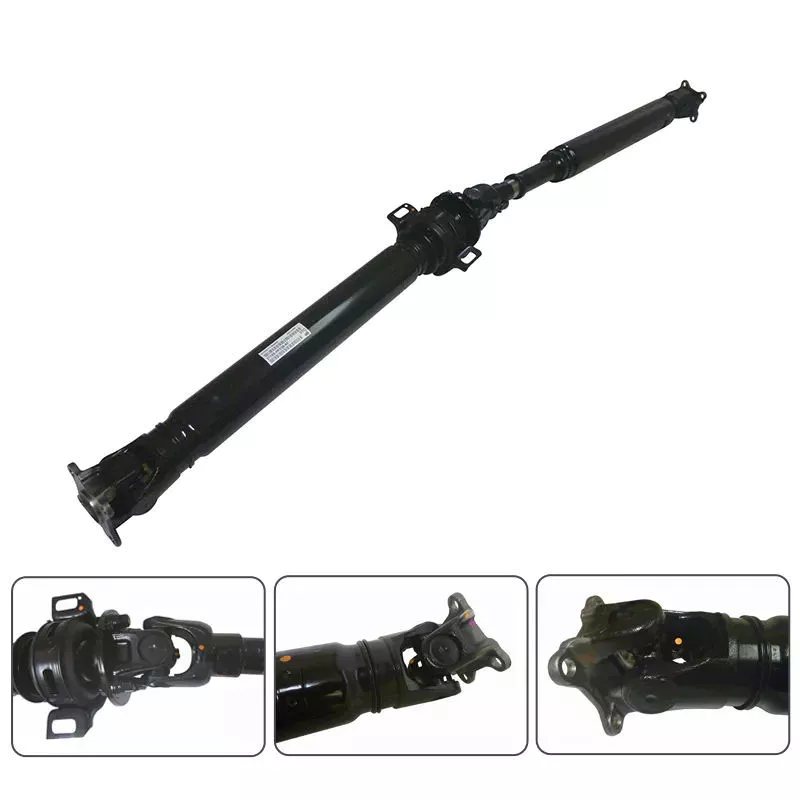
Product Description
Universal joints Cross Joints U-Joints for For Agricultural Machine
Product Name:Universal joints/ Cross Joints/U-Joints for For Agricultural/ Machine /For Europe Vehicle /Brackets Tapered U-Joint Kits
Quick Details:
|
Material |
Plastic |
|
Place of Origin |
ZheJiang , China (Mainland) |
|
Usage |
car/truck/Agricultural Machine /Steering Gear |
|
Car Make |
Japanese, American and European vehicle |
|
Port: |
ZheJiang or HangZhou port |
|
Packaging Details: |
per cartons and wooden pallets |
|
Delivery Time: |
10-30days |
|
Payment Terms: |
L/C,T/T,Western Union |
|
Supply Ability: |
20000 Unit/Units per Day |
| SKF FAG CZPT NTN NACHI BRAND | ||
| GMB | ORIGINAL NO | KOYO NO. |
| GUT-11 | 5711-10011 | T2057 |
| GUT-12 | 5711-30011 | T2680C |
| GUT-13 | 5711-2571 | T2667 |
| GUT-14 | 5711-6571 | T2978 |
| GUT-15 | 5711-55011 | T34107 |
| GUT-16 | 5711-55571 | T40119 |
| GUT-17 | 5711-3571 | T2977 |
| GUT-19 | 5711-1571 | T2057 |
| GUT-20 | 5711-36571 | T32921 |
| GUT-21 | 5711-35571 | |
| GUT-23 | 5711-35030 | |
| GUT-24 | ||
| MAZADA | ||
| GMB NO. | ORIGINAL NO. | KOYO NO. |
| GUMZ1(5) | 0136-25-060 | TM2564A |
| GUMZ2 | 0180-25-060 | TM2055 |
| GUMZ3(4) | 0164-25-060 | TM2880 |
| GUMZ6 | 0706-80-251 | GM2564B~E |
| GUMZ7 | 5719-25-060 | TM37104 |
| GUMZ8 | 0727-25-060 | |
| GUMZ9 | 1757-89-251 | |
| GUMZ10 | 3919-89-251 | |
| Honda | ||
| GMB NO. | ORIGINAL NO. | KOYO NO. |
| GUH-02 | 40150-567-003 | HD2564LS |
| GUH-03 | 44330-538-004 | HD2265C |
| GUH-65 | ||
| GUH-68 | ||
| GUH-72 | ||
| GUH-73 | ||
| ISUZU | ||
| GMB NO. | ORIGINAL NO. | KOYO NO. |
| GUIS 51 | 9-37300-017 | 12461 |
| GUIS 52 | 9-37300-065 | 12976 |
| GUIS 54 | 9-37300-055 | 136101 |
| GUIS 55 | 9-37300-150 | 142129A |
| GUIS 56 | 9-37300-609 | |
| GUIS 57 | 9-37300-163 | 148149 |
| GUIS 58 | 9-37300-112 | 136101A |
| GUIS 59 | 44135-060 | |
| GUIS 60 | 9-37300-139 | 070004R-1 |
| GUIS 61 | 9-37300-031 | |
| GUIS 62 | 1-37300-0130 | 1351041 |
| GUIS 63 | 942571-1 | |
| GUIS 64 | 1-37300-147-0 | |
| GUIS 65 | 1-37300-004-0 | |
| GUIS 66 | 5-37300-032-0 | |
| Nissan | ||
| GMB | ORIGINAL NO. | KOYO NO. |
| GUN-26 | 37125-11975 | N2461 |
| GUN-27 | 37125-14627 | N2563 |
| GUN-28 | 37125-18571 | N2057 |
| GUN-29 | 39625-21571 | N2880BA |
| GUN-30 | 37125-85461 | N3092 |
| GUN-31 | 37125-50001 | N32111 |
| GUN-32 | 37125-58026 | N36119 |
| GUN-33 | 37125-99901 | ND43128 |
| GUN-34 | 37125-76571 | N2580 |
| GUN-36 | 23571-4101(65109) | N2578 |
| GUN-38 | 37125-68200 | |
| GUN-41 | 37125-90128 | ND43142 |
| GUN-42 | 37125-99900 | ND40124 |
| GUN-43 | 37125-90571 | ND43128B |
| GUN-44 | 48155-99000 | |
| GUN-45 | 37000-H8500 | |
| GUN-46 | 37125-01G25 | |
| GUN-47 | ||
| SUZUKI | ||
| GMB NO. | ORIGINAL NO. | |
| GUS1 | 27200-58833 | |
| GUS2 | 27100-67000 | |
| GUS7 | ||
| GUS6 | 27200-6571 | |
Part Number (1):
5-279X, 5-280X, 5-4070X, 5-281X, 5-279X-1, 5-280X-1, 5-407X-1, 5-281X-1, G5-2172, 2C-2T, 4C-2T, G5-4143, G5-5177, G5-6128, 1822, 1841, 1843, G5-7126, GUIS-67, 1868, 5-324X,CT42, CT53
Part Number (2):
GUIS55, GUN41-1, , GUM-90, GUM-80, GUH-72, GUIS57, GUIS68, GUM-83, 5050, 5800, 5801, 5870, 5030, 5041
Part Number (3):
GUD-88, 5-170X, GUMZ-7, GUN-27, GUT-13, GUT-12,5-353X, 5-3147X , TT-177, 5-297X, TT-120, 5-1510X, 5-1500X, 5-1505X, 5-1516X, 5-1206X, 5-1306X, 5-1204X, 365, YH1571, YH1012, YH1058, 5-100X, 5-105X, 5-1200X, 5-1203X, 5-212X, 5-260X, 5-456X, 5-3147X, TT-121, GUM-93, 5-1301X, GUMZ-3, ST-1640, C01, AP165, GUT-11, APO-10, AP1-00, EG10, IU50, EG20, GU-500, IU-40, GUMZ-1, AP3-11, AP4-21, 5-200X, 50.724.000, 5-134X, 5-153X, 5-130X5-130X, GU1100, EG30, 5-160X, 3240AF, GUM-87, AP500, AP723, 5-178X, EG60-1, C06, EG50, AM35R, APO-35, 3287AF, 4265AF, 5-155X-1, 5-188X, AP36,4225BF, 5-165X
Screw Shaft Types and Uses
Various uses for the screw shaft are numerous. Its major diameter is the most significant characteristic, while other aspects include material and function are important. Let us explore these topics in more detail. There are many different types of screw shafts, which include bronze, brass, titanium, and stainless steel. Read on to learn about the most common types. Listed below are some of the most common uses for a screw shaft. These include: C-clamps, screw jacks, vises, and more.
Major diameter of a screw shaft
A screw’s major diameter is measured in fractions of an inch. This measurement is commonly found on the screw label. A screw with a major diameter less than 1/4″ is labeled #0 to #14; those with a larger diameter are labeled fractions of an inch in a corresponding decimal scale. The length of a screw, also known as the shaft, is another measure used for the screw.
The major diameter of a screw shaft is the greater of its 2 outer diameters. When determining the major diameter of a screw, use a caliper, micrometer, or steel rule to make an accurate measurement. Generally, the first number in the thread designation refers to the major diameter. Therefore, if a screw has a thread of 1/2-10 Acme, the major diameter of the thread is.500 inches. The major diameter of the screw shaft will be smaller or larger than the original diameter, so it’s a good idea to measure the section of the screw that’s least used.
Another important measurement is the pitch. This measures the distance between 1 thread’s tip and the next thread’s corresponding point. Pitch is an important measurement because it refers to the distance a screw will advance in 1 turn. While lead and pitch are 2 separate concepts, they are often used interchangeably. As such, it’s important to know how to use them properly. This will make it easier to understand how to select the correct screw.
There are 3 different types of threads. The UTS and ISO metric threads are similar, but their common values for Dmaj and Pmaj are different. A screw’s major diameter is the largest diameter, while the minor diameter is the lowest. A nut’s major diameter, or the minor diameter, is also called the nut’s inside diameter. A bolt’s major diameter and minor diameter are measured with go/no-go gauges or by using an optical comparator.
The British Association and American Society of Mechanical Engineers standardized screw threads in the 1840s. A standard named “British Standard Whitworth” became a common standard for screw threads in the United States through the 1860s. In 1864, William Sellers proposed a new standard that simplified the Whitworth thread and had a 55 degree angle at the tip. Both standards were widely accepted. The major diameter of a screw shaft can vary from 1 manufacturer to another, so it’s important to know what size screw you’re looking for.
In addition to the thread angle, a screw’s major diameter determines the features it has and how it should be used. A screw’s point, or “thread”, is usually spiky and used to drill into an object. A flat tipped screw, on the other hand, is flat and requires a pre-drilled hole for installation. Finally, the diameter of a screw bolt is determined by the major and minor diameters.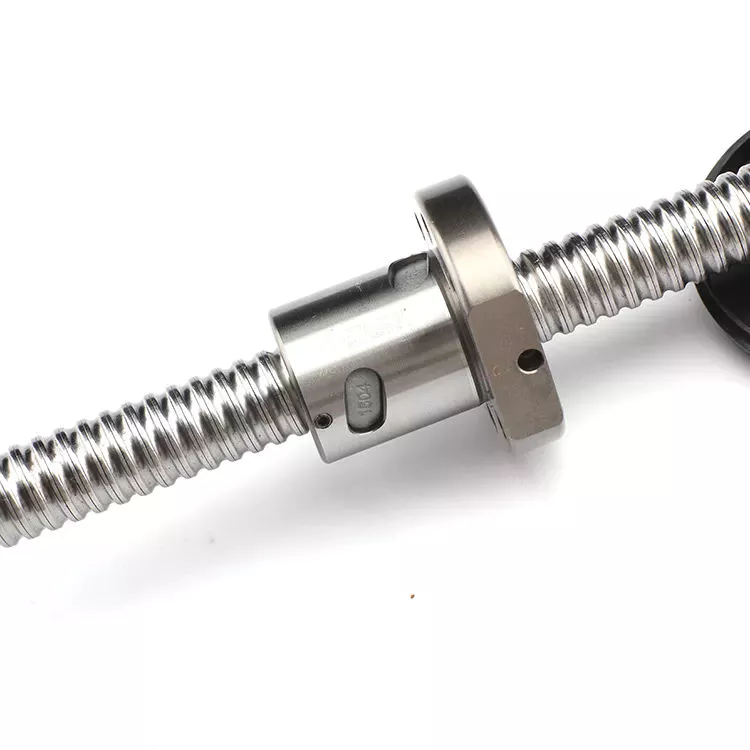
Material of a screw shaft
A screw shaft is a piece of machine equipment used to move raw materials. The screw shaft typically comprises a raw material w. For a particular screw to function correctly, the raw material must be sized properly. In general, screw shafts should have an axial-direction length L equal to the moving amount k per 1/2 rotation of the screw. The screw shaft must also have a proper contact angle ph1 in order to prevent raw material from penetrating the screw shaft.
The material used for the shaft depends on its application. A screw with a ball bearing will work better with a steel shaft than 1 made of aluminum. Aluminum screw shafts are the most commonly used for this application. Other materials include titanium. Some manufacturers also prefer stainless steel. However, if you want a screw with a more modern appearance, a titanium shaft is the way to go. In addition to that, screws with a chromium finish have better wear resistance.
The material of a screw shaft is important for a variety of applications. It needs to have high precision threads and ridges to perform its function. Manufacturers often use high-precision CNC machines and lathes to create screw shafts. Different screw shafts can have varying sizes and shapes, and each 1 will have different applications. Listed below are the different materials used for screw shafts. If you’re looking for a high-quality screw shaft, you should shop around.
A lead screw has an inverse relationship between contact surface pressure and sliding velocity. For heavier axial loads, a reduced rotation speed is needed. This curve will vary depending on the material used for the screw shaft and its lubrication conditions. Another important factor is end fixity. The material of a screw shaft can be either fixed or free, so make sure to consider this factor when choosing the material of your screw. The latter can also influence the critical speed and rigidity of the screw.
A screw shaft’s major diameter is the distance between the outer edge of the thread and the inner smooth part. Screw shafts are typically between 2 and 16 millimeters in diameter. They feature a cylindrical shape, a pointy tip, and a wider head and drive than the former. There are 2 basic types of screw heads: threaded and non-threaded. These have different properties and purposes.
Lead screws are a cost-effective alternative to ball screws, and are used for low power and light to medium-duty applications. They offer some advantages, but are not recommended for continuous power transmission. But lead screws are often quieter and smaller, which make them useful for many applications. Besides, they are often used in a kinematic pair with a nut object. They are also used to position objects.
Function of a screw shaft
When choosing a screw for a linear motion system, there are many factors that should be considered, such as the position of the actuator and the screw and nut selection. Other considerations include the overall length of travel, the fastest move profile, the duty cycle, and the repeatability of the system. As a result, screw technology plays a critical role in the overall performance of a system. Here are the key factors to consider when choosing a screw.
Screws are designed with an external threading that digs out material from a surface or object. Not all screw shafts have complete threading, however. These are known as partially threaded screws. Fully threaded screws feature complete external threading on the shaft and a pointed tip. In addition to their use as fasteners, they can be used to secure and tighten many different types of objects and appliances.
Another factor to consider is axial force. The higher the force, the bigger the screw needs to be. Moreover, screws are similar to columns that are subject to both tension and compression loads. During the compression load, bowing or deflection is not desirable, so the integrity of the screw is important. So, consider the design considerations of your screw shaft and choose accordingly. You can also increase the torque by using different shaft sizes.
Shaft collars are also an important consideration. These are used to secure and position components on the shaft. They also act as stroke limiters and to retain sprocket hubs, bearings, and shaft protectors. They are available in several different styles. In addition to single and double split shaft collars, they can be threaded or set screw. To ensure that a screw collar will fit tightly to the shaft, the cap must not be overtightened.
Screws can be cylindrical or conical and vary in length and diameter. They feature a thread that mates with a complementary helix in the material being screwed into. A self-tapping screw will create a complementary helix during driving, creating a complementary helix that allows the screw to work with the material. A screw head is also an essential part of a screw, providing gripping power and compression to the screw.
A screw’s pitch and lead are also important parameters to consider. The pitch of the screw is the distance between the crests of the threads, which increases mechanical advantage. If the pitch is too small, vibrations will occur. If the pitch is too small, the screw may cause excessive wear and tear on the machine and void its intended purpose. The screw will be useless if it can’t be adjusted. And if it can’t fit a shaft with the required diameter, then it isn’t a good choice.
Despite being the most common type, there are various types of screws that differ in their functions. For example, a machine screw has a round head, while a truss head has a lower-profile dome. An oval-its point screw is a good choice for situations where the screw needs to be adjusted frequently. Another type is a soft nylon tip, which looks like a Half-dog point. It is used to grip textured or curved surfaces.