in the Amazon region collect latex sap from the bark of rubber trees. Then they put their feet on the fire to solidify the sap.
it has a U-shaped connector
The drive shaft has a U-joint that transfers rotational energy from the engine to the axle. Defective gimbal joints can cause vibrations when the vehicle is in motion. This vibration is often mistaken for a wheel balance problem. Wheel balance problems can cause the vehicle to vibrate while driving, while a U-joint failure can cause the vehicle to vibrate when decelerating and accelerating, and stop when the vehicle is stopped.
The drive shaft is connected to the transmission and differential using a U-joint. It allows for small changes in position between the 2 components. This prevents the differential and transmission from remaining perfectly aligned. The U-joint also allows the drive shaft to be connected unconstrained, allowing the vehicle to move. Its main purpose is to transmit electricity. Of all types of elastic couplings, U-joints are the oldest.
Your vehicle’s U-joints should be inspected at least twice a year, and the joints should be greased. When checking the U-joint, you should hear a dull sound when changing gears. A clicking sound indicates insufficient grease in the bearing. If you hear or feel vibrations when shifting gears, you may need to service the bearings to prolong their life.
it has a slide-in tube
The telescopic design is a modern alternative to traditional driveshaft designs. This innovative design is based on an unconventional design philosophy that combines advances in material science and manufacturing processes. Therefore, they are more efficient and lighter than conventional designs. Slide-in tubes are a simple and efficient design solution for any vehicle application. Here are some of its benefits. Read on to learn why this type of shaft is ideal for many applications.
The telescopic drive shaft is an important part of the traditional automobile transmission system. These driveshafts allow linear motion of the 2 components, transmitting torque and rotation throughout the vehicle’s driveline. They also absorb energy if the vehicle collides. Often referred to as foldable driveshafts, their popularity is directly dependent on the evolution of the automotive industry.
It uses a bearing press to replace worn or damaged U-joints
A bearing press is a device that uses a rotary press mechanism to install or remove worn or damaged U-joints from a drive shaft. With this tool, you can replace worn or damaged U-joints in your car with relative ease. The first step involves placing the drive shaft in the vise. Then, use the 11/16″ socket to press the other cup in far enough to install the clips. If the cups don’t fit, you can use a bearing press to remove them and repeat the process. After removing the U-joint, use a grease nipple Make sure the new grease nipple is installed correctly.
Worn or damaged U-joints are a major source of driveshaft failure. If 1 of them were damaged or damaged, the entire driveshaft could dislocate and the car would lose power. Unless you have a professional mechanic doing the repairs, you will have to replace the entire driveshaft. Fortunately, there are many ways to do this yourself.
If any of these warning signs appear on your vehicle, you should consider replacing the damaged or worn U-joint. Common symptoms of damaged U-joints include rattling or periodic squeaking when moving, rattling when shifting, wobbling when turning, or rusted oil seals. If you notice any of these symptoms, take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic for a full inspection. Neglecting to replace a worn or damaged u-joint on the driveshaft can result in expensive and dangerous repairs and can cause significant damage to your vehicle.


China Best Sales OEM/ODM CE Certificate Farm Agriculture Machine Tractor Parts Drive Cardan Propeller Pto Shaft for Wood Chipper near me supplier
Product Description
OEM/ODM Ce Certificate Farm Agriculture Machine Tractor Parts Drive Cardan Propeller Pto Shaft for Wood Chipper
Power Take Off Shafts for all applications
A power take-off or power takeoff (PTO) is any of several methods for taking power from a power source, such as a running engine, and transmitting it to an application such as an attached implement or separate machines.
Most commonly, it is a splined drive shaft installed on a tractor or truck allowing implements with mating fittings to be powered directly by the engine.
Semi-permanently mounted power take-offs can also be found on industrial and marine engines. These applications typically use a drive shaft and bolted joint to transmit power to a secondary implement or accessory. In the case of a marine application, such shafts may be used to power fire pumps.
We offer high-quality PTO shaft parts and accessories, including clutches, tubes, and yokes for your tractor and implements, including an extensive range of pto driveline. Request our pto shaft products at the best rate possible.
What does a power take off do?
Power take-off (PTO) is a device that transfers an engine’s mechanical power to another piece of equipment. A PTO allows the hosting energy source to transmit power to additional equipment that does not have its own engine or motor. For example, a PTO helps to run a jackhammer using a tractor engine.
What’s the difference between 540 and 1000 PTO?
When a PTO shaft is turning 540, the ratio must be adjusted (geared up or down) to meet the needs of the implement, which is usually higher RPM’s than that. Since 1000 RPM’s is almost double that of 540, there is less “”Gearing Up”” designed in the implement to do the job required.”
If you are looking for a PTO speed reducer visit here
| Function | Power transmission |
| Use | Tractors and various farm implements |
| Place of Origin | HangZhou ,ZHangZhoug, China (Mainland) |
| Brand Name | EPT |
| Yoke Type | push pin/quick release/collar/double push pin/bolt pins/split pins |
| Processing Of Yoke | Forging |
| Plastic Cover | YW;BW;YS;BS |
| Color | Yellow;black |
| Series | T series; L series; S series |
| Tube Type | Trianglar/star/lemon |
| Processing Of Tube | Cold drawn |
| Spline Type | 1 3/8″ Z6; 1 3/8 Z21 ;1 3/4 Z20;1 1/8 Z6; 1 3/4 Z6; |
Related Products
Application:
Company information:
How to Select a Worm Shaft and Gear For Your Project
You will learn about axial pitch PX and tooth parameters for a Worm Shaft 20 and Gear 22. Detailed information on these 2 components will help you select a suitable Worm Shaft. Read on to learn more….and get your hands on the most advanced gearbox ever created! Here are some tips for selecting a Worm Shaft and Gear for your project!…and a few things to keep in mind.
Gear 22
The tooth profile of Gear 22 on Worm Shaft 20 differs from that of a conventional gear. This is because the teeth of Gear 22 are concave, allowing for better interaction with the threads of the worm shaft 20. The worm’s lead angle causes the worm to self-lock, preventing reverse motion. However, this self-locking mechanism is not entirely dependable. Worm gears are used in numerous industrial applications, from elevators to fishing reels and automotive power steering.
The new gear is installed on a shaft that is secured in an oil seal. To install a new gear, you first need to remove the old gear. Next, you need to unscrew the 2 bolts that hold the gear onto the shaft. Next, you should remove the bearing carrier from the output shaft. Once the worm gear is removed, you need to unscrew the retaining ring. After that, install the bearing cones and the shaft spacer. Make sure that the shaft is tightened properly, but do not over-tighten the plug.
To prevent premature failures, use the right lubricant for the type of worm gear. A high viscosity oil is required for the sliding action of worm gears. In two-thirds of applications, lubricants were insufficient. If the worm is lightly loaded, a low-viscosity oil may be sufficient. Otherwise, a high-viscosity oil is necessary to keep the worm gears in good condition.
Another option is to vary the number of teeth around the gear 22 to reduce the output shaft’s speed. This can be done by setting a specific ratio (for example, 5 or 10 times the motor’s speed) and modifying the worm’s dedendum accordingly. This process will reduce the output shaft’s speed to the desired level. The worm’s dedendum should be adapted to the desired axial pitch.
Worm Shaft 20
When selecting a worm gear, consider the following things to consider. These are high-performance, low-noise gears. They are durable, low-temperature, and long-lasting. Worm gears are widely used in numerous industries and have numerous benefits. Listed below are just some of their benefits. Read on for more information. Worm gears can be difficult to maintain, but with proper maintenance, they can be very reliable.
The worm shaft is configured to be supported in a frame 24. The size of the frame 24 is determined by the center distance between the worm shaft 20 and the output shaft 16. The worm shaft and gear 22 may not come in contact or interfere with 1 another if they are not configured properly. For these reasons, proper assembly is essential. However, if the worm shaft 20 is not properly installed, the assembly will not function.
Another important consideration is the worm material. Some worm gears have brass wheels, which may cause corrosion in the worm. In addition, sulfur-phosphorous EP gear oil activates on the brass wheel. These materials can cause significant loss of load surface. Worm gears should be installed with high-quality lubricant to prevent these problems. There is also a need to choose a material that is high-viscosity and has low friction.
Speed reducers can include many different worm shafts, and each speed reducer will require different ratios. In this case, the speed reducer manufacturer can provide different worm shafts with different thread patterns. The different thread patterns will correspond to different gear ratios. Regardless of the gear ratio, each worm shaft is manufactured from a blank with the desired thread. It will not be difficult to find 1 that fits your needs.
Gear 22’s axial pitch PX
The axial pitch of a worm gear is calculated by using the nominal center distance and the Addendum Factor, a constant. The Center Distance is the distance from the center of the gear to the worm wheel. The worm wheel pitch is also called the worm pitch. Both the dimension and the pitch diameter are taken into consideration when calculating the axial pitch PX for a Gear 22.
The axial pitch, or lead angle, of a worm gear determines how effective it is. The higher the lead angle, the less efficient the gear. Lead angles are directly related to the worm gear’s load capacity. In particular, the angle of the lead is proportional to the length of the stress area on the worm wheel teeth. A worm gear’s load capacity is directly proportional to the amount of root bending stress introduced by cantilever action. A worm with a lead angle of g is almost identical to a helical gear with a helix angle of 90 deg.
In the present invention, an improved method of manufacturing worm shafts is described. The method entails determining the desired axial pitch PX for each reduction ratio and frame size. The axial pitch is established by a method of manufacturing a worm shaft that has a thread that corresponds to the desired gear ratio. A gear is a rotating assembly of parts that are made up of teeth and a worm.
In addition to the axial pitch, a worm gear’s shaft can also be made from different materials. The material used for the gear’s worms is an important consideration in its selection. Worm gears are usually made of steel, which is stronger and corrosion-resistant than other materials. They also require lubrication and may have ground teeth to reduce friction. In addition, worm gears are often quieter than other gears.
Gear 22’s tooth parameters
A study of Gear 22’s tooth parameters revealed that the worm shaft’s deflection depends on various factors. The parameters of the worm gear were varied to account for the worm gear size, pressure angle, and size factor. In addition, the number of worm threads was changed. These parameters are varied based on the ISO/TS 14521 reference gear. This study validates the developed numerical calculation model using experimental results from Lutz and FEM calculations of worm gear shafts.
Using the results from the Lutz test, we can obtain the deflection of the worm shaft using the calculation method of ISO/TS 14521 and DIN 3996. The calculation of the bending diameter of a worm shaft according to the formulas given in AGMA 6022 and DIN 3996 show a good correlation with test results. However, the calculation of the worm shaft using the root diameter of the worm uses a different parameter to calculate the equivalent bending diameter.
The bending stiffness of a worm shaft is calculated through a finite element model (FEM). Using a FEM simulation, the deflection of a worm shaft can be calculated from its toothing parameters. The deflection can be considered for a complete gearbox system as stiffness of the worm toothing is considered. And finally, based on this study, a correction factor is developed.
For an ideal worm gear, the number of thread starts is proportional to the size of the worm. The worm’s diameter and toothing factor are calculated from Equation 9, which is a formula for the worm gear’s root inertia. The distance between the main axes and the worm shaft is determined by Equation 14.
Gear 22’s deflection
To study the effect of toothing parameters on the deflection of a worm shaft, we used a finite element method. The parameters considered are tooth height, pressure angle, size factor, and number of worm threads. Each of these parameters has a different influence on worm shaft bending. Table 1 shows the parameter variations for a reference gear (Gear 22) and a different toothing model. The worm gear size and number of threads determine the deflection of the worm shaft.
The calculation method of ISO/TS 14521 is based on the boundary conditions of the Lutz test setup. This method calculates the deflection of the worm shaft using the finite element method. The experimentally measured shafts were compared to the simulation results. The test results and the correction factor were compared to verify that the calculated deflection is comparable to the measured deflection.
The FEM analysis indicates the effect of tooth parameters on worm shaft bending. Gear 22’s deflection on Worm Shaft can be explained by the ratio of tooth force to mass. The ratio of worm tooth force to mass determines the torque. The ratio between the 2 parameters is the rotational speed. The ratio of worm gear tooth forces to worm shaft mass determines the deflection of worm gears. The deflection of a worm gear has an impact on worm shaft bending capacity, efficiency, and NVH. The continuous development of power density has been achieved through advancements in bronze materials, lubricants, and manufacturing quality.
The main axes of moment of inertia are indicated with the letters A-N. The three-dimensional graphs are identical for the seven-threaded and one-threaded worms. The diagrams also show the axial profiles of each gear. In addition, the main axes of moment of inertia are indicated by a white cross.


China best Universal Joints Shaft Coupling Motor Disc Coupling Machine Shaft Coupler near me supplier
Product Description
Coupling,
1. The couplings offer a range of hub and element selection to meet different demands.
2. They can absorb shock and cater for incidental misalignment and damp out small amplitude vibrations.
3. NBR, Urethane, Hytrel elements.
4. Customized requirement is available.
Main Products:
1. Timing Belt Pulley (Synchronous Pulley), Timing Bar, Clamping Plate;
2. Forging, Casting, Stampling Part;
3. V Belt Pulley and Taper Lock Bush; Sprocket, Idler and Plate Wheel;Spur Gear, Bevel Gear, Rack;
4. Shaft Locking Device: could be alternative for Ringfeder, Sati, Chiaravalli, Tollok, etc.;
5. Shaft Coupling: including Miniature couplings, Curved tooth coupling, Chain coupling, HRC coupling,
Normex coupling, Type coupling, GE Coupling, torque limiter, Universal Joint;
6. Shaft Collars: including Setscrew Type, Single Split and Double Splits;
7. Gear & Rack: Spur gear/rack, bevel gear, helical gear/rack.
8. Other customized Machining Parts according to drawings (OEM) Forging, Casting, Stamping Parts.
PACKING
| Packaging | |
| Packing
|
We use standard export wooden case, carton and pallet, but we can also pack it as per your special requirements. |
OUR COMPANY
ZheJiang Mighty Machinery Co., Ltd. specializes in offering best service and the most competitive price for our customer.
After over 10 years’ hard work, MIGHTY’s business has grown rapidly and become an important partner for oversea clients in the industrial field and become a holding company for 3 manufacturing factories.
MIGHTY’s products have obtained reputation of domestic and oversea customers with taking advantage of technology, management, quality and very competitive price.
Your satisfaction is the biggest motivation for our work, choose us to get high quality products and best service.
OUR FACTORY
FAQ
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
A: We are factory.
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: Generally it is 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-20 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ?
A: Yes, we could offer the sample for free charge but do not pay the cost of freight.
Q: What is your terms of payment ?
A: Payment=1000USD, 30% T/T in advance ,balance before shippment.
We warmly welcome friends from domestic and abroad come to us for business negotiation and cooperation for mutual benefit.To supply customers excellent quality products with good price and punctual delivery time is our responsibility.
Screw Shaft Types and Uses
Various uses for the screw shaft are numerous. Its major diameter is the most significant characteristic, while other aspects include material and function are important. Let us explore these topics in more detail. There are many different types of screw shafts, which include bronze, brass, titanium, and stainless steel. Read on to learn about the most common types. Listed below are some of the most common uses for a screw shaft. These include: C-clamps, screw jacks, vises, and more.
Major diameter of a screw shaft
A screw’s major diameter is measured in fractions of an inch. This measurement is commonly found on the screw label. A screw with a major diameter less than 1/4″ is labeled #0 to #14; those with a larger diameter are labeled fractions of an inch in a corresponding decimal scale. The length of a screw, also known as the shaft, is another measure used for the screw.
The major diameter of a screw shaft is the greater of its 2 outer diameters. When determining the major diameter of a screw, use a caliper, micrometer, or steel rule to make an accurate measurement. Generally, the first number in the thread designation refers to the major diameter. Therefore, if a screw has a thread of 1/2-10 Acme, the major diameter of the thread is.500 inches. The major diameter of the screw shaft will be smaller or larger than the original diameter, so it’s a good idea to measure the section of the screw that’s least used.
Another important measurement is the pitch. This measures the distance between 1 thread’s tip and the next thread’s corresponding point. Pitch is an important measurement because it refers to the distance a screw will advance in 1 turn. While lead and pitch are 2 separate concepts, they are often used interchangeably. As such, it’s important to know how to use them properly. This will make it easier to understand how to select the correct screw.
There are 3 different types of threads. The UTS and ISO metric threads are similar, but their common values for Dmaj and Pmaj are different. A screw’s major diameter is the largest diameter, while the minor diameter is the lowest. A nut’s major diameter, or the minor diameter, is also called the nut’s inside diameter. A bolt’s major diameter and minor diameter are measured with go/no-go gauges or by using an optical comparator.
The British Association and American Society of Mechanical Engineers standardized screw threads in the 1840s. A standard named “British Standard Whitworth” became a common standard for screw threads in the United States through the 1860s. In 1864, William Sellers proposed a new standard that simplified the Whitworth thread and had a 55 degree angle at the tip. Both standards were widely accepted. The major diameter of a screw shaft can vary from 1 manufacturer to another, so it’s important to know what size screw you’re looking for.
In addition to the thread angle, a screw’s major diameter determines the features it has and how it should be used. A screw’s point, or “thread”, is usually spiky and used to drill into an object. A flat tipped screw, on the other hand, is flat and requires a pre-drilled hole for installation. Finally, the diameter of a screw bolt is determined by the major and minor diameters.
Material of a screw shaft
A screw shaft is a piece of machine equipment used to move raw materials. The screw shaft typically comprises a raw material w. For a particular screw to function correctly, the raw material must be sized properly. In general, screw shafts should have an axial-direction length L equal to the moving amount k per 1/2 rotation of the screw. The screw shaft must also have a proper contact angle ph1 in order to prevent raw material from penetrating the screw shaft.
The material used for the shaft depends on its application. A screw with a ball bearing will work better with a steel shaft than 1 made of aluminum. Aluminum screw shafts are the most commonly used for this application. Other materials include titanium. Some manufacturers also prefer stainless steel. However, if you want a screw with a more modern appearance, a titanium shaft is the way to go. In addition to that, screws with a chromium finish have better wear resistance.
The material of a screw shaft is important for a variety of applications. It needs to have high precision threads and ridges to perform its function. Manufacturers often use high-precision CNC machines and lathes to create screw shafts. Different screw shafts can have varying sizes and shapes, and each 1 will have different applications. Listed below are the different materials used for screw shafts. If you’re looking for a high-quality screw shaft, you should shop around.
A lead screw has an inverse relationship between contact surface pressure and sliding velocity. For heavier axial loads, a reduced rotation speed is needed. This curve will vary depending on the material used for the screw shaft and its lubrication conditions. Another important factor is end fixity. The material of a screw shaft can be either fixed or free, so make sure to consider this factor when choosing the material of your screw. The latter can also influence the critical speed and rigidity of the screw.
A screw shaft’s major diameter is the distance between the outer edge of the thread and the inner smooth part. Screw shafts are typically between 2 and 16 millimeters in diameter. They feature a cylindrical shape, a pointy tip, and a wider head and drive than the former. There are 2 basic types of screw heads: threaded and non-threaded. These have different properties and purposes.
Lead screws are a cost-effective alternative to ball screws, and are used for low power and light to medium-duty applications. They offer some advantages, but are not recommended for continuous power transmission. But lead screws are often quieter and smaller, which make them useful for many applications. Besides, they are often used in a kinematic pair with a nut object. They are also used to position objects.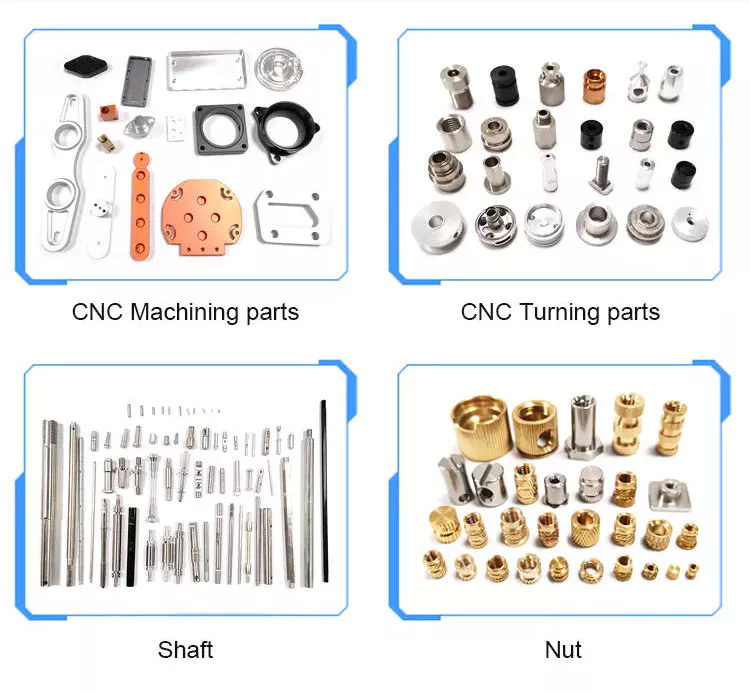
Function of a screw shaft
When choosing a screw for a linear motion system, there are many factors that should be considered, such as the position of the actuator and the screw and nut selection. Other considerations include the overall length of travel, the fastest move profile, the duty cycle, and the repeatability of the system. As a result, screw technology plays a critical role in the overall performance of a system. Here are the key factors to consider when choosing a screw.
Screws are designed with an external threading that digs out material from a surface or object. Not all screw shafts have complete threading, however. These are known as partially threaded screws. Fully threaded screws feature complete external threading on the shaft and a pointed tip. In addition to their use as fasteners, they can be used to secure and tighten many different types of objects and appliances.
Another factor to consider is axial force. The higher the force, the bigger the screw needs to be. Moreover, screws are similar to columns that are subject to both tension and compression loads. During the compression load, bowing or deflection is not desirable, so the integrity of the screw is important. So, consider the design considerations of your screw shaft and choose accordingly. You can also increase the torque by using different shaft sizes.
Shaft collars are also an important consideration. These are used to secure and position components on the shaft. They also act as stroke limiters and to retain sprocket hubs, bearings, and shaft protectors. They are available in several different styles. In addition to single and double split shaft collars, they can be threaded or set screw. To ensure that a screw collar will fit tightly to the shaft, the cap must not be overtightened.
Screws can be cylindrical or conical and vary in length and diameter. They feature a thread that mates with a complementary helix in the material being screwed into. A self-tapping screw will create a complementary helix during driving, creating a complementary helix that allows the screw to work with the material. A screw head is also an essential part of a screw, providing gripping power and compression to the screw.
A screw’s pitch and lead are also important parameters to consider. The pitch of the screw is the distance between the crests of the threads, which increases mechanical advantage. If the pitch is too small, vibrations will occur. If the pitch is too small, the screw may cause excessive wear and tear on the machine and void its intended purpose. The screw will be useless if it can’t be adjusted. And if it can’t fit a shaft with the required diameter, then it isn’t a good choice.
Despite being the most common type, there are various types of screws that differ in their functions. For example, a machine screw has a round head, while a truss head has a lower-profile dome. An oval-its point screw is a good choice for situations where the screw needs to be adjusted frequently. Another type is a soft nylon tip, which looks like a Half-dog point. It is used to grip textured or curved surfaces.


China supplier China Ws Type Universal Joint Shaft with Double Cross near me factory
Product Description
WS Type Universal Joint Shaft
Features:
1. It is suitable for transmission coupling space on the same plane of 2 axis angle beta β≤45°, the nominal torque transmission 11.2-1120N.
2.The WSD type is a single cross universal coupling, and the WS type is a double cross universal coupling.
3.Each section between the largest axis angle 45º.
4.The finished hole H7, according to the requirements of keyseating, 6 square hole and square hole.
5.The angle between the 2 axes is allowed in a limited range as the work requirements change.
|
NO |
Tn/N·m |
d(H7) |
D |
L0 |
L |
L1 |
m/kg |
I/kg·m2 |
||||||||||
|
WSD |
WS |
WSD |
WS |
WSD |
WS |
|||||||||||||
|
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
|||||
|
WS1 WSD1 |
11.2 |
8 |
16 |
60 |
– |
80 |
– |
20 |
– |
20 |
0.23 |
– |
0.32 |
– |
0.06 |
– |
0.08 |
– |
|
9 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
10 |
66 |
60 |
86 |
80 |
25 |
22 |
0.2 |
0.29 |
0.05 |
0.07 |
||||||||
|
WS2 WSD2 |
22.4 |
10 |
20 |
70 |
64 |
96 |
90 |
26 |
0.64 |
0.57 |
0.93 |
0.88 |
0.1 |
0.09 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
||
|
11 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
12 |
84 |
74 |
110 |
100 |
32 |
27 |
||||||||||||
|
WS3 WSD3 |
45 |
12 |
25 |
90 |
80 |
122 |
112 |
32 |
1.45 |
1.3 |
2.1 |
1.95 |
0.17 |
0.15 |
0.24 |
0.22 |
||
|
14 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS4 WSD4 |
71 |
16 |
32 |
116 |
82 |
154 |
130 |
42 |
30 |
38 |
5.92 |
4.86 |
8.56 |
0.48 |
0.39 |
0.32 |
0.56 |
0.49 |
|
18 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS5 WSD5 |
140 |
19 |
40 |
144 |
116 |
192 |
164 |
48 |
16.3 |
12.9 |
24 |
20.6 |
0.72 |
0.59 |
1.04 |
0.91 |
||
|
20 |
52 |
38 |
||||||||||||||||
|
22 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS6 WSD6 |
280 |
24 |
50 |
152 |
124 |
210 |
182 |
52 |
38 |
58 |
45.7 |
36.7 |
68.9 |
59.7 |
1.28 |
1.03 |
1.89 |
1.64 |
|
25 |
172 |
136 |
330 |
194 |
62 |
44 |
||||||||||||
|
28 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS7 WSD7 |
560 |
30 |
60 |
226 |
182 |
296 |
252 |
82 |
60 |
70 |
148 |
117 |
207 |
177 |
2.82 |
2.31 |
3.9 |
3.38 |
|
32 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
35 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS8 WSD8 |
1120 |
38 |
75 |
240 |
196 |
332 |
288 |
92 |
396 |
338 |
585 |
525 |
5.03 |
4.41 |
7.25 |
6.63 |
||
|
40 |
300 |
244 |
392 |
336 |
112 |
84 |
||||||||||||
|
42 |
||||||||||||||||||
Pictures
Huading is a professional manufacturer and supplier for cardan shaft, universal joint and coupling(diaphragm coupling, flexible coupling, gear coupling etc.), our products have been exported to North America, Italy, France, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Mid East and other countries.
Our Services
24 hours online service
Enquiry will be replied in 2 hours
Factory Address:
No. 11, HangZhou Road, ChengNan Industrial Park, HangZhou, HangZhou, ZheJiang , China
Web: http://huadingcoupling
FAQ
1. Are u a manufacturer?
We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing cardan shaft and various series of couplings. We supply couplings for the wholesalers and dealers from different countries.
2. Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks of PDF or AI format.
3. How does your factory do regarding quality control?
Quality is priority! We always attach great importance to quality controlling from the very beginning to the very end:
1) Firstly, we have specialized QC department to control the quality, and we also accept the third official government to inspect the cargoes before delivery.
2) Secondly, we have all detailed records for nonconformity products, then we will make summary according to these records, avoid it happen again.
3) Thirdly, We do observe the relevant codes of conduct & laws from government in environment, human right aspects like no children labor, no prisoner labor and so on.
4. How can I get samples?
We are appreciated that new clients pay for the express fee for samples and this charge will be deducted once orders are released.
Welcome to customize products from our factory and pls send us more details about your purchasing.
Thank you for your time and attention.
The Different Types of Splines in a Splined Shaft
A splined shaft is a machine component with internal and external splines. The splines are formed in 4 different ways: Involute, Parallel, Serrated, and Ball. You can learn more about each type of spline in this article. When choosing a splined shaft, be sure to choose the right 1 for your application. Read on to learn about the different types of splines and how they affect the shaft’s performance.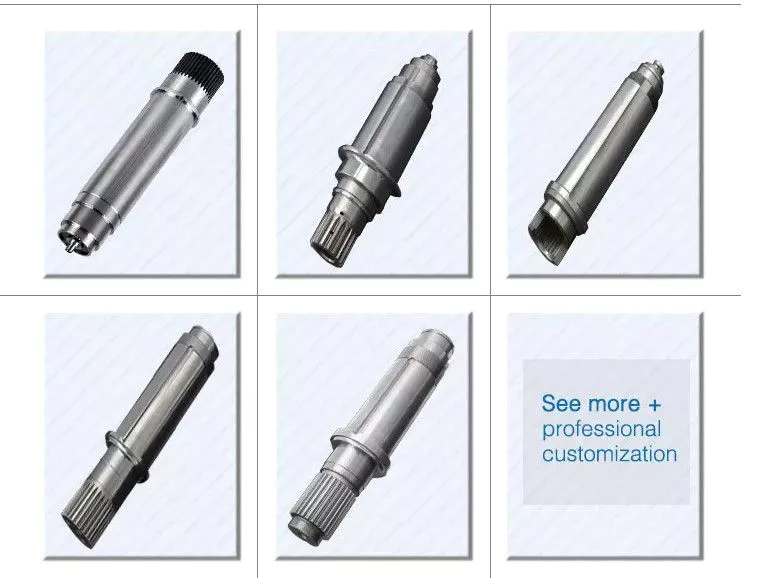
Involute splines
Involute splines in a splined shaft are used to secure and extend mechanical assemblies. They are smooth, inwardly curving grooves that resist separation during operation. A shaft with involute splines is often longer than the shaft itself. This feature allows for more axial movement. This is beneficial for many applications, especially in a gearbox.
The involute spline is a shaped spline, similar to a parallel spline. It is angled and consists of teeth that create a spiral pattern that enables linear and rotatory motion. It is distinguished from other splines by the serrations on its flanks. It also has a flat top. It is a good option for couplers and other applications where angular movement is necessary.
Involute splines are also called involute teeth because of their shape. They are flat on the top and curved on the sides. These teeth can be either internal or external. As a result, involute splines provide greater surface contact, which helps reduce stress and fatigue. Regardless of the shape, involute splines are generally easy to machine and fit.
Involute splines are a type of splines that are used in splined shafts. These splines have different names, depending on their diameters. An example set of designations is for a 32-tooth male spline, a 2,500-tooth module, and a 30 degree pressure angle. An example of a female spline, a fillet root spline, is used to describe the diameter of the splined shaft.
The effective tooth thickness of splines is dependent on the number of keyways and the type of spline. Involute splines in splined shafts should be designed to engage 25 to 50 percent of the spline teeth during the coupling. Involute splines should be able to withstand the load without cracking.
Parallel splines
Parallel splines are formed on a splined shaft by putting 1 or more teeth into another. The male spline is positioned at the center of the female spline. The teeth of the male spline are also parallel to the shaft axis, but a common misalignment causes the splines to roll and tilt. This is common in many industrial applications, and there are a number of ways to improve the performance of splines.
Typically, parallel splines are used to reduce friction in a rotating part. The splines on a splined shaft are narrower on the end face than the interior, which makes them more prone to wear. This type of spline is used in a variety of industries, such as machinery, and it also allows for greater efficiency when transmitting torque.
Involute splines on a splined shaft are the most common. They have equally spaced teeth, and are therefore less likely to crack due to fatigue. They also tend to be easy to cut and fit. However, they are not the best type of spline. It is important to understand the difference between parallel and involute splines before deciding on which spline to use.
The difference between splined and involute splines is the size of the grooves. Involute splines are generally larger than parallel splines. These types of splines provide more torque to the gear teeth and reduce stress during operation. They are also more durable and have a longer life span. And because they are used on farm machinery, they are essential in this type of application.
Serrated splines
A Serrated Splined Shaft has several advantages. This type of shaft is highly adjustable. Its large number of teeth allows large torques, and its shorter tooth width allows for greater adjustment. These features make this type of shaft an ideal choice for applications where accuracy is critical. Listed below are some of the benefits of this type of shaft. These benefits are just a few of the advantages. Learn more about this type of shaft.
The process of hobbing is inexpensive and highly accurate. It is useful for external spline shafts, but is not suitable for internal splines. This type of process forms synchronized shapes on the shaft, reducing the manufacturing cycle and stabilizing the relative phase between spline and thread. It uses a grinding wheel to shape the shaft. CZPT Manufacturing has a large inventory of Serrated Splined Shafts.
The teeth of a Serrated Splined Shaft are designed to engage with the hub over the entire circumference of the shaft. The teeth of the shaft are spaced uniformly around the spline, creating a multiple-tooth point of contact over the entire length of the shaft. The results of these analyses are usually satisfactory. But there are some limitations. To begin with, the splines of the Serrated Splined Shaft should be chosen carefully. If the application requires large-scale analysis, it may be necessary to modify the design.
The splines of the Serrated Splined Shaft are also used for other purposes. They can be used to transmit torque to another device. They also act as an anti-rotational device and function as a linear guide. Both the design and the type of splines determine the function of the Splined Shaft. In the automobile industry, they are used in vehicles, aerospace, earth-moving machinery, and many other industries.
Ball splines
The invention relates to a ball-spinned shaft. The shaft comprises a plurality of balls that are arranged in a series and are operatively coupled to a load path section. The balls are capable of rolling endlessly along the path. This invention also relates to a ball bearing. Here, a ball bearing is 1 of the many types of gears. The following discussion describes the features of a ball bearing.
A ball-splined shaft assembly comprises a shaft with at least 1 ball-spline groove and a plurality of circumferential step grooves. The shaft is held in a first holding means that extends longitudinally and is rotatably held by a second holding means. Both the shaft and the first holding means are driven relative to 1 another by a first driving means. It is possible to manufacture a ball-splined shaft in a variety of ways.
A ball-splined shaft features a nut with recirculating balls. The ball-splined nut rides in these grooves to provide linear motion while preventing rotation. A splined shaft with a nut that has recirculating balls can also provide rotary motion. A ball splined shaft also has higher load capacities than a ball bushing. For these reasons, ball splines are an excellent choice for many applications.
In this invention, a pair of ball-spinned shafts are housed in a box under a carrier device 40. Each of the 2 shafts extends along a longitudinal line of arm 50. One end of each shaft is supported rotatably by a slide block 56. The slide block also has a support arm 58 that supports the center arm 50 in a cantilever fashion.
Sector no-go gage
A no-go gauge is a tool that checks the splined shaft for oversize. It is an effective way to determine the oversize condition of a splined shaft without removing the shaft. It measures external splines and serrations. The no-go gage is available in sizes ranging from 19mm to 130mm with a 25mm profile length.
The sector no-go gage has 2 groups of diametrally opposed teeth. The space between them is manufactured to a maximum space width and the tooth thickness must be within a predetermined tolerance. This gage would be out of tolerance if the splines were measured with a pin. The dimensions of this splined shaft can be found in the respective ANSI or DIN standards.
The go-no-go gage is useful for final inspection of thread pitch diameter. It is also useful for splined shafts and threaded nuts. The thread of a screw must match the contour of the go-no-go gage head to avoid a no-go condition. There is no substitute for a quality machine. It is an essential tool for any splined shaft and fastener manufacturer.
The NO-GO gage can detect changes in tooth thickness. It can be calibrated under ISO17025 standards and has many advantages over a non-go gage. It also gives a visual reference of the thickness of a splined shaft. When the teeth match, the shaft is considered ready for installation. It is a critical process. In some cases, it is impossible to determine the precise length of the shaft spline.
The 45-degree pressure angle is most commonly used for axles and torque-delivering members. This pressure angle is the most economical in terms of tool life, but the splines will not roll neatly like a 30 degree angle. The 45-degree spline is more likely to fall off larger than the other two. Oftentimes, it will also have a crowned look. The 37.5 degree pressure angle is a compromise between the other 2 pressure angles. It is often used when the splined shaft material is harder than usual.

