Product Description
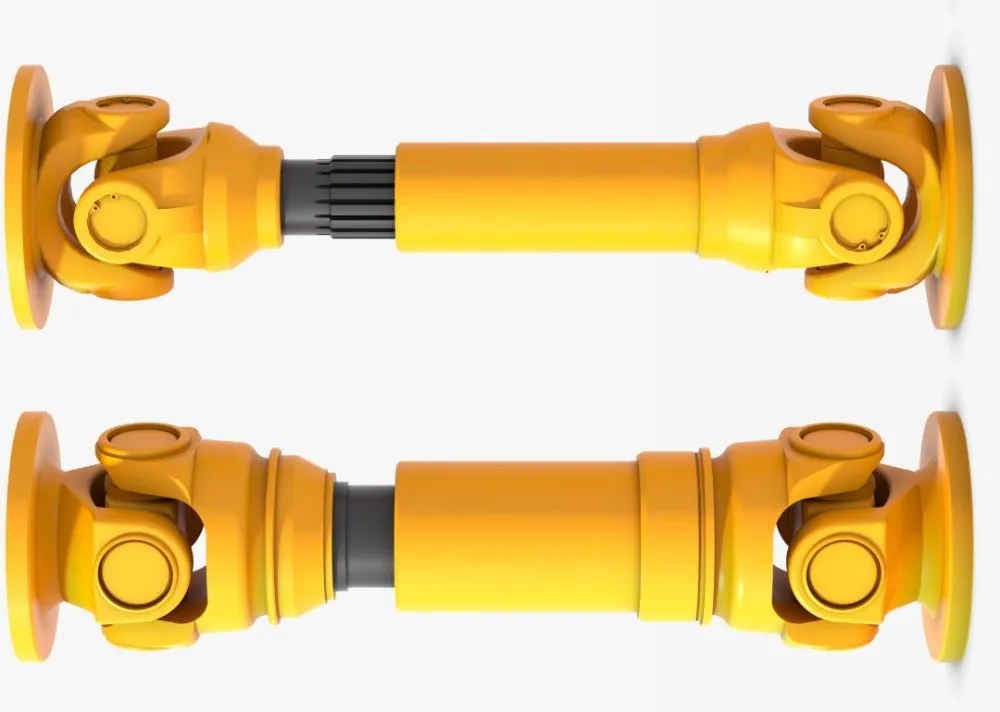
WS Type Universal Joint Shaft
Features:
1. It is suitable for transmission coupling space on the same plane of 2 axis angle beta β≤45°, the nominal torque transmission 11.2-1120N.
2.The WSD type is a single cross universal coupling, and the WS type is a double cross universal coupling.
3.Each section between the largest axis angle 45º.
4.The finished hole H7, according to the requirements of keyseating, 6 square hole and square hole.
5.The angle between the 2 axes is allowed in a limited range as the work requirements change.
|
NO |
Tn/N·m |
d(H7) |
D |
L0 |
L |
L1 |
m/kg |
I/kg·m2 |
||||||||||
|
WSD |
WS |
WSD |
WS |
WSD |
WS |
|||||||||||||
|
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
|||||
|
WS1 WSD1 |
11.2 |
8 |
16 |
60 |
– |
80 |
– |
20 |
– |
20 |
0.23 |
– |
0.32 |
– |
0.06 |
– |
0.08 |
– |
|
9 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
10 |
66 |
60 |
86 |
80 |
25 |
22 |
0.2 |
0.29 |
0.05 |
0.07 |
||||||||
|
WS2 WSD2 |
22.4 |
10 |
20 |
70 |
64 |
96 |
90 |
26 |
0.64 |
0.57 |
0.93 |
0.88 |
0.1 |
0.09 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
||
|
11 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
12 |
84 |
74 |
110 |
100 |
32 |
27 |
||||||||||||
|
WS3 WSD3 |
45 |
12 |
25 |
90 |
80 |
122 |
112 |
32 |
1.45 |
1.3 |
2.1 |
1.95 |
0.17 |
0.15 |
0.24 |
0.22 |
||
|
14 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS4 WSD4 |
71 |
16 |
32 |
116 |
82 |
154 |
130 |
42 |
30 |
38 |
5.92 |
4.86 |
8.56 |
0.48 |
0.39 |
0.32 |
0.56 |
0.49 |
|
18 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS5 WSD5 |
140 |
19 |
40 |
144 |
116 |
192 |
164 |
48 |
16.3 |
12.9 |
24 |
20.6 |
0.72 |
0.59 |
1.04 |
0.91 |
||
|
20 |
52 |
38 |
||||||||||||||||
|
22 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS6 WSD6 |
280 |
24 |
50 |
152 |
124 |
210 |
182 |
52 |
38 |
58 |
45.7 |
36.7 |
68.9 |
59.7 |
1.28 |
1.03 |
1.89 |
1.64 |
|
25 |
172 |
136 |
330 |
194 |
62 |
44 |
||||||||||||
|
28 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS7 WSD7 |
560 |
30 |
60 |
226 |
182 |
296 |
252 |
82 |
60 |
70 |
148 |
117 |
207 |
177 |
2.82 |
2.31 |
3.9 |
3.38 |
|
32 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
35 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS8 WSD8 |
1120 |
38 |
75 |
240 |
196 |
332 |
288 |
92 |
396 |
338 |
585 |
525 |
5.03 |
4.41 |
7.25 |
6.63 |
||
|
40 |
300 |
244 |
392 |
336 |
112 |
84 |
||||||||||||
|
42 |
||||||||||||||||||
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
HangZhou CHINAMFG Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the design and manufacture of various types of coupling. There are 86 employees in our company, including 2 senior engineers and no fewer than 20 mechanical design and manufacture, heat treatment, welding, and other professionals.
Advanced and reasonable process, complete detection means. Our company actively introduces foreign advanced technology and equipment, on the basis of the condition, we make full use of the advantage and do more research and innovation. Strict to high quality and operate strictly in accordance with the ISO9000 quality certification system standard mode.
Our company supplies different kinds of products. High quality and reasonable price. We stick to the principle of “quality first, service first, continuous improvement and innovation to meet the customers” for the management and “zero defect, zero complaints” as the quality objective.
Our Services
1. Design Services
Our design team has experience in Cardan shafts relating to product design and development. If you have any needs for your new product or wish to make further improvements, we are here to offer our support.
2. Product Services
raw materials → Cutting → Forging →Rough machining →Shot blasting →Heat treatment →Testing →Fashioning →Cleaning→ Assembly→Packing→Shipping
3. Samples Procedure
We could develop the sample according to your requirement and amend the sample constantly to meet your need.
4. Research & Development
We usually research the new needs of the market and develop new models when there are new cars in the market.
5. Quality Control
Every step should be a particular test by Professional Staff according to the standard of ISO9001 and TS16949.
FAQ
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing
various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all customers with customized PDF or AI format artwork.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: Do you provide samples? Is it free or extra?
Yes, we could offer the sample but not for free. Actually, we have an excellent price principle, when you make the bulk order the cost of the sample will be deducted.
Q 5: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 6: What is the MOQ?
A: Usually our MOQ is 1pcs.
Q 7: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 8: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory.
Q 9: What’s your payment?
A:1) T/T.
♦Contact Us
Web: huadingcoupling
Add: No.11 HangZhou Road,Chengnan park,HangZhou City,ZheJiang Province,China
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 14mm |
| Speed: | 9000r/M |
| Structure: | Flexible |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with a universal joint?
Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with a universal joint involves modifying or adding components to integrate the universal joint into the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the retrofitting process:
To retrofit an existing mechanical system with a universal joint, follow these steps:
- Evaluate the System: Begin by thoroughly assessing the existing mechanical system. Understand its design, components, and the type of motion it requires. Identify the specific area where the universal joint needs to be incorporated and determine the necessary modifications or additions.
- Design Considerations: Take into account the operating conditions, load requirements, and available space in the system. Consider the size, type, and specifications of the universal joint that will best suit the retrofit. This includes selecting the appropriate joint size, torque capacity, operating angles, and any additional features required for compatibility with the system.
- Measurements and Alignment: Accurately measure the dimensions and alignment of the existing system, particularly the shafts involved in the retrofit. Ensure that the required modifications or additions align properly with the system’s existing components. Precise measurements are crucial for a successful retrofit.
- Modify Existing Components: In some cases, it may be necessary to modify certain components of the existing system to accommodate the universal joint. This could involve machining or welding to create attachment points or adjust the dimensions of the system’s components to ensure proper fitment of the universal joint and its associated parts.
- Integrate the Universal Joint: Install the universal joint into the retrofit area according to the system’s requirements and design considerations. This involves securely attaching the universal joint to the modified or existing components using appropriate fasteners or connection methods as specified by the manufacturer. Ensure that the joint is properly aligned with the shafts to facilitate smooth and efficient motion transfer.
- Supporting Components: Depending on the specific retrofit requirements, additional supporting components may be needed. This can include yokes, bearings, shaft couplings, or guards to ensure proper functioning and protection of the universal joint assembly and the overall system.
- Testing and Adjustment: Once the retrofit is complete, thoroughly test the system to ensure that the universal joint operates smoothly and meets the desired performance requirements. Make any necessary adjustments to align the system and optimize its functionality. It is essential to verify that the retrofit does not introduce any adverse effects or compromise the overall operation of the mechanical system.
Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with a universal joint requires careful planning, precise measurements, and proper integration of the joint into the system. By following these steps and considering the design considerations and compatibility, it is possible to successfully incorporate a universal joint into an existing mechanical system and enhance its functionality and performance.
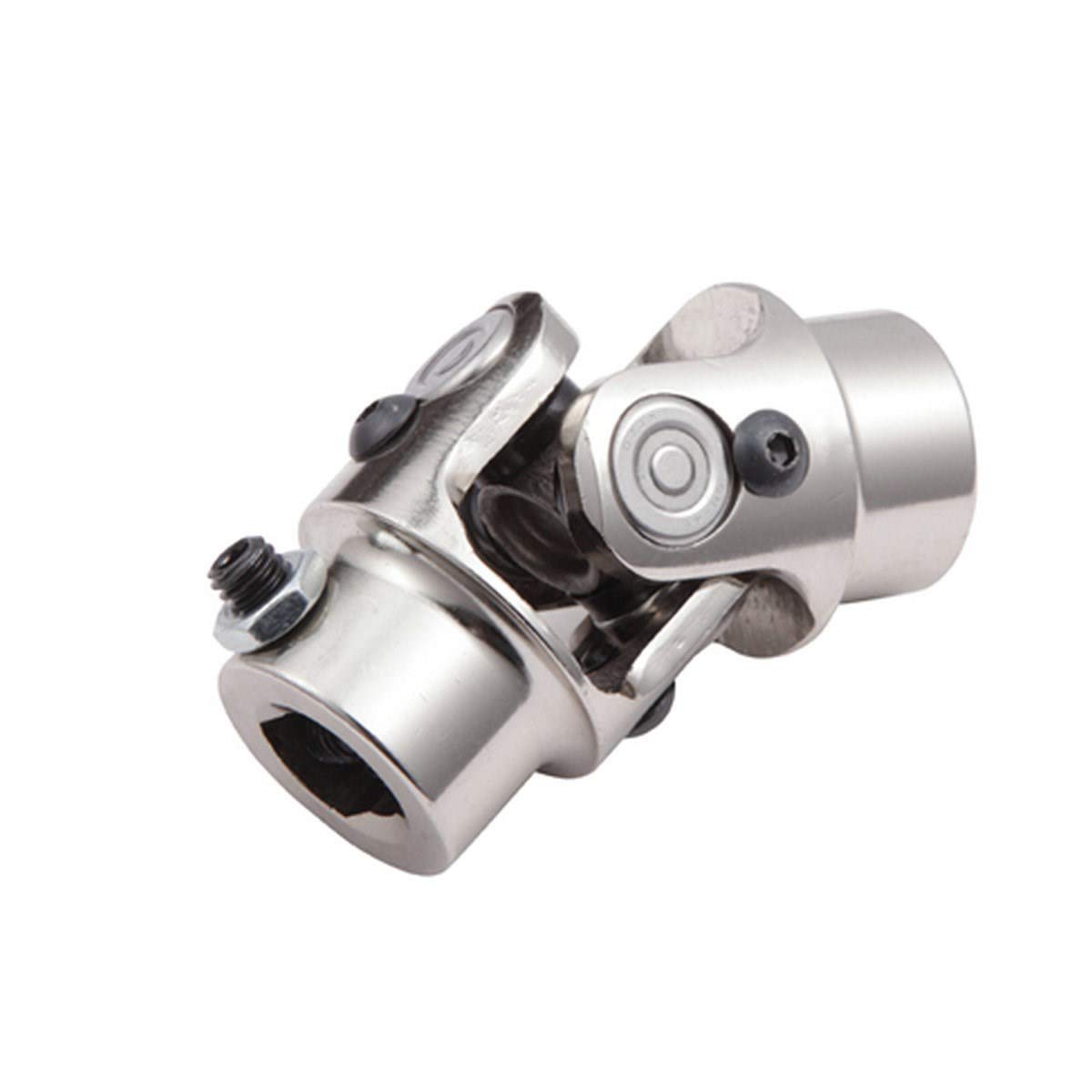

What is the lifespan of a typical universal joint?
The lifespan of a typical universal joint can vary depending on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The lifespan of a universal joint depends on various factors, including the quality of the joint, operating conditions, maintenance practices, and the specific application. While it is challenging to provide an exact lifespan, considering the following factors can help estimate the longevity of a universal joint:
- Quality and Materials: The quality of the universal joint and the materials used in its construction play a significant role in determining its lifespan. High-quality joints made from durable materials, such as alloy steels or stainless steels, tend to have longer lifespans compared to lower-quality or less robust joints made from inferior materials.
- Operating Conditions: The operating conditions in which the universal joint is used can significantly impact its lifespan. Factors such as torque levels, rotational speed, angular misalignment, vibration, temperature, and exposure to contaminants can all affect the joint’s performance and longevity. Operating the joint within its specified limits, avoiding excessive or extreme conditions, and providing proper maintenance can help extend its lifespan.
- Maintenance Practices: Regular maintenance is essential for maximizing the lifespan of a universal joint. Proper lubrication, periodic inspection for wear or damage, and timely replacement of worn components can help prevent premature failure. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and guidelines is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Application Requirements: The specific application requirements and demands placed on the universal joint influence its lifespan. Heavy-duty applications with high torque, frequent load fluctuations, or extreme operating conditions may result in increased stress and wear on the joint, potentially shortening its lifespan. Selecting a universal joint that is specifically designed and rated for the application’s requirements can help ensure a longer lifespan.
Given these factors, it is challenging to provide a precise lifespan for a typical universal joint. In some applications with proper maintenance and suitable operating conditions, a universal joint can last for several years. However, in demanding or harsh operating environments, or if subjected to excessive loads or misalignment, the lifespan of the joint may be shorter, requiring more frequent replacements.
It’s important to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the specific universal joint being used, as they can provide more accurate information regarding its expected lifespan under different operating conditions. Additionally, monitoring the joint’s performance, conducting regular inspections, and addressing any signs of wear or deterioration can help identify the need for replacement and ensure safe and reliable operation.
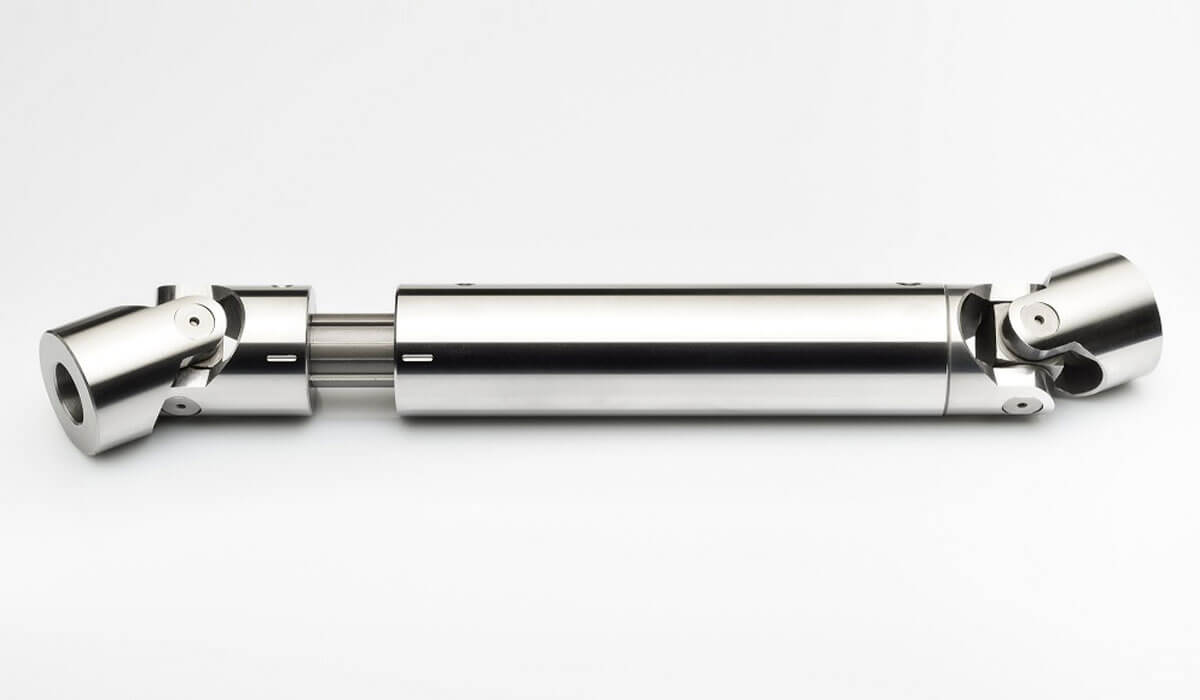

Are there different types of universal joints available?
Yes, there are different types of universal joints available to suit various applications and requirements. Let’s explore some of the commonly used types:
- Single Joint (Cardan Joint): The single joint, also known as a Cardan joint, is the most basic and widely used type of universal joint. It consists of two yokes connected by a cross-shaped center piece. The yokes are typically 90 degrees out of phase with each other, allowing for angular displacement and misalignment between shafts. Single joints are commonly used in automotive drivelines and industrial applications.
- Double Joint: A double joint, also referred to as a double Cardan joint or a constant velocity joint, is an advanced version of the single joint. It consists of two single joints connected in series with an intermediate shaft in between. The use of two joints in series helps to cancel out the velocity fluctuations and reduce vibration caused by the single joint. Double joints are commonly used in automotive applications, especially in front-wheel-drive vehicles, to provide constant velocity power transmission.
- Tracta Joint: The Tracta joint, also known as a tripod joint or a three-roller joint, is a specialized type of universal joint. It consists of three rollers or balls mounted on a spider-shaped center piece. The rollers are housed in a three-lobed cup, allowing for flexibility and articulation. Tracta joints are commonly used in automotive applications, particularly in front-wheel-drive systems, to accommodate high-speed rotation and transmit torque smoothly.
- Rzeppa Joint: The Rzeppa joint is another type of constant velocity joint commonly used in automotive applications. It features six balls positioned in grooves on a central sphere. The balls are held in place by an outer housing with an inner race. Rzeppa joints provide smooth power transmission and reduced vibration, making them suitable for applications where constant velocity is required, such as drive axles in vehicles.
- Thompson Coupling: The Thompson coupling, also known as a tripodal joint, is a specialized type of universal joint. It consists of three interconnected rods with spherical ends. The arrangement allows for flexibility and misalignment compensation. Thompson couplings are often used in applications where high torque transmission is required, such as industrial machinery and power transmission systems.
These are just a few examples of the different types of universal joints available. Each type has its own advantages and is suitable for specific applications based on factors such as torque requirements, speed, angular displacement, and vibration reduction. The selection of the appropriate type of universal joint depends on the specific needs of the application.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
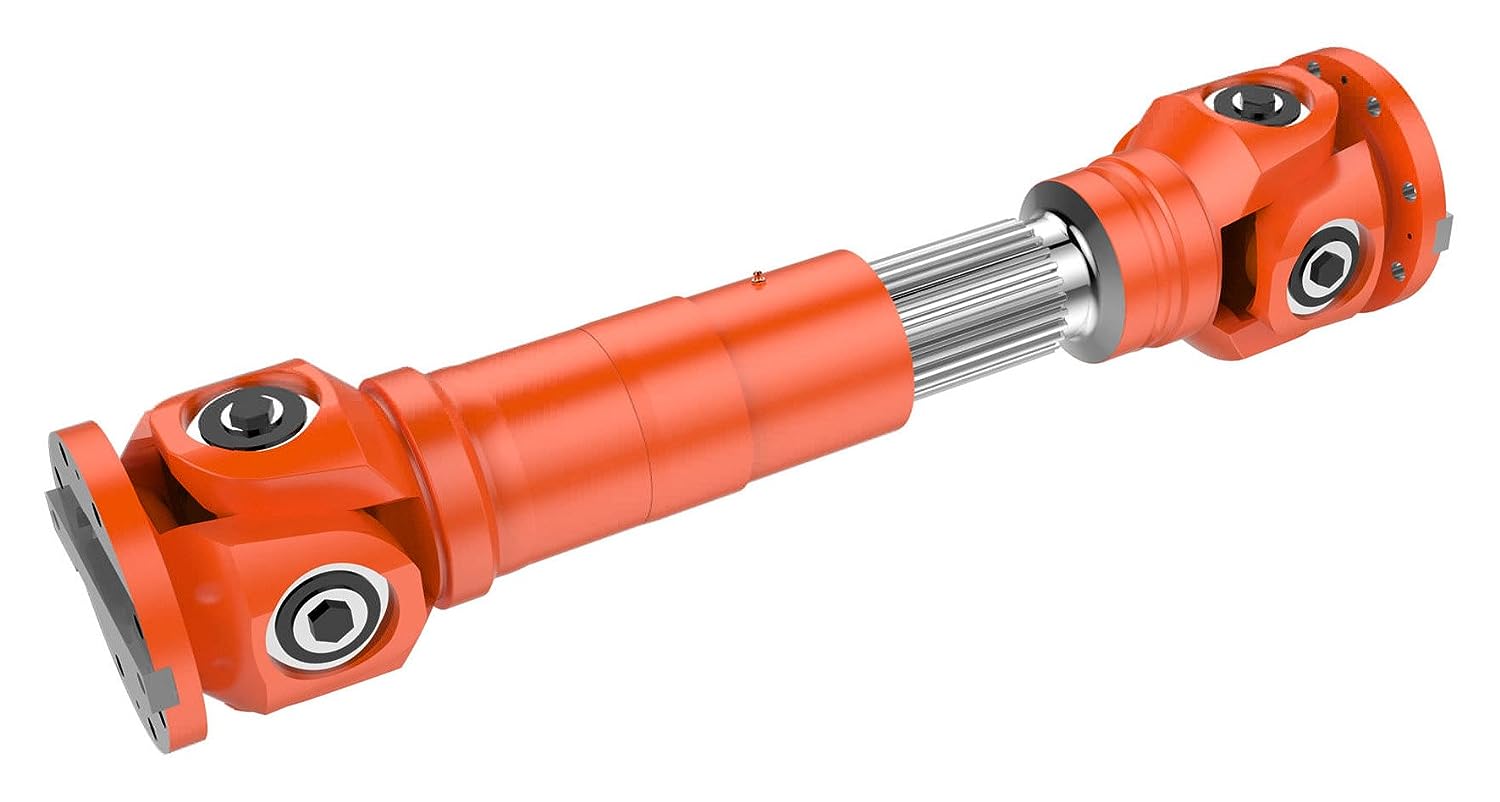
China Custom High Quality Long Nontelescopic Cardan Shaft Swp-D Type Universal Coupling Universal Joints
Product Description
High quality Long Nontelescopic Cardan Shaft SWP-D Type Universal Coupling Universal joints
Description:
The SWP-D long non bending universal joint coupling is a universal joint designed specifically for applications with long distances between 2 shafts. It is a double joint universal joint, which means it can work at an angle of 90 degrees. The “long” CHINAMFG indicates that the main body of the joint is longer than the standard SWP-D universal coupling, which allows it to adapt to more bending in the transmission system. The ‘no flexibility’ CHINAMFG indicates that the joint does not have a flexible coupling, which makes it harder and less susceptible to vibration. SWP-D long flexible universal joint couplings are commonly used in agricultural, construction, and mining equipment. It is also used in some automotive applications, such as transmission shafts and transfer boxes. The following are some characteristics of the SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling: Double joint design, with a working angle of up to 90 degrees Extending the body to make the powertrain system more flexible No flexible coupling, with rigidity and vibration resistance Used in agriculture, construction, mining, and automotive applications
Advantages:
The SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling has many advantages, including: 1. Can adapt to long distances between 2 shafts: The long body of the joint allows SWP-D to be long without flexible universal joint couplings, in order to adapt to more flexibility in the transmission system, which is very important for applications where 2 shafts are far apart. 2. Operable at angles up to 90 degrees: The double joint design of the SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling allows it to operate at angles up to 90%, which is crucial for applications where 2 shafts are misaligned. 3. More rigid and less susceptible to vibration: SWP-D lacks flexible couplings, and the long-term absence of flexible universal joint couplings makes it more rigid and less susceptible to vibration. This is very important for applications where the transmission system is subjected to high vibration loads. 4. Durability and Durability: The SWP-D long non bending universal joint coupling is made of high-quality materials and designed for durability and durability. 5. Reducing noise and vibration: The rigid design of the SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling helps to reduce noise and vibration in the transmission system. 6. Improving efficiency: The SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling helps to improve the efficiency of the transmission system by reducing power loss. 7. Improving safety: The SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling helps to improve safety by reducing the risk of transmission system failures.
Paramters:
Packing & shipping:
1 Prevent from damage.
2. As customers’ requirements, in perfect condition.
3. Delivery : As per contract delivery on time
4. Shipping : As per client request. We can accept CIF, Door to Door etc. or client authorized agent we supply all the necessary assistant.
FAQ:
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks in PDF or AI format.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 5: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 6: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 19mm |
| Speed: | 4000r/M |
| Structure: | Rigid |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
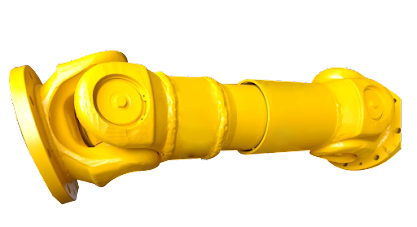
Can cardan joints be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment. Cardan joints, also known as universal joints, are versatile mechanical couplings that transmit torque between misaligned shafts. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of why cardan joints can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment:
- Torque Transmission: Cardan joints are capable of transmitting high levels of torque between misaligned shafts. This makes them well-suited for heavy-duty applications that require the transfer of substantial power. The design of the joint allows for smooth torque transmission, even in cases where the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
- Misalignment Compensation: In heavy-duty machinery and equipment, misalignments between shafts can occur due to factors such as thermal expansion, vibration, or structural flexing. Cardan joints excel at compensating for such misalignments. Their flexible design accommodates angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, allowing for reliable operation in challenging industrial environments.
- Durability and Strength: Heavy-duty machinery and equipment often operate under demanding conditions, subjecting components to high loads and harsh environments. Cardan joints are typically constructed from durable materials such as alloy steels, which provide excellent strength and resistance to fatigue and wear. This durability enables them to withstand the heavy loads and prolonged operation associated with heavy-duty applications.
- Compact Design: Cardan joints have a compact design, which is advantageous in heavy-duty machinery and equipment where space constraints may be present. Their compactness allows for efficient installation and integration within the system, making them suitable for applications where minimizing size and weight is important.
- Versatility: Cardan joints are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different heavy-duty applications. They can be customized to meet specific torque and speed requirements, making them versatile for use in a wide range of machinery and equipment, including industrial machinery, construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and more.
While cardan joints are generally suitable for heavy-duty applications, it is important to consider certain factors to ensure optimal performance. These factors include proper selection of the joint size and type based on the application requirements, adherence to specified torque and speed limits, regular maintenance to prevent wear and ensure proper lubrication, and consideration of any environmental factors that may affect the joint’s performance.
In summary, cardan joints can indeed be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment due to their excellent torque transmission capabilities, ability to compensate for misalignments, durability, compact design, and versatility. By considering the specific requirements of the application and following appropriate maintenance practices, cardan joints can provide reliable and efficient operation in heavy-duty industrial settings.

How do you calculate the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly?
Calculating the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly involves evaluating the power loss in the joint and comparing it to the input power. Efficiency is typically expressed as a percentage and provides an indication of how effectively the cardan joint transfers power from the input shaft to the output shaft. Here’s a detailed explanation:
To calculate the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly, follow these steps:
1. Measure Input Power: Determine the power being supplied to the cardan joint assembly. This can be measured using appropriate instruments such as a dynamometer or by utilizing the known power rating of the input source.
2. Measure Output Power: Measure the power being delivered by the output shaft of the cardan joint assembly. This can be done using a dynamometer or by utilizing the known power rating of the output device or load.
3. Calculate Power Loss: Calculate the power loss in the cardan joint assembly by subtracting the output power from the input power. The power loss represents the amount of power dissipated or wasted within the joint.
Power Loss = Input Power – Output Power
4. Calculate Efficiency: Divide the output power by the input power and multiply the result by 100 to obtain the efficiency as a percentage.
Efficiency = (Output Power / Input Power) * 100
The efficiency of the cardan joint assembly can be interpreted as the percentage of input power that is effectively transmitted to the output shaft. A higher efficiency indicates a more efficient power transfer, while a lower efficiency suggests a higher level of power loss within the joint.
It’s important to note that the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly can be influenced by various factors, including misalignments, lubrication conditions, wear, and operating speeds. Additionally, the efficiency may vary at different operating conditions and under varying loads. Therefore, it is advisable to perform efficiency calculations under representative operating conditions and consider the specific characteristics of the cardan joint assembly being analyzed.
By calculating the efficiency, engineers and designers can assess the performance of the cardan joint assembly, identify potential areas for improvement, and optimize the power transmission system for enhanced efficiency and overall effectiveness.
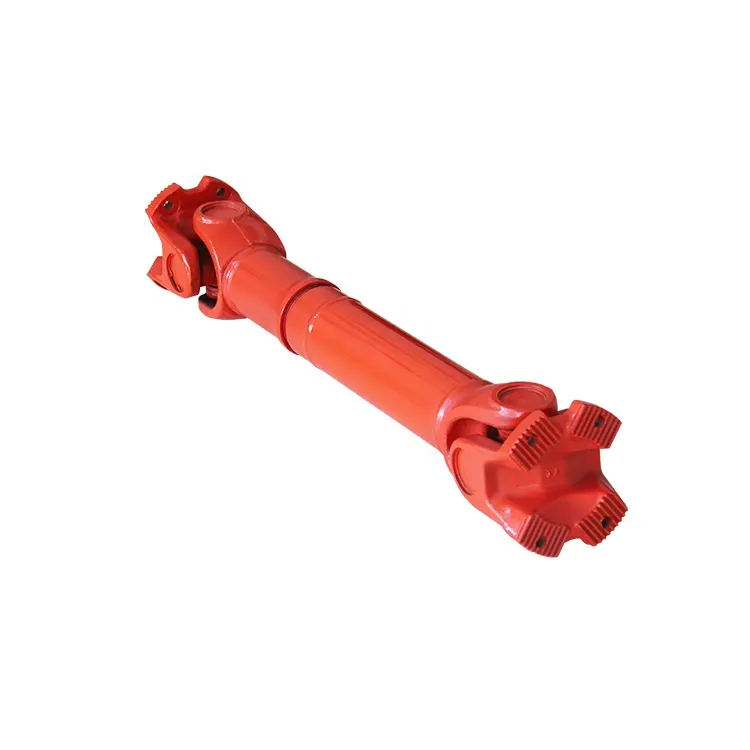

Are there different types of cardan joints available?
Yes, there are different types of cardan joints available to suit various applications and requirements. The design and configuration of a cardan joint can vary based on factors such as load capacity, torque transmission, operating conditions, and installation constraints. Here’s a detailed explanation of some commonly used types of cardan joints:
- Single Universal Joint: The single universal joint is the most basic and commonly used type of cardan joint. It consists of two yokes connected by a cross, forming a single joint. This type of cardan joint allows for angular misalignment between the input and output shafts. It is often used in applications where misalignment angles are relatively small, and flexibility is required.
- Double Cardan Joint: The double cardan joint, also known as a constant velocity joint (CV joint), is an enhanced version of the single universal joint. It consists of two single universal joints connected by an intermediate shaft. This configuration helps to cancel out the velocity fluctuations and torque variations that can occur with a single joint. Double cardan joints are commonly used in applications where smooth and constant power transmission is required, such as in front-wheel drive vehicles.
- Tractor Joint: A tractor joint is a specialized type of cardan joint used in agricultural machinery, particularly in power take-off (PTO) systems. It consists of three yokes connected by two crosses. The tractor joint allows for higher torque transmission and can accommodate larger misalignment angles. It is designed to handle the demanding conditions and heavy loads often encountered in agricultural applications.
- Ball-and-Socket Joint: The ball-and-socket joint, also known as a Hooke’s joint, is another variant of the cardan joint. It consists of a cross with a spherical ball at each end, which fits into a corresponding socket in the yokes. The ball-and-socket joint provides greater flexibility and can accommodate larger angles of misalignment. It is commonly used in applications where significant angular movement is required, such as steering systems in vehicles.
- Flexible Coupling: While not strictly a cardan joint, flexible couplings serve a similar purpose in accommodating misalignment. Flexible couplings are often used in applications where the misalignment is minimal and torque transmission is a primary concern. They utilize elastomeric or flexible elements to provide flexibility and compensate for small misalignments between shafts.
These are some of the commonly used types of cardan joints. Each type offers specific advantages and is suitable for different applications based on factors such as misalignment requirements, torque transmission, and operating conditions. The selection of the appropriate cardan joint type depends on the specific needs of the application and the desired performance characteristics.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China supplier Stainless Steel Double Braided Exhaust Flexible Corrugated Bellows Pipe Car Exhaust Coupling Flex Joint
Product Description
Product Description
Product Name: Universal Exhaust Flexible Pipe for Exhaust System
Materials: Stainless Steel SS201/SS304 for Bellow, Braid and Interlock
Aluminized Steel / Stainless Steel 409 for Collars and Nipples
Structures: Outer Braid/Outer Wire Mesh+ Single/Double Layers Bellow + Inner Braid/Interlock/Nothing
Specifications:
– Help to reduce air pollution.
– Easy to install and extend the role of exhaust muffler system life.
– Adopt corrugated molding technology, good flexibility, good air tightness.
– Automobile exhaust system component.
– Installed between engine and muffer.
– Used to decrease engine noise and vibration.
– Compensates for exhaust converter misalignment.
Detailed Photos
Product Parameters
| Inner Diameter | Overall Length | Inner Diameter | Overall Length | Inner Diameter | Overall Length |
| I.D | O/L | I.D | O/L | I.D | O/L |
| 1-3/4 ” (45mm) | 4 ” (102mm) | 2-1/2 “(63.5mm) | 4 ” (102mm) | 43mm | 120mm |
| 6 ” (152mm) | 6 ” (152mm) | 165mm | |||
| 8 ” (203mm) | 8 ” (203mm) | 180mm | |||
| 9 ” (230mm) | 9 ” (230mm) | 50mm(52mm) | 120mm | ||
| 10 ” (254mm) | 10 ” (254mm) | 165mm | |||
| 11 ” (280mm) | 11 ” (280mm) | 54.5mm | 120mm | ||
| 2″(51mm) | 12 ” (305mm) | 12 ” (305mm) | 150mm | ||
| 4 ” (102mm) | 3 “(76.2mm) | 4 ” (102mm) | 180mm | ||
| 6 ” (152mm) | 6 ” (152mm) | 200mm | |||
| 8 ” (203mm) | 8 ” (203mm) | 250mm | |||
| 9 ” (230mm) | 10 ” (254mm) | 60mm(61mm) | 160mm | ||
| 10 ” (254mm) | 12 ” (305mm) | 200mm | |||
| 2-1/4 ” (57.2mm) | 11 ” (280mm) | 6 ” (152mm) | 240mm | ||
| 12 ” (305mm) | 3-1/2″ (89mm) | 8 ” (203mm) | 65mm | 150mm | |
| 4 ” (102mm) | 10 ” (254mm) | 200mm | |||
| 6 ” (152mm) | 12 ” (305mm) | 70mm | 100m | ||
| 8 ” (203mm) | 4″ (102mm) | 8 ” (203mm) | 120mm | ||
| 9 ” (230mm) | 10 ” (254mm) | 150mm | |||
| 10 ” (254mm) | 12 ” (305mm) | 200mm | |||
| 11 ” (280mm) | ID 25~150mm OL 100~400mm Customized size, design, drawing and logo are welcome ! |
||||
| 12 ” (305mm) | |||||
Packaging & Shipping
Our Advantages
We are the top 10 leading brand. We have more than 20 years of exhaust system and industrial pipe.
1.Founded in 2002 and experienced in the field of exhaust system and industrial pipe more than 20 years.
2.We have large capacity, over 10000pcs/month.
3.Management system certification:ISO9001.TSI16949.
4.We have our own technical and mould department, ready for any customized products.
5.We have all kinds of products can be adapt any environment. you can choose which 1 is suitable to your products.
6.Pls tell us about your requirements,we will reply you immediately, looking CHINAMFG to hearing from you.
Company Profile
FAQ
Q1. Can we make our logo on the product?
Yes. Please send us your logo, provided that your logo is authorized
Q2. Can you provide samples?
Yes.
Q3. how can we guarantee quality?
Always a pre-production sample before mass production
Q4.what can you buy from us?
Catalytic Converter,Exhaust Muffler,Exhaust Tips,Flexible Pipe,Aluminized steel pipe,Motorcycle Muffler ETC
Q5. Is it possible to provide OEM service?
Yes, customers can customize the design and size of the product. We have a professional R & D department to cooperate with your design.
Q6. What is the minimum order quantity?
There is no minimum order quantity if the products are in stock.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Car Make: | Universal |
| Car Model: | Universal |
| Engine Type: | Universal |
| Type: | Exhaust Pipe |
| Samples: |
US$ 5.88/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can universal joints be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations?
Yes, universal joints can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Universal joints are mechanical devices designed to transmit rotary motion between two shafts that are not in a straight line alignment. They consist of a cross-shaped or H-shaped yoke with bearings at each end that connect to the shafts. The design of universal joints allows them to accommodate angular misalignment between the shafts, making them suitable for various applications, including both horizontal and vertical orientations.
When used in a horizontal orientation, universal joints can transmit rotational motion between shafts that are positioned at different angles or offsets. They are commonly found in drivetrain systems of vehicles, where they transfer power from the engine to the wheels, even when the drivetrain components are not perfectly aligned. In this configuration, universal joints can effectively handle the torque requirements and misalignment caused by uneven terrain, suspension movement, or steering angles.
In a vertical orientation, universal joints can also be utilized to transfer rotational motion between shafts that are positioned vertically. This arrangement is often seen in applications such as industrial equipment, machinery, or agricultural implements. For example, in a vertical power transmission system, a universal joint can be used to connect a vertical driving shaft to a vertical driven shaft, enabling power transfer and accommodating any angular misalignment that may occur due to variations in shaft positions or vibrations.
It’s important to note that the specific design and selection of universal joints for different orientations should consider factors such as the torque requirements, operating conditions, and the manufacturer’s specifications. The orientation of the universal joint may affect factors such as lubrication, load-bearing capacity, and the need for additional support or stabilization mechanisms.
In summary, universal joints can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations. Their ability to accommodate angular misalignment makes them versatile components for transmitting rotary motion between shafts that are not in a straight line alignment, regardless of the orientation.
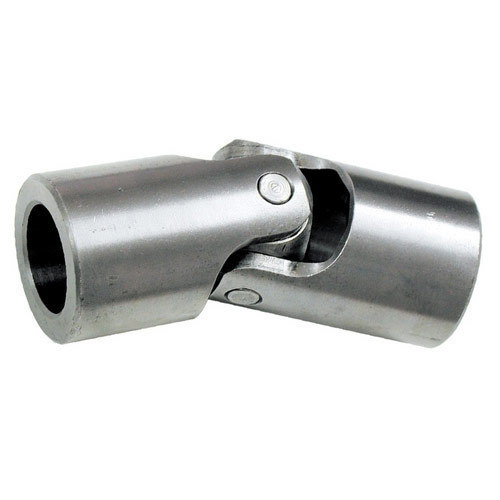

Can universal joints be used in agricultural equipment?
Yes, universal joints can be used in agricultural equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Universal joints are commonly employed in various types of agricultural equipment and machinery. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for agricultural applications. Here are some key points to consider:
- Torque Transmission: Agricultural equipment often requires the transmission of high torque levels to perform tasks such as plowing, tilling, harvesting, or powering other implements. Universal joints are capable of transmitting significant amounts of torque, making them suitable for handling the power requirements of agricultural machinery.
- Flexibility: Agricultural equipment frequently operates in uneven terrain or encounters obstacles that can cause angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. Universal joints can accommodate such misalignment and transmit torque even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned. This flexibility allows agricultural machinery to navigate uneven surfaces and maintain power transfer.
- Durability: Universal joints can be constructed from materials that provide high strength and durability, such as alloy steels. Agricultural equipment often operates in demanding conditions, including exposure to dust, moisture, and vibrations. Robust universal joints can withstand these harsh environments and repetitive motions, ensuring reliable performance and longevity.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Universal joints offer a cost-effective solution for torque transmission in agricultural equipment. Compared to alternative power transmission methods, such as complex gear systems or hydraulic drives, universal joints can provide a more economical option while still delivering adequate performance and reliability.
- Wide Application Range: Universal joints can be used in various agricultural equipment, including tractors, combine harvesters, balers, seeders, sprayers, and more. They are versatile components that can be integrated into different systems and configurations, allowing for efficient power transmission in a wide range of agricultural applications.
It’s important to note that the specific design and selection of universal joints for agricultural equipment should consider factors such as the torque requirements, operating conditions, maintenance practices, and safety considerations. Proper sizing, lubrication, and regular inspections are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and preventing premature wear or failure.
In summary, universal joints can indeed be used in agricultural equipment. Their torque transmission capabilities, flexibility, durability, cost-effectiveness, and versatility make them a suitable choice for power transmission in various agricultural machinery and equipment.

What industries commonly use universal joints?
Universal joints, also known as U-joints, are utilized in various industries where the transmission of rotary motion between misaligned shafts is required. Here are some of the industries that commonly use universal joints:
- Automotive: The automotive industry extensively employs universal joints in vehicles. Universal joints are essential components in drivelines, connecting the transmission to the drive shaft and allowing power to be transmitted to the wheels. They accommodate the misalignment caused by the suspension system and enable smooth power transfer.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Universal joints find widespread use in industrial manufacturing applications. They are employed in machinery and equipment such as conveyors, mixers, pumps, printing presses, and machine tools. Universal joints facilitate the transmission of motion at angles, enabling efficient operation and flexibility in various manufacturing processes.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry utilizes universal joints in aircraft and spacecraft systems. They are used in control mechanisms for movable surfaces such as wings, flaps, and rudders. Universal joints enable the transfer of motion and control inputs between different components, ensuring precise and reliable operation of aerospace systems.
- Marine: Universal joints are commonly employed in the marine industry for various applications. They are used in propulsion systems to transmit power from the engine to the propeller shaft. Universal joints also find application in steering systems, allowing for the transfer of motion between the steering wheel and the rudder or outboard motor.
- Agriculture: The agricultural industry relies on universal joints in various machinery and equipment used in farming operations. Tractors, combines, harvesters, and other agricultural machinery utilize universal joints to transmit power between different components, accommodating misalignment caused by the terrain and articulation requirements.
- Construction and Heavy Equipment: Universal joints are commonly found in construction and heavy equipment. They are used in machinery such as cranes, excavators, loaders, and concrete mixers. Universal joints enable the transmission of power and motion between different parts of the equipment, accommodating misalignment and articulation required in construction and heavy-duty operations.
- Railway: The railway industry relies on universal joints for various applications. They are used in drivetrain systems to transmit motion between different components, such as the engine, gearbox, and axles. Universal joints allow for smooth power transfer while accommodating the misalignment caused by the movement and suspension of trains.
- Robotics and Automation: Universal joints are utilized in robotics and automation systems. They enable the transmission of motion between misaligned components in robotic arms, manipulators, and other automated systems. Universal joints provide flexibility and precise movement, allowing for efficient operation of robotic and automated processes.
These are just a few examples of the industries that commonly use universal joints. Their ability to transmit rotary motion between misaligned shafts makes them essential components in a wide range of applications, enabling efficient and reliable operation across various industries.


editor by CX 2024-05-13
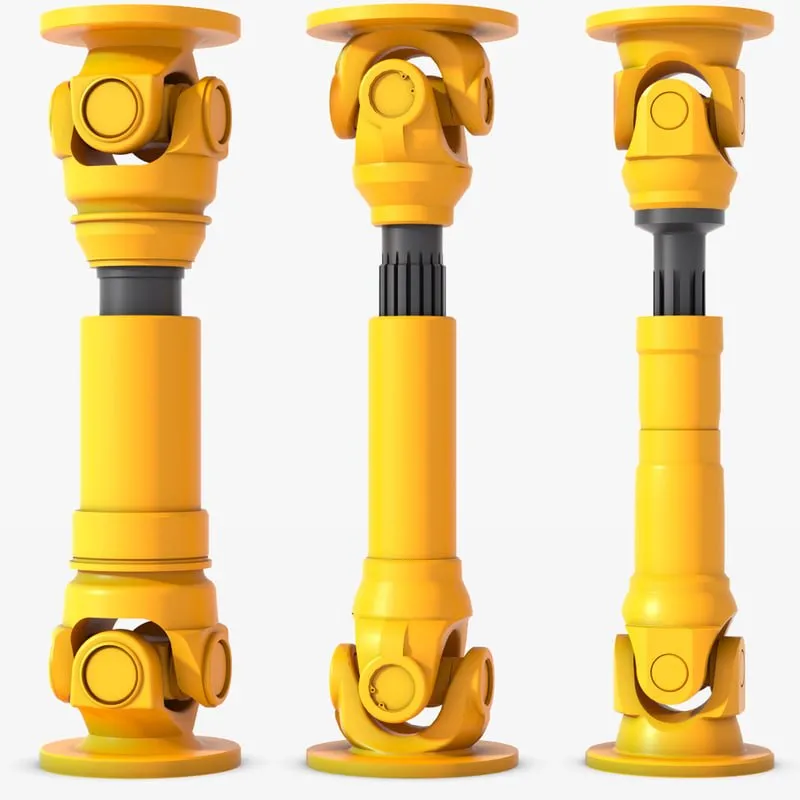
China supplier CZPT Ws Type Cardan Shaft Coupling Universal Joint
Product Description
WS Type Universal Joint Shaft
Features:
1. It is suitable for transmission coupling space on the same plane of 2 axis angle beta β≤45°, the nominal torque transmission 11.2-1120N.
2.The WSD type is a single cross universal coupling, and the WS type is a double cross universal coupling.
3.Each section between the largest axis angle 45º.
4.The finished hole H7, according to the requirements of keyseating, 6 square hole and square hole.
5.The angle between the 2 axes is allowed in a limited range as the work requirements change.
|
NO |
Tn/N·m |
d(H7) |
D |
L0 |
L |
L1 |
m/kg |
I/kg·m2 |
||||||||||
|
WSD |
WS |
WSD |
WS |
WSD |
WS |
|||||||||||||
|
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
Y |
J1 |
|||||
|
WS1 WSD1 |
11.2 |
8 |
16 |
60 |
– |
80 |
– |
20 |
– |
20 |
0.23 |
– |
0.32 |
– |
0.06 |
– |
0.08 |
– |
|
9 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
10 |
66 |
60 |
86 |
80 |
25 |
22 |
0.2 |
0.29 |
0.05 |
0.07 |
||||||||
|
WS2 WSD2 |
22.4 |
10 |
20 |
70 |
64 |
96 |
90 |
26 |
0.64 |
0.57 |
0.93 |
0.88 |
0.1 |
0.09 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
||
|
11 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
12 |
84 |
74 |
110 |
100 |
32 |
27 |
||||||||||||
|
WS3 WSD3 |
45 |
12 |
25 |
90 |
80 |
122 |
112 |
32 |
1.45 |
1.3 |
2.1 |
1.95 |
0.17 |
0.15 |
0.24 |
0.22 |
||
|
14 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS4 WSD4 |
71 |
16 |
32 |
116 |
82 |
154 |
130 |
42 |
30 |
38 |
5.92 |
4.86 |
8.56 |
0.48 |
0.39 |
0.32 |
0.56 |
0.49 |
|
18 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS5 WSD5 |
140 |
19 |
40 |
144 |
116 |
192 |
164 |
48 |
16.3 |
12.9 |
24 |
20.6 |
0.72 |
0.59 |
1.04 |
0.91 |
||
|
20 |
52 |
38 |
||||||||||||||||
|
22 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS6 WSD6 |
280 |
24 |
50 |
152 |
124 |
210 |
182 |
52 |
38 |
58 |
45.7 |
36.7 |
68.9 |
59.7 |
1.28 |
1.03 |
1.89 |
1.64 |
|
25 |
172 |
136 |
330 |
194 |
62 |
44 |
||||||||||||
|
28 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS7 WSD7 |
560 |
30 |
60 |
226 |
182 |
296 |
252 |
82 |
60 |
70 |
148 |
117 |
207 |
177 |
2.82 |
2.31 |
3.9 |
3.38 |
|
32 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
35 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
WS8 WSD8 |
1120 |
38 |
75 |
240 |
196 |
332 |
288 |
92 |
396 |
338 |
585 |
525 |
5.03 |
4.41 |
7.25 |
6.63 |
||
|
40 |
300 |
244 |
392 |
336 |
112 |
84 |
||||||||||||
|
42 |
||||||||||||||||||
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
HangZhou CHINAMFG Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the design and manufacture of various types of coupling. There are 86 employees in our company, including 2 senior engineers and no fewer than 20 mechanical design and manufacture, heat treatment, welding, and other professionals.
Advanced and reasonable process, complete detection means. Our company actively introduces foreign advanced technology and equipment, on the basis of the condition, we make full use of the advantage and do more research and innovation. Strict to high quality and operate strictly in accordance with the ISO9000 quality certification system standard mode.
Our company supplies different kinds of products. High quality and reasonable price. We stick to the principle of “quality first, service first, continuous improvement and innovation to meet the customers” for the management and “zero defect, zero complaints” as the quality objective.
Our Services
1. Design Services
Our design team has experience in Cardan shafts relating to product design and development. If you have any needs for your new product or wish to make further improvements, we are here to offer our support.
2. Product Services
raw materials → Cutting → Forging →Rough machining →Shot blasting →Heat treatment →Testing →Fashioning →Cleaning→ Assembly→Packing→Shipping
3. Samples Procedure
We could develop the sample according to your requirement and amend the sample constantly to meet your need.
4. Research & Development
We usually research the new needs of the market and develop new models when there are new cars in the market.
5. Quality Control
Every step should be a particular test by Professional Staff according to the standard of ISO9001 and TS16949.
FAQ
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing
various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all customers with customized PDF or AI format artwork.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: Do you provide samples? Is it free or extra?
Yes, we could offer the sample but not for free. Actually, we have an excellent price principle, when you make the bulk order the cost of the sample will be deducted.
Q 5: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 6: What is the MOQ?
A: Usually our MOQ is 1pcs.
Q 7: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 8: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory.
Q 9: What’s your payment?
A:1) T/T.
♦Contact Us
Web: huadingcoupling
Add: No.11 HangZhou Road,Chengnan park,HangZhou City,ZheJiang Province,China
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 14mm |
| Speed: | 9000r/M |
| Structure: | Flexible |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can cardan joints be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment. Cardan joints, also known as universal joints, are versatile mechanical couplings that transmit torque between misaligned shafts. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of why cardan joints can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment:
- Torque Transmission: Cardan joints are capable of transmitting high levels of torque between misaligned shafts. This makes them well-suited for heavy-duty applications that require the transfer of substantial power. The design of the joint allows for smooth torque transmission, even in cases where the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
- Misalignment Compensation: In heavy-duty machinery and equipment, misalignments between shafts can occur due to factors such as thermal expansion, vibration, or structural flexing. Cardan joints excel at compensating for such misalignments. Their flexible design accommodates angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, allowing for reliable operation in challenging industrial environments.
- Durability and Strength: Heavy-duty machinery and equipment often operate under demanding conditions, subjecting components to high loads and harsh environments. Cardan joints are typically constructed from durable materials such as alloy steels, which provide excellent strength and resistance to fatigue and wear. This durability enables them to withstand the heavy loads and prolonged operation associated with heavy-duty applications.
- Compact Design: Cardan joints have a compact design, which is advantageous in heavy-duty machinery and equipment where space constraints may be present. Their compactness allows for efficient installation and integration within the system, making them suitable for applications where minimizing size and weight is important.
- Versatility: Cardan joints are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different heavy-duty applications. They can be customized to meet specific torque and speed requirements, making them versatile for use in a wide range of machinery and equipment, including industrial machinery, construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and more.
While cardan joints are generally suitable for heavy-duty applications, it is important to consider certain factors to ensure optimal performance. These factors include proper selection of the joint size and type based on the application requirements, adherence to specified torque and speed limits, regular maintenance to prevent wear and ensure proper lubrication, and consideration of any environmental factors that may affect the joint’s performance.
In summary, cardan joints can indeed be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment due to their excellent torque transmission capabilities, ability to compensate for misalignments, durability, compact design, and versatility. By considering the specific requirements of the application and following appropriate maintenance practices, cardan joints can provide reliable and efficient operation in heavy-duty industrial settings.

Can cardan joints be used in industrial machinery and manufacturing?
Yes, cardan joints are commonly used in industrial machinery and manufacturing applications due to their versatility, durability, and ability to transmit torque at various angles. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Torque Transmission: Industrial machinery often requires the transmission of torque between different components or shafts that may not be in a perfectly aligned position. Cardan joints excel at transmitting torque even at significant angles and misalignments, allowing for flexible power transmission in industrial applications. They can efficiently transfer high torque loads and handle varying operating conditions.
2. Misalignment Compensation: Cardan joints are designed to accommodate misalignments and angular variations, making them ideal for industrial machinery. They can compensate for misalignments caused by structural deflection, thermal expansion, or other factors, ensuring smooth and reliable power transmission. This capability helps to minimize stress and wear on connected components and extends the life of the machinery.
3. Flexibility and Articulation: Industrial machinery often requires flexibility and articulation to adapt to different production processes or accommodate dynamic movements. Cardan joints provide rotational freedom and allow for angular movement, enabling the machinery to adjust to changing requirements. Their universal joint design allows for smooth rotation and accommodates the required range of motion.
4. Compact Design: Cardan joints have a relatively compact design, making them suitable for integration into industrial machinery where space is often limited. Their compact size allows for efficient packaging within the machinery, optimizing overall design and minimizing footprint. This is especially beneficial in applications where multiple joints are required within a confined space.
5. Durability and Strength: Industrial machinery operates under demanding conditions, including heavy loads, high speeds, and harsh environments. Cardan joints are often constructed using durable materials such as alloy steels or high-strength alloys, providing the necessary strength and resilience to withstand industrial applications. They are designed to handle the demanding loads and forces encountered in manufacturing processes.
6. Easy Maintenance and Serviceability: Cardan joints are generally low-maintenance components. They require periodic inspection, lubrication, and replacement of worn parts, but their design often allows for easy access and replacement if needed. This facilitates maintenance activities and minimizes downtime in industrial machinery.
7. Versatility: Cardan joints are available in various configurations, sizes, and load capacities, allowing them to be tailored to specific industrial machinery requirements. They can be customized to accommodate different shaft sizes, torque ratings, and mounting arrangements, making them adaptable to a wide range of manufacturing applications.
8. Cost-Effectiveness: Cardan joints offer a cost-effective solution for torque transmission in industrial machinery. Their durability, reliability, and long service life contribute to reduced maintenance and replacement costs. Additionally, their ability to compensate for misalignments can help minimize wear on other machinery components, further reducing overall maintenance expenses.
When integrating cardan joints into industrial machinery and manufacturing systems, it is important to consider the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and load characteristics. Proper design, selection, and installation practices should be followed to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Consulting with engineers or experts specializing in drivetrain systems and industrial machinery design can provide valuable insights and guidance on the selection, integration, and maintenance of cardan joints for specific industrial applications.

What are the applications of a cardan joint?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, has a wide range of applications across various industries. Its ability to transmit rotational motion and accommodate misalignment between shafts makes it suitable for different systems and machines. Here’s a detailed explanation of the applications of a cardan joint:
- Automotive Drivetrains: One of the primary applications of cardan joints is in automotive drivetrains. They are used in vehicles with rear-wheel drive, all-wheel drive, and four-wheel drive systems. Cardan joints help transmit power from the engine to the driveshaft, allowing the rotational motion to be transferred to the rear axle or all four wheels. They provide flexibility and compensation for misalignment between the engine, transmission, and rear differential.
- Industrial Machinery: Cardan joints find extensive use in various industrial machinery applications. They are commonly employed in power transmission systems, especially when there is a need to transmit rotational motion between non-collinear shafts. Cardan joints are used in conveyor systems, printing presses, machine tools, pumps, mixers, and many other industrial machines that require efficient transmission of rotational power.
- Aerospace and Aviation: Cardan joints have applications in the aerospace and aviation industries. They are used in aircraft control systems, such as the control linkages between the control surfaces (elevator, rudder, ailerons) and the cockpit controls. Cardan joints allow for the transmission of pilot input to the control surfaces while accommodating any misalignment or changes in angles during flight.
- Marine Propulsion: In marine applications, cardan joints are utilized in propulsion systems. They are commonly used in boat drivetrains to transfer rotational motion from the engine to the propeller shaft. Cardan joints enable the engine to be mounted at an angle or in a different position from the propeller shaft, compensating for the misalignment that can arise due to the boat’s hull shape and design.
- Railway Systems: Cardan joints play a role in railway systems, particularly in drivetrains and couplings. They are used in locomotives and train cars to transfer rotational motion between different components, such as the engine, gearbox, and wheel axle. Cardan joints provide flexibility and accommodate misalignment that may occur due to the movement and articulation of train cars on curved tracks.
- Mining and Construction Equipment: Cardan joints are employed in heavy-duty mining and construction equipment. They are used in applications such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and off-highway trucks. Cardan joints help transmit power and motion between different components of these machines, allowing them to operate efficiently and withstand the demanding conditions of mining and construction environments.
- Industrial Robotics: Cardan joints find applications in industrial robotics and automation. They are used in robotic arms and manipulators to transmit rotational motion between different segments or joints of the robotic system. Cardan joints enable precise and flexible movement, allowing robots to perform complex tasks in manufacturing, assembly, and other industrial processes.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of cardan joints. Their ability to handle misalignment, transmit rotational motion at varying angles, and provide flexibility make them a fundamental component in numerous systems and machines across industries.


editor by CX 2024-05-07
China factory Swp-D Type No Telescopic Long Universal Coupling Flexible Cardan Shaft Universal Joint
Product Description
SWP-D Type No Telescopic Long Universal Coupling Flexible Cardan Shaft Universal Joint
Description:
The SWP-D long non bending universal joint coupling is a universal joint designed specifically for applications with long distances between 2 shafts. It is a double joint universal joint, which means it can work at an angle of 90 degrees. The “long” CHINAMFG indicates that the main body of the joint is longer than the standard SWP-D universal coupling, which allows it to adapt to more bending in the transmission system. The ‘no flexibility’ CHINAMFG indicates that the joint does not have a flexible coupling, which makes it harder and less susceptible to vibration. SWP-D long flexible universal joint couplings are commonly used in agricultural, construction, and mining equipment. It is also used in some automotive applications, such as transmission shafts and transfer boxes. The following are some characteristics of the SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling: Double joint design, with a working angle of up to 90 degrees Extending the body to make the powertrain system more flexible No flexible coupling, with rigidity and vibration resistance Used in agriculture, construction, mining, and automotive applications
Advantages:
The SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling has many advantages, including: 1. Can adapt to long distances between 2 shafts: The long body of the joint allows SWP-D to be long without flexible universal joint couplings, in order to adapt to more flexibility in the transmission system, which is very important for applications where 2 shafts are far apart. 2. Operable at angles up to 90 degrees: The double joint design of the SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling allows it to operate at angles up to 90%, which is crucial for applications where 2 shafts are misaligned. 3. More rigid and less susceptible to vibration: SWP-D lacks flexible couplings, and the long-term absence of flexible universal joint couplings makes it more rigid and less susceptible to vibration. This is very important for applications where the transmission system is subjected to high vibration loads. 4. Durability and Durability: The SWP-D long non bending universal joint coupling is made of high-quality materials and designed for durability and durability. 5. Reducing noise and vibration: The rigid design of the SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling helps to reduce noise and vibration in the transmission system. 6. Improving efficiency: The SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling helps to improve the efficiency of the transmission system by reducing power loss. 7. Improving safety: The SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling helps to improve safety by reducing the risk of transmission system failures.
Paramters:
Packing & shipping:
1 Prevent from damage.
2. As customers’ requirements, in perfect condition.
3. Delivery : As per contract delivery on time
4. Shipping : As per client request. We can accept CIF, Door to Door etc. or client authorized agent we supply all the necessary assistant.
FAQ:
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks in PDF or AI format.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 5: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 6: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 19mm |
| Speed: | 4000r/M |
| Structure: | Rigid |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
Can cardan joints be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations. Cardan joints, also known as universal joints, are flexible mechanical couplings that transmit torque between misaligned shafts. Their design allows for angular movement and compensation of misalignments in various orientations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how cardan joints can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations:
Horizontal Orientation: In a horizontal orientation, the input and output shafts of the cardan joint are aligned horizontally, typically parallel to the ground. The joint is capable of transmitting torque smoothly and efficiently between the misaligned shafts while accommodating angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. This makes it suitable for a wide range of horizontal applications, including automotive drivetrains, industrial machinery, and agricultural equipment.
Vertical Orientation: In a vertical orientation, the input and output shafts of the cardan joint are aligned vertically, with one shaft positioned above the other. The joint is still capable of transmitting torque and compensating for misalignments in this configuration. However, it is important to consider the effects of gravity and the additional load imposed on the joint due to the weight of the shafts and any connected components. Adequate support and proper bearing selection should be considered to ensure reliable operation in vertical applications.
Whether in horizontal or vertical orientations, cardan joints offer several advantages that make them versatile for various applications:
- Misalignment Compensation: Cardan joints excel at compensating for angular, parallel, and axial misalignments between shafts. This flexibility allows for smooth torque transmission and reduces stress on the connected components.
- Torque Transmission: Cardan joints are capable of transmitting high levels of torque between misaligned shafts. This makes them suitable for applications that require the transfer of substantial power.
- Durability: Cardan joints are typically constructed from durable materials, such as alloy steels, which provide excellent strength and resistance to fatigue and wear. This durability enables them to withstand the demands of various orientations and operating conditions.
- Compact Design: Cardan joints have a compact design, allowing for efficient installation and integration within the system, regardless of the orientation. This is particularly advantageous in applications with space constraints.
- Versatility: Cardan joints are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different orientations and applications. They can be customized to meet specific torque and speed requirements.
It is important to note that specific considerations may apply depending on the application and the magnitude of misalignments. Factors such as load capacity, lubrication, bearing arrangement, and maintenance should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the cardan joint.
In summary, cardan joints can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations due to their ability to compensate for misalignments and transmit torque between shafts. Their versatility, durability, and compact design make them suitable for a wide range of applications in various orientations.

How do you ensure reliable and consistent performance in a cardan joint?
Ensuring reliable and consistent performance in a cardan joint requires attention to various factors, including proper design, maintenance, and operating practices. By following best practices and considering key considerations, the reliability and performance of a cardan joint can be optimized. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Proper Design and Selection: The first step is to ensure the cardan joint is properly designed and selected for the intended application. Consider factors such as load requirements, operating conditions (including speed and temperature), misalignment angles, and torque transmission needs. Choose a cardan joint that is appropriately sized and rated to handle the specific demands of the application.
2. Material Selection: Selecting the appropriate materials for the cardan joint is crucial for long-term performance. Consider factors such as strength, fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance. The materials should be compatible with the operating environment and any potential exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures.
3. Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Implement a regular inspection and maintenance schedule to identify any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. This includes checking for excessive play, backlash, or abnormal vibrations. Regularly lubricate the joint as per the manufacturer’s recommendations and ensure that seals are intact to prevent contamination.
4. Alignment and Installation: Proper alignment during installation is critical for optimal performance. Ensure that the joint is aligned correctly with the connected shafts to minimize misalignment and reduce stress on the joint. Precise alignment helps to minimize wear, maximize torque transmission efficiency, and extend the life of the joint.
5. Load Considerations: Be mindful of the loads applied to the cardan joint. Avoid exceeding the recommended load limits and consider factors such as shock loads, torsional forces, and variations in load during operation. Excessive loads can lead to premature wear, fatigue, and failure of the joint.
6. Temperature Management: Maintain suitable operating temperatures for the cardan joint. Excessive heat or extreme temperature fluctuations can affect the performance and longevity of the joint. Ensure proper cooling or lubrication mechanisms are in place if operating conditions generate significant heat.
7. Training and Operator Awareness: Provide proper training to operators and maintenance personnel regarding the cardan joint’s operation, maintenance requirements, and potential failure modes. Encourage regular inspection and reporting of any abnormalities to address issues promptly.
8. Consider Additional Measures: Depending on the application and specific requirements, additional measures can be implemented to enhance performance and reliability. This may include incorporating backlash compensation systems, using precision-aligned cardan joints, or integrating monitoring systems to detect early signs of wear or misalignment.
By considering these factors and implementing best practices, reliable and consistent performance can be achieved in a cardan joint. Regular monitoring, maintenance, and prompt corrective actions are essential to ensure the joint operates optimally and delivers the expected performance throughout its service life.

How do you install a cardan joint?
Installing a cardan joint involves several steps to ensure proper alignment, secure attachment, and reliable operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of the process for installing a cardan joint:
- Prepare the Components: Gather all the necessary components for the installation, including the cardan joint, yokes, bearings, retaining rings, and any additional hardware required. Ensure that the components are clean and free from dirt, debris, or damage.
- Align the Shafts: Position the input and output shafts that will be connected by the cardan joint. Align the shafts as closely as possible to minimize misalignment. The shafts should be collinear and positioned at the desired angle or position for the specific application.
- Attach the Yokes: Attach the yokes to the input and output shafts. The yokes typically have holes or bores that match the diameter of the shafts. Securely fasten the yokes to the shafts using appropriate fasteners, such as set screws or bolts. Ensure that the yokes are tightly secured to prevent any movement or slippage during operation.
- Assemble the Cardan Joint: Assemble the cardan joint by connecting the yokes with the cross-shaped component. The cross should fit snugly into the yoke holes or bores. Apply a suitable lubricant to the bearings to ensure smooth rotation and reduce friction. Some cardan joints may have retaining rings or clips to secure the bearings in place. Make sure all the components are properly aligned and seated.
- Check for Clearance: Verify that there is adequate clearance between the cardan joint and any surrounding components, such as chassis or housing. Ensure that the cardan joint can rotate freely without any obstructions or interference. If necessary, adjust the positioning or mounting of the cardan joint to provide sufficient clearance.
- Perform a Trial Run: Before finalizing the installation, perform a trial run to check the functionality of the cardan joint. Rotate the connected shafts manually or with a suitable power source and observe the movement of the joint. Ensure that there are no unusual noises, binding, or excessive play. If any issues are detected, investigate and address them before proceeding.
- Secure the Cardan Joint: Once the functionality is confirmed, secure the cardan joint in its final position. This may involve tightening additional fasteners or locking mechanisms to keep the joint in place. Use the appropriate torque specifications provided by the manufacturer to ensure proper tightening without damaging the components.
- Perform Final Checks: Double-check all the connections, fasteners, and clearances to ensure that everything is properly installed and secured. Verify that the cardan joint operates smoothly and without any issues. Inspect the entire system for any signs of misalignment, excessive vibration, or other abnormalities.
It is important to follow the specific installation instructions provided by the manufacturer of the cardan joint, as different designs and configurations may have specific requirements. If you are unsure or unfamiliar with the installation process, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or seek assistance from a qualified professional to ensure a proper and safe installation of the cardan joint.


editor by CX 2024-05-02
China supplier Quality Assurance Spindle Coupling Bearing U-Joint Cardan Cross Universal Joint Universal Joint 04371-60070 for Hilux Parts
Product Description
Product Parameters
|
item |
value |
|
Warranty |
6-12 Month |
|
Applicable Industries |
Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Retail, Construction works , Energy & Mining |
|
Customized support |
OEM, ODM, OBM |
|
Structure |
Single |
|
Material |
20CR 40CR |
|
Operating Angle |
35 degree |
|
Place of CHINAMFG |
China |
|
Product Name |
Cross Universal Coupling |
|
Structure |
Single Double Telescopic |
|
Packing |
Under Client’s Requestment |
|
Application |
Automotive.tractor.construction Machinery.rolling Mill |
|
Feature |
Low Noise. Long Life |
|
Precision |
ABEC1 ABEC3 ABEC 5 ABEC7 |
|
Quality |
Original Parts Standard |
|
Service |
OEM Customized Services |
|
MOQ |
10 Pcs |
|
Lead Time |
3-10 days |
Certifications
Company Profile
HangZhou CHINAMFG BEARING Co., Ltd is specialized in bearings areas since 2013, we create an innovative sales service of bearings to satisfy diffierent kinds of application.
We are located in HangZhou city, ZHangZhoug province, China, near HangZhou and ZheJiang port, which has recognized by special ISO, with CE certificiate, The various bearings we produce there have been inspected and confirmed by SGS to be RoHS compliant.
We Registered “GNYAR” in 2014, registered “MAJC” in 2018, both was received in high-performance praise, and earned high reputation. Our products is widely used to mining machinery, motorcycle parts, agricultural machine, auto parts and embroidery machine spare parts, Power tools, bicycle, Semiconductor Facilities. Fitness Equipments, Toys, fishing, industrial using design, etc.
After years of development, we believe that by establishing a mutually beneficial relationship with our customers we can both continue to grow and prosper, we wish and hope to always grant you satisfaction.
Packaging & Shipping
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Type: | Universal Joint |
| Material: | Steel |
| Market Type: | After-Market |
| Delivery Time: | 15 – 45days |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can cardan joints be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations. Cardan joints, also known as universal joints, are flexible mechanical couplings that transmit torque between misaligned shafts. Their design allows for angular movement and compensation of misalignments in various orientations. Here’s a detailed explanation of how cardan joints can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations:
Horizontal Orientation: In a horizontal orientation, the input and output shafts of the cardan joint are aligned horizontally, typically parallel to the ground. The joint is capable of transmitting torque smoothly and efficiently between the misaligned shafts while accommodating angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. This makes it suitable for a wide range of horizontal applications, including automotive drivetrains, industrial machinery, and agricultural equipment.
Vertical Orientation: In a vertical orientation, the input and output shafts of the cardan joint are aligned vertically, with one shaft positioned above the other. The joint is still capable of transmitting torque and compensating for misalignments in this configuration. However, it is important to consider the effects of gravity and the additional load imposed on the joint due to the weight of the shafts and any connected components. Adequate support and proper bearing selection should be considered to ensure reliable operation in vertical applications.
Whether in horizontal or vertical orientations, cardan joints offer several advantages that make them versatile for various applications:
- Misalignment Compensation: Cardan joints excel at compensating for angular, parallel, and axial misalignments between shafts. This flexibility allows for smooth torque transmission and reduces stress on the connected components.
- Torque Transmission: Cardan joints are capable of transmitting high levels of torque between misaligned shafts. This makes them suitable for applications that require the transfer of substantial power.
- Durability: Cardan joints are typically constructed from durable materials, such as alloy steels, which provide excellent strength and resistance to fatigue and wear. This durability enables them to withstand the demands of various orientations and operating conditions.
- Compact Design: Cardan joints have a compact design, allowing for efficient installation and integration within the system, regardless of the orientation. This is particularly advantageous in applications with space constraints.
- Versatility: Cardan joints are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different orientations and applications. They can be customized to meet specific torque and speed requirements.
It is important to note that specific considerations may apply depending on the application and the magnitude of misalignments. Factors such as load capacity, lubrication, bearing arrangement, and maintenance should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the cardan joint.
In summary, cardan joints can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations due to their ability to compensate for misalignments and transmit torque between shafts. Their versatility, durability, and compact design make them suitable for a wide range of applications in various orientations.

Can cardan joints be used in robotics and automation?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in robotics and automation applications, depending on the specific requirements and constraints of the system. Cardan joints offer certain advantages and considerations that make them suitable for certain robotic and automation tasks. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Flexibility and Misalignment Compensation: Cardan joints are designed to accommodate misalignment between rotating shafts. In robotics and automation, where multiple axes of movement are often involved, cardan joints can provide the necessary flexibility to handle misalignments and angular variations. They can compensate for misalignments resulting from assembly tolerances, thermal expansion, or mechanical deflections, allowing smooth and continuous motion.
2. Torque Transmission: Cardan joints are capable of transmitting torque between shafts at various angles. In robotics and automation, where power needs to be transferred between different components or joints, cardan joints can efficiently transmit torque, even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned. This enables the robot or automated system to perform complex tasks involving multi-axis motion and power transmission.
3. Rotational Freedom: Cardan joints provide rotational freedom and allow for angular movement. This is advantageous in robotics and automation applications where the system requires articulation and maneuverability. The universal joint design of cardan joints allows for smooth rotation and enables the robot or automated system to reach different orientations and perform tasks in various configurations.
4. Compact Design: Cardan joints have a relatively compact design, which can be beneficial in space-constrained robotics and automation setups. The compact size allows for efficient integration into robotic arms, end-effectors, or other automated mechanisms, minimizing the overall footprint and maximizing the utilization of available space.
5. Considerations for Precision and Backlash: When considering the use of cardan joints in robotics and automation, it’s important to account for precision requirements. Cardan joints have inherent clearances or play, which can introduce backlash and affect the system’s accuracy. In applications where high precision is crucial, additional measures such as backlash compensation mechanisms or precision-aligned cardan joints may be necessary.
It’s important to note that the suitability of cardan joints in robotics and automation depends on the specific application requirements, load conditions, precision needs, and other factors. Careful evaluation, system design, and integration are necessary to ensure that the cardan joints function optimally and meet the desired performance criteria.
When considering the use of cardan joints in robotics and automation, it is advisable to consult with engineers or experts specializing in robotics, automation, and power transmission systems. They can provide valuable insights and guidance on the selection, integration, and maintenance of cardan joints for specific robotic and automation applications.

How is a cardan joint different from other types of universal joints?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, is a specific type of universal joint design. While there are different variations of universal joints, the cardan joint has distinct characteristics that set it apart from other types. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a cardan joint differs from other universal joints:
1. Design and Structure: The cardan joint consists of two yokes and a cross-shaped member called the cross or spider. The yokes are typically fork-shaped and attached to the shafts, while the cross sits in the center, connecting the yokes. In contrast, other types of universal joints, such as the constant-velocity (CV) joint or Rzeppa joint, have different designs and structures. CV joints often use a combination of bearings and balls to transmit motion and maintain constant velocity, making them suitable for applications requiring smooth rotation without speed fluctuations.
2. Misalignment Compensation: One of the primary functions of a cardan joint is to accommodate misalignment between shafts. It can handle angular misalignment, axial misalignment, or a combination of both. The design of the cardan joint allows for the tilting of the cross as the input and output shafts rotate at different speeds. This tilting action compensates for misalignment and allows the joint to transmit motion. Other types of universal joints, such as the Oldham coupling or Hooke’s joint, have different mechanisms for compensating misalignment. For example, the Oldham coupling uses sliding slots and intermediate disks to accommodate misalignment, while Hooke’s joint uses a combination of rotating links and flexible connections.
3. Operating Range: Cardan joints are commonly used in applications where a wide range of operating angles is required. They can effectively transmit motion and torque at various angles, making them suitable for applications with non-collinear shafts. Other types of universal joints may have specific limitations or operating ranges. For instance, some types of CV joints are designed for constant velocity applications and are optimized for specific operating angles or speed ranges.
4. Applications: Cardan joints find applications in various industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, and more. They are commonly used in drivetrain systems, power transmission systems, and applications that require flexibility, misalignment compensation, and reliable motion transmission. Other types of universal joints have their own specific applications. For example, CV joints are commonly used in automotive applications, particularly in front-wheel drive systems, where they provide smooth and constant power transmission while accommodating suspension movements.
5. Limitations: While cardan joints offer flexibility and misalignment compensation, they also have certain limitations. At extreme operating angles, cardan joints can introduce non-uniform motion, increased vibration, backlash, and potential loss of efficiency. Other types of universal joints may have their own limitations and considerations depending on their specific design and application requirements.
In summary, a cardan joint, or universal joint, is a specific type of universal joint design that can accommodate misalignment between shafts and transmit motion at various angles. Its structure, misalignment compensation mechanism, operating range, and applications differentiate it from other types of universal joints. Understanding these distinctions is crucial when selecting the appropriate joint for a specific application.


editor by CX 2024-04-26
China supplier SWC-Wd Type Coupling Nontelescopic Shorten Cardan Shaft Coupling Universal Joint
Product Description
SWC-WD type coupling Nontelescopic Shorten Cardan Shaft Coupling
Product Description
SWC-WD-type cross shaft universal coupling is 1 of the most common coupling. With its characteristic structure enables not on the same axis or the axis angle greater or axial movement of a larger two-axis continuous constant angular velocity rotation, and reliably transmit torque and motion. Can be widely used in metallurgy, lifting, engineering, transportation, mining, oil, shipbuilding, coal, rubber, paper machinery and other heavy machinery industry, mechanical shafting transmitting torque.
Product Parameters
Advantages
1. The ability to have a large angle compensation.
2. The structure is compact and reasonable. SWC-WD type with integral fork, so carrying more reliable.
3. The carrying capacity. Compared with other types of the same diameter rotary joint axis, it delivers more torque, the turning diameter of restricted mechanical equipment, the complete range is more advantageous.
4. High transmission efficiency. Its transmission efficiency of 98-99.8% for high-power transmission, energy-saving effect.
5. carrying smooth, low noise, easy maintenance, assembly and disassembly.
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing
various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks in PDF or AI format.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 5: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 6: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 19mm |
| Speed: | 4000r/M |
| Structure: | Rigid |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the potential limitations or drawbacks of using cardan joints?
While cardan joints offer numerous advantages in transmitting rotational motion between misaligned shafts, they also have certain limitations and drawbacks to consider. Here are some potential limitations associated with the use of cardan joints:
- Angular Limitations: Cardan joints have limited angularity or operating angles. They are designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and exceeding these angles can cause accelerated wear, increased vibration, and potential joint failure. Extreme operating angles can lead to binding, decreased efficiency, and reduced power transmission capacity. In applications where large operating angles are required, alternative flexible coupling mechanisms or constant velocity joints may be more suitable.
- Backlash and Torsional Stiffness: Cardan joints inherently exhibit some degree of backlash, which is the clearance or free play between the mating components. This can result in a slight delay in power transmission and can affect the precision of motion in certain applications. Additionally, cardan joints may have higher torsional stiffness compared to other coupling mechanisms, which can transmit higher vibrations and shocks to the connected components.
- Maintenance Requirements: Cardan joints require regular maintenance to ensure proper lubrication, alignment, and performance. The lubricant needs to be regularly replenished or replaced, and the joint should be inspected for wear, misalignment, or other issues. Failure to perform adequate maintenance can result in premature wear, reduced efficiency, and potential joint failure. Maintenance procedures may require specialized tools and expertise.
- Space and Weight: Cardan joints can occupy a significant amount of space due to their design and the need for perpendicular shafts. In applications with limited space constraints, finding suitable locations for cardan joints can be challenging. Additionally, the weight of cardan joints, especially in heavy-duty applications, can add to the overall weight of the system, which may have implications for fuel efficiency, payload capacity, or overall performance.
- Cost: Cardan joints, particularly high-quality and precision-engineered ones, can be relatively expensive compared to other coupling mechanisms. The complex design, manufacturing tolerances, and specialized materials involved contribute to their higher cost. In cost-sensitive applications, alternative coupling solutions may be considered if the angular limitations and other drawbacks of cardan joints are not critical.
- High-Speed Limitations: At high rotational speeds, cardan joints can experience increased vibration, imbalance, and potential for fatigue failure. The rotating components of the joint can generate centrifugal forces that impact the balance and stability of the system. In high-speed applications, careful design considerations, including balancing and vibration analysis, may be necessary to mitigate these issues.
It is important to evaluate the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and limitations when considering the use of cardan joints. While they offer versatility and flexibility in many scenarios, alternative coupling mechanisms may be more suitable in cases where the limitations and drawbacks of cardan joints pose significant challenges.

How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint?
When retrofitting an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint, careful planning and consideration of various factors are necessary to ensure a successful integration. The retrofitting process involves modifying the system to accommodate the cardan joint’s requirements for torque transmission and misalignment compensation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to retrofit an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint:
- Evaluate the Existing System: Begin by thoroughly evaluating the existing mechanical system to understand its design, components, and operational requirements. Identify the areas where a cardan joint can be integrated effectively and assess the feasibility of retrofitting.
- Identify the Integration Points: Determine the specific locations within the system where the cardan joint will be installed. This could include areas where torque transmission or misalignment compensation is required, such as connections between shafts, pulleys, or other rotating components.
- Measurements and Compatibility: Take accurate measurements of the existing components and spaces where the cardan joint will be installed. Ensure that the dimensions and specifications of the cardan joint are compatible with the available space and the system’s requirements. Consider factors such as shaft sizes, torque ratings, misalignment angles, and operating conditions.
- Design Modifications: Based on the evaluation and measurements, make necessary design modifications to accommodate the cardan joint. This may involve modifying shaft ends, adding or removing components, or adjusting mounting positions. Ensure that the modifications do not compromise the structural integrity or functionality of the system.
- Installation and Alignment: Install the cardan joint at the identified integration points according to the manufacturer’s guidelines and engineering best practices. Pay attention to proper alignment, ensuring that the joint aligns with the shafts and other connected components. Precise alignment is crucial for efficient torque transmission and to prevent excessive wear or failure.
- Secure Mounting: Properly secure the cardan joint to the system, ensuring that it is firmly and securely mounted. Use appropriate fasteners, couplings, or brackets to hold the joint in place and prevent any movement or vibration that could affect its performance.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication and maintenance of the cardan joint. Proper lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the joint. Establish a maintenance schedule to regularly inspect and maintain the retrofit components to prevent any potential issues.
- Testing and Validation: After the retrofitting is complete, perform thorough testing to validate the functionality and performance of the retrofitted system. Test for torque transmission, misalignment compensation, and overall system operation. Monitor the system during operation to ensure that the cardan joint performs as expected and does not introduce any adverse effects.
It is essential to consult with experienced engineers or professionals specializing in retrofitting and cardan joint applications during the process. They can provide valuable guidance, expertise, and assistance in selecting the appropriate cardan joint, making design modifications, and ensuring a successful retrofit of the existing mechanical system.

How is a cardan joint different from other types of universal joints?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, is a specific type of universal joint design. While there are different variations of universal joints, the cardan joint has distinct characteristics that set it apart from other types. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a cardan joint differs from other universal joints:
1. Design and Structure: The cardan joint consists of two yokes and a cross-shaped member called the cross or spider. The yokes are typically fork-shaped and attached to the shafts, while the cross sits in the center, connecting the yokes. In contrast, other types of universal joints, such as the constant-velocity (CV) joint or Rzeppa joint, have different designs and structures. CV joints often use a combination of bearings and balls to transmit motion and maintain constant velocity, making them suitable for applications requiring smooth rotation without speed fluctuations.
2. Misalignment Compensation: One of the primary functions of a cardan joint is to accommodate misalignment between shafts. It can handle angular misalignment, axial misalignment, or a combination of both. The design of the cardan joint allows for the tilting of the cross as the input and output shafts rotate at different speeds. This tilting action compensates for misalignment and allows the joint to transmit motion. Other types of universal joints, such as the Oldham coupling or Hooke’s joint, have different mechanisms for compensating misalignment. For example, the Oldham coupling uses sliding slots and intermediate disks to accommodate misalignment, while Hooke’s joint uses a combination of rotating links and flexible connections.
3. Operating Range: Cardan joints are commonly used in applications where a wide range of operating angles is required. They can effectively transmit motion and torque at various angles, making them suitable for applications with non-collinear shafts. Other types of universal joints may have specific limitations or operating ranges. For instance, some types of CV joints are designed for constant velocity applications and are optimized for specific operating angles or speed ranges.
4. Applications: Cardan joints find applications in various industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, and more. They are commonly used in drivetrain systems, power transmission systems, and applications that require flexibility, misalignment compensation, and reliable motion transmission. Other types of universal joints have their own specific applications. For example, CV joints are commonly used in automotive applications, particularly in front-wheel drive systems, where they provide smooth and constant power transmission while accommodating suspension movements.
5. Limitations: While cardan joints offer flexibility and misalignment compensation, they also have certain limitations. At extreme operating angles, cardan joints can introduce non-uniform motion, increased vibration, backlash, and potential loss of efficiency. Other types of universal joints may have their own limitations and considerations depending on their specific design and application requirements.
In summary, a cardan joint, or universal joint, is a specific type of universal joint design that can accommodate misalignment between shafts and transmit motion at various angles. Its structure, misalignment compensation mechanism, operating range, and applications differentiate it from other types of universal joints. Understanding these distinctions is crucial when selecting the appropriate joint for a specific application.


editor by CX 2024-04-25
China Best Sales Ductile Iron Wide Range Universal Flexible Connection Dresser Pipe Coupling Joint
Product Description
Dedicated Couplings Adaptors for Ductile Iron Pipes ISO 2531/EN545 EN 14525, ANSI/AWWA C219
Description
SYI can supply the Dedicated Couplings dedicated Couplings, dedicated to connect the ductile iron pipe (upto DN2200)
SYI Dedicated Couplings DIMENSIONS
|
CHINAMFG S. N. |
DN |
pipe O.D. |
O.D. Tolerance |
D2 |
H |
L |
Min. pipe end prepared length |
|
|
|
mm |
|||||||
|
DC40 |
40 |
56 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
120 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC50 |
50 |
66 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
126 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC60 |
60 |
77 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
135 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC65 |
65 |
82 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
156 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC80 |
80 |
98 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
184 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC100 |
100 |
118 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
205 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC125 |
125 |
144 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
232 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC150 |
150 |
170 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
264 |
102 |
173 |
100 |
|
DC200 |
200 |
222 |
+1.0 |
-3.5 |
315 |
102 |
173 |
100 |
|
DC250 |
250 |
274 |
+1.0 |
-3.5 |
374 |
102 |
173 |
100 |
|
DC300 |
300 |
326 |
+1.0 |
-3.5 |
426 |
102 |
173 |
100 |
|
DC350 |
350 |
378 |
+1.0 |
-3.5 |
494 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC400 |
400 |
429 |
+1.0 |
-4.0 |
544 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC450 |
450 |
480 |
+1.0 |
-4.0 |
595 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC500 |
500 |
532 |
+1.0 |
-4.0 |
650 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC600 |
600 |
635 |
+1.0 |
-4.5 |
753 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC700 |
700 |
738 |
+1.0 |
-4.5 |
858 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC800 |
800 |
842 |
+1.0 |
-4.5 |
962 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC900 |
900 |
945 |
+1.0 |
-5.0 |
1070 |
178 |
280 |
150 |
|
DC1000 |
1000 |
1048 |
+1.0 |
-5.0 |
1173 |
178 |
280 |
150 |
|
DC1100 |
1100 |
1152 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
1282 |
178 |
280 |
150 |
|
DC1200 |
1200 |
1255 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
1385 |
178 |
280 |
150 |
|
DC1400 |
1400 |
1462 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
1592 |
178 |
295 |
150 |
|
DC1500 |
1500 |
1565 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
1691 |
178 |
295 |
150 |
|
DC1600 |
1600 |
1668 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
1798 |
178 |
295 |
150 |
|
DC1800 |
1800 |
1875 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
2015 |
254 |
375 |
150/300 |
|
DC2000 |
2000 |
2082 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
2222 |
254 |
375 |
150/300 |
|
DC2200 |
2200 |
2288 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
2415 |
254 |
375 |
150/300 |
For other sizes not mentioned above, please contact us. We have right to change the data without further notice.
1. Material
BODY: Ductile Iron grade 500-7/450-10 in accordance with ISO 1083 or 70-50-05/65-45-12 with ASTM A536
GLAND: Ductile Iron grade 500-7/450-10 in accordance with ISO 1083 or 70-50-05/65-45-12 with ASTM A536
GASKET: Rubber E.P.D.M./SBR/NBR in accordance with EN 681.1
D-BOLTS AND NUTS: Carbon Steel Grade 8.8 with dacromet coating
2. Working Pressure: 16 Bar or 250 PSI
3. Fluid Temperature: 0°C – 50°C, excluding frost
4. Allowed Angular Deflection: 6°
5. Joint Gap:19mm
6. Coating
|
External Coatings: |
Internal Coatings: |
7.Reference Rules
Designed and tested in accordance with EN14525, ANSI/AWWA C219 and EN545
Package
Packing: Different package CHINAMFG your request,like wood cases&pallets,ply-wood crates&pallets,steel crates&pallets and etc.
Quality Control
Company Profile
CHINAMFG has continually invested in better technology and production facilities. More than 4,000 patterns
are ready. We are capable to finish all the production processes from moulding, shot-blasting, machining, coating to packaging. We have over 100,000 m2 foundry land including:
-10,000 m2 of the pattern, sand mixing, polishing, machining, hydraulic pressure, coating, packaging workshops;
-4,000 m2 of 3 green sand moulding workshops and 1 resin sand moulding workshops;
-3,000 m2 of automatic moulding machine line and epoxy coating line
-professional laboratory
-machining shop
-and our own tooling shop
Strict process and operating regulations together with perfect quality assurance system making every production step under control. All the products are subject to tests and inspections including composition analysis, metallographic examination, dimension & surface finish inspection, ring test, tensile test, hardness test, hydrostatic test, CHINAMFG and coating test to be sure that the products meet the requirements of the standards.
Since 2009, CHINAMFG Pipeline has developed from a pipes & fittings seller to a professional project solution provider, including the 1 stop service and solution from pipes, fittings, couplings & flanged adaptors, valves, fire hydrants, to water CHINAMFG and accessories.
SYI products have served 111 countries CHINAMFG up to now!
Most of these customers cooperated with CHINAMFG for more than 20 years!
We value long term cooperation relationship mostly!
Welcome to send us an inquiry for more details and price!!!
P
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Solution |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Connection: | Press Connection |
| Structure: | Universal |
| Flexible or Rigid: | Flexible |
| Material: | Iron |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can universal joints be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations?
Yes, universal joints can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Universal joints are mechanical devices designed to transmit rotary motion between two shafts that are not in a straight line alignment. They consist of a cross-shaped or H-shaped yoke with bearings at each end that connect to the shafts. The design of universal joints allows them to accommodate angular misalignment between the shafts, making them suitable for various applications, including both horizontal and vertical orientations.
When used in a horizontal orientation, universal joints can transmit rotational motion between shafts that are positioned at different angles or offsets. They are commonly found in drivetrain systems of vehicles, where they transfer power from the engine to the wheels, even when the drivetrain components are not perfectly aligned. In this configuration, universal joints can effectively handle the torque requirements and misalignment caused by uneven terrain, suspension movement, or steering angles.
In a vertical orientation, universal joints can also be utilized to transfer rotational motion between shafts that are positioned vertically. This arrangement is often seen in applications such as industrial equipment, machinery, or agricultural implements. For example, in a vertical power transmission system, a universal joint can be used to connect a vertical driving shaft to a vertical driven shaft, enabling power transfer and accommodating any angular misalignment that may occur due to variations in shaft positions or vibrations.
It’s important to note that the specific design and selection of universal joints for different orientations should consider factors such as the torque requirements, operating conditions, and the manufacturer’s specifications. The orientation of the universal joint may affect factors such as lubrication, load-bearing capacity, and the need for additional support or stabilization mechanisms.
In summary, universal joints can be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations. Their ability to accommodate angular misalignment makes them versatile components for transmitting rotary motion between shafts that are not in a straight line alignment, regardless of the orientation.

Are universal joints suitable for both high-torque and high-speed applications?
Universal joints have certain limitations when it comes to high-torque and high-speed applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Universal joints are commonly used to transmit torque between non-aligned or angularly displaced shafts. They offer advantages in terms of flexibility and compactness. However, their suitability for high-torque and high-speed applications depends on several factors:
- High-Torque Applications: Universal joints can handle high-torque applications to a certain extent. The torque capacity of a universal joint depends on factors such as the material strength, joint size, and design. In general, larger universal joints with stronger materials have higher torque ratings. However, when subjected to extremely high torques, universal joints may experience increased stress, accelerated wear, and potential failure. In such cases, alternative power transmission solutions like gearboxes or direct drives may be more suitable for handling high-torque applications.
- High-Speed Applications: Universal joints may not be the ideal choice for high-speed applications. At high rotational speeds, universal joints can experience several challenges. These include increased vibration, imbalance, and decreased precision. The design characteristics of universal joints, such as the presence of backlash and variations in joint geometry, can become more pronounced at high speeds, leading to reduced performance and potential failure. In high-speed applications, alternative solutions like flexible couplings or constant velocity (CV) joints are often preferred due to their ability to provide smoother operation, improved balance, and constant velocity output.
It’s important to note that the specific torque and speed limitations of a universal joint can vary depending on factors such as the joint’s size, design, quality, and the application’s requirements. Manufacturers provide torque and speed ratings for their universal joints, and it’s crucial to adhere to these specifications for reliable and safe operation.
In summary, while universal joints can handle moderate torque and speed levels, they may not be suitable for extremely high-torque or high-speed applications. Understanding the limitations of universal joints and considering alternative power transmission solutions when necessary can help ensure optimal performance and reliability in different operating conditions.

What are the potential limitations or drawbacks of using universal joints?
While universal joints offer several advantages in transmitting torque between non-aligned or angularly displaced shafts, they also have some limitations and drawbacks to consider. Here are some potential limitations of using universal joints:
- Angular limitations: Universal joints have specific angular limits within which they can operate efficiently. If the angle between the input and output shafts exceeds these limits, it can lead to increased wear, vibration, and decreased power transmission efficiency. Operating a universal joint at extreme angles or near its angular limits can result in premature failure or reduced service life.
- Backlash and play: Universal joints can have inherent backlash and play due to the design and clearance between the components. This can result in a loss of precision in torque transmission, especially in applications that require accurate positioning or minimal rotational play.
- Maintenance and lubrication: Universal joints require regular maintenance and proper lubrication to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Failing to adhere to the recommended lubrication intervals or using inadequate lubricants can lead to increased friction, wear, and potential joint failure.
- Limited misalignment compensation: While universal joints can accommodate some misalignment between the input and output shafts, they have limitations in compensating for large misalignments. Excessive misalignment can cause increased stress, wear, and potential binding or seizure of the joint.
- Non-constant velocity: Standard universal joints, also known as Cardan joints, do not provide constant velocity output. As the joint rotates, the output shaft speed fluctuates due to the changing angular velocity caused by the joint’s design. Applications that require constant velocity output may necessitate the use of alternative joint types, such as constant velocity (CV) joints.
- Limitations in high-speed applications: Universal joints may not be suitable for high-speed applications due to the potential for vibration, imbalance, and increased stress on the joint components. At high rotational speeds, the joint’s limitations in balance and precision can become more pronounced, leading to reduced performance and potential failure.
- Space and weight considerations: Universal joints require space to accommodate their design, including the yokes, cross, and bearings. In compact or weight-conscious applications, the size and weight of the universal joint may pose challenges, requiring careful design considerations and trade-offs.
It’s important to evaluate these limitations and drawbacks in the context of the specific application and system requirements. In some cases, alternative power transmission solutions, such as flexible couplings, CV joints, gearboxes, or direct drives, may be more suitable depending on the desired performance, efficiency, and operating conditions.


editor by CX 2024-04-24
China factory Ductile Iron Wide Range Universal Flexible Connection Dresser Pipe Coupling Joint
Product Description
Dedicated Couplings Adaptors for Ductile Iron Pipes ISO 2531/EN545 EN 14525, ANSI/AWWA C219
Description
SYI can supply the Dedicated Couplings dedicated Couplings, dedicated to connect the ductile iron pipe (upto DN2200)
SYI Dedicated Couplings DIMENSIONS
|
CHINAMFG S. N. |
DN |
pipe O.D. |
O.D. Tolerance |
D2 |
H |
L |
Min. pipe end prepared length |
|
|
|
mm |
|||||||
|
DC40 |
40 |
56 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
120 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC50 |
50 |
66 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
126 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC60 |
60 |
77 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
135 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC65 |
65 |
82 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
156 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC80 |
80 |
98 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
184 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC100 |
100 |
118 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
205 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC125 |
125 |
144 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
232 |
102 |
166 |
100 |
|
DC150 |
150 |
170 |
+1.0 |
-3.0 |
264 |
102 |
173 |
100 |
|
DC200 |
200 |
222 |
+1.0 |
-3.5 |
315 |
102 |
173 |
100 |
|
DC250 |
250 |
274 |
+1.0 |
-3.5 |
374 |
102 |
173 |
100 |
|
DC300 |
300 |
326 |
+1.0 |
-3.5 |
426 |
102 |
173 |
100 |
|
DC350 |
350 |
378 |
+1.0 |
-3.5 |
494 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC400 |
400 |
429 |
+1.0 |
-4.0 |
544 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC450 |
450 |
480 |
+1.0 |
-4.0 |
595 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC500 |
500 |
532 |
+1.0 |
-4.0 |
650 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC600 |
600 |
635 |
+1.0 |
-4.5 |
753 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC700 |
700 |
738 |
+1.0 |
-4.5 |
858 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC800 |
800 |
842 |
+1.0 |
-4.5 |
962 |
152 |
254 |
150 |
|
DC900 |
900 |
945 |
+1.0 |
-5.0 |
1070 |
178 |
280 |
150 |
|
DC1000 |
1000 |
1048 |
+1.0 |
-5.0 |
1173 |
178 |
280 |
150 |
|
DC1100 |
1100 |
1152 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
1282 |
178 |
280 |
150 |
|
DC1200 |
1200 |
1255 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
1385 |
178 |
280 |
150 |
|
DC1400 |
1400 |
1462 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
1592 |
178 |
295 |
150 |
|
DC1500 |
1500 |
1565 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
1691 |
178 |
295 |
150 |
|
DC1600 |
1600 |
1668 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
1798 |
178 |
295 |
150 |
|
DC1800 |
1800 |
1875 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
2015 |
254 |
375 |
150/300 |
|
DC2000 |
2000 |
2082 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
2222 |
254 |
375 |
150/300 |
|
DC2200 |
2200 |
2288 |
+1.0 |
-6.0 |
2415 |
254 |
375 |
150/300 |
For other sizes not mentioned above, please contact us. We have right to change the data without further notice.
1. Material
BODY: Ductile Iron grade 500-7/450-10 in accordance with ISO 1083 or 70-50-05/65-45-12 with ASTM A536
GLAND: Ductile Iron grade 500-7/450-10 in accordance with ISO 1083 or 70-50-05/65-45-12 with ASTM A536
GASKET: Rubber E.P.D.M./SBR/NBR in accordance with EN 681.1
D-BOLTS AND NUTS: Carbon Steel Grade 8.8 with dacromet coating
2. Working Pressure: 16 Bar or 250 PSI
3. Fluid Temperature: 0°C – 50°C, excluding frost
4. Allowed Angular Deflection: 6°
5. Joint Gap:19mm
6. Coating
|
External Coatings: |
Internal Coatings: |
7.Reference Rules
Designed and tested in accordance with EN14525, ANSI/AWWA C219 and EN545
Package
Packing: Different package CHINAMFG your request,like wood cases&pallets,ply-wood crates&pallets,steel crates&pallets and etc.
Quality Control
Company Profile
CHINAMFG has continually invested in better technology and production facilities. More than 4,000 patterns
are ready. We are capable to finish all the production processes from moulding, shot-blasting, machining, coating to packaging. We have over 100,000 m2 foundry land including:
-10,000 m2 of the pattern, sand mixing, polishing, machining, hydraulic pressure, coating, packaging workshops;
-4,000 m2 of 3 green sand moulding workshops and 1 resin sand moulding workshops;
-3,000 m2 of automatic moulding machine line and epoxy coating line
-professional laboratory
-machining shop
-and our own tooling shop
Strict process and operating regulations together with perfect quality assurance system making every production step under control. All the products are subject to tests and inspections including composition analysis, metallographic examination, dimension & surface finish inspection, ring test, tensile test, hardness test, hydrostatic test, CHINAMFG and coating test to be sure that the products meet the requirements of the standards.
Since 2009, CHINAMFG Pipeline has developed from a pipes & fittings seller to a professional project solution provider, including the 1 stop service and solution from pipes, fittings, couplings & flanged adaptors, valves, fire hydrants, to water CHINAMFG and accessories.
SYI products have served 111 countries CHINAMFG up to now!
Most of these customers cooperated with CHINAMFG for more than 20 years!
We value long term cooperation relationship mostly!
Welcome to send us an inquiry for more details and price!!!
P
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Solution |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Connection: | Press Connection |
| Structure: | Universal |
| Flexible or Rigid: | Flexible |
| Material: | Iron |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the potential challenges in designing and manufacturing universal joints?
Designing and manufacturing universal joints can present various challenges that need to be addressed to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Misalignment Compensation: Universal joints are primarily designed to accommodate angular misalignment between two shafts. Designing a universal joint that can effectively compensate for misalignment while maintaining smooth power transmission can be challenging. The joint must provide flexibility without sacrificing strength or introducing excessive play, which could lead to vibration, noise, or premature wear.
2. Torque Transmission: Universal joints are often used in applications that require the transfer of high torque loads. Designing the joint to handle these loads without failure or excessive wear is a significant challenge. The selection of appropriate materials, heat treatment processes, and bearing designs becomes crucial to ensure the strength, durability, and reliability of the joint.
3. Lubrication and Sealing: Universal joints require proper lubrication to minimize friction, heat generation, and wear between the moving components. Designing an effective lubrication system that ensures sufficient lubricant supply to all critical areas can be challenging. Additionally, designing seals and protective covers to prevent contamination and retain lubrication presents a challenge, as the joint must maintain flexibility while ensuring adequate sealing.
4. Bearing Design and Wear: Universal joints rely on bearings to facilitate smooth rotation and to support the shafts. Designing the bearing arrangement to withstand the loads, maintain proper alignment, and resist wear is essential. Choosing the appropriate bearing type, such as needle bearings or plain bearings, and optimizing their size, material, and lubrication conditions are key challenges in the design process.
5. Manufacturability: Manufacturing universal joints with precision and consistency can be challenging due to their complex geometries and the need for tight tolerances. The manufacturing process must ensure accurate machining, assembly, and balancing of the joint components to achieve proper fit, alignment, and balance. Specialized machining techniques and quality control measures are often required to meet the desired specifications.
6. Cost and Size Optimization: Designing universal joints that are cost-effective and compact while meeting performance requirements can be a challenging task. Balancing the need for robustness, durability, and material efficiency with cost considerations requires careful engineering and optimization. Designers must strike a balance between performance, weight, space constraints, and manufacturing costs to create an efficient and economical universal joint.
7. Application-Specific Considerations: Designing universal joints for specific applications may introduce additional challenges. Factors such as environmental conditions, temperature extremes, exposure to corrosive substances, high-speed operation, or heavy-duty applications need to be carefully considered and addressed in the design and material selection process. Customization and adaptation of universal joints to meet unique application requirements can pose additional challenges.
Addressing these challenges in the design and manufacturing process requires a combination of engineering expertise, material science knowledge, advanced manufacturing techniques, and thorough testing and validation procedures. Collaboration between design engineers, manufacturing engineers, and quality control personnel is crucial to ensure the successful development and production of reliable universal joints.
In summary, the potential challenges in designing and manufacturing universal joints include misalignment compensation, torque transmission, lubrication and sealing, bearing design and wear, manufacturability, cost and size optimization, and application-specific considerations. Overcoming these challenges requires careful engineering, precision manufacturing processes, and consideration of various factors to achieve high-performance and reliable universal joints.

What is the effect of varying operating angles on the performance of a universal joint?
Varying operating angles can have a significant effect on the performance of a universal joint. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A universal joint is designed to transmit rotational motion between two shafts that are not collinear or have a constant angular relationship. The operating angle refers to the angle between the input and output shafts of the joint. The effects of varying operating angles on the performance of a universal joint are as follows:
- Changes in Torque and Speed: As the operating angle of a universal joint increases or decreases, the torque and speed transmitted through the joint can be affected. At small operating angles, the torque and speed transmission are relatively efficient. However, as the operating angle increases, the torque and speed capacity of the joint may decrease. This reduction in torque and speed capability is due to increased non-uniform loading and bending moments on the joint’s components.
- Increased Vibrations and Noise: Varying operating angles can introduce vibrations and noise in a universal joint. As the operating angle becomes more extreme, the joint experiences higher levels of dynamic imbalance and misalignment. This imbalance can lead to increased vibration levels, which may affect the overall performance and lifespan of the joint. Additionally, the non-uniform motion and increased stress on the joint’s components can generate additional noise during operation.
- Angular Misalignment Compensation: One of the primary advantages of universal joints is their ability to compensate for angular misalignment between shafts. By accommodating varying operating angles, the joint allows for flexibility in transmitting motion even when the input and output shafts are not perfectly aligned. However, extreme operating angles may challenge the joint’s ability to compensate for misalignment effectively. Very large operating angles can lead to increased wear, decreased joint life, and potential loss of motion transmission efficiency.
- Increased Wear and Fatigue: Varying operating angles can contribute to increased wear and fatigue on the universal joint’s components. As the operating angle increases, the joint experiences higher levels of stress and non-uniform loading. This stress concentration can lead to accelerated wear and fatigue, especially at critical areas such as the bearing caps and needle bearings. Continuous operation at extreme operating angles without proper lubrication and maintenance can significantly reduce the joint’s lifespan.
- Heat Generation: Extreme operating angles can result in increased heat generation within the universal joint. The non-uniform motion and increased friction caused by high operating angles can lead to elevated temperatures. Excessive heat can accelerate lubricant breakdown, increase wear rates, and potentially cause premature failure of the joint. Adequate cooling and proper lubrication are essential to mitigate the effects of heat generation in such cases.
- Efficiency and Power Loss: Varying operating angles can impact the overall efficiency of a universal joint. At small to moderate operating angles, the joint can transmit motion with relatively high efficiency. However, as the operating angle increases, the joint’s efficiency may decrease due to increased friction, bending moments, and non-uniform loading. This reduction in efficiency can result in power loss and decreased overall system performance.
Therefore, it is crucial to consider the effects of varying operating angles on the performance of a universal joint. Proper design, careful selection of operating angles within the joint’s specified limits, regular maintenance, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines can help mitigate the potential negative effects and ensure optimal performance and longevity of the joint.

What lubrication is required for a universal joint?
Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth and efficient operation of a universal joint. The type and amount of lubrication required may vary depending on the specific design and manufacturer’s recommendations. Here are some general guidelines:
- High-quality lubricant: It is important to use a high-quality lubricant that is specifically recommended for universal joints. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or technical documentation to determine the appropriate lubricant type and viscosity for your universal joint.
- Grease or oil: Universal joints can be lubricated with either grease or oil, depending on the design and application requirements. Grease is commonly used as it provides good lubrication and helps to seal out contaminants. Oil can be used in applications that require constant lubrication or when specified by the manufacturer.
- Quantity of lubrication: Apply the recommended quantity of lubricant as specified by the manufacturer. Over-greasing or under-greasing can lead to problems such as excessive heat, increased friction, or inadequate lubrication. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure the optimal amount of lubricant is applied.
- Lubrication points: Identify the lubrication points on the universal joint. These are typically located at the cross bearings or bearing cups where the cross interfaces with the yoke. Apply the lubricant directly to these points to ensure proper lubrication of the moving components.
- Lubrication intervals: Establish a lubrication schedule based on the operating conditions and manufacturer’s recommendations. Regularly inspect and lubricate the universal joint according to the specified intervals. Factors such as operating speed, load, temperature, and environmental conditions may influence the frequency of lubrication.
- Re-lubrication: In some cases, universal joints may have provisions for re-lubrication. This involves purging old lubricant and replenishing it with fresh lubricant. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the re-lubrication procedure, including the recommended interval and method.
- Environmental considerations: Consider the operating environment when selecting the lubricant. Factors such as temperature extremes, exposure to moisture or chemicals, and the presence of contaminants can affect the choice and performance of the lubricant. Choose a lubricant that is suitable for the specific environmental conditions of your application.
- Maintenance and inspection: Regularly inspect the universal joint for signs of inadequate lubrication, excessive wear, or contamination. Monitor the temperature of the joint during operation, as excessive heat can indicate insufficient lubrication. Address any lubrication issues promptly to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the universal joint.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for lubrication specific to your universal joint model. Following the proper lubrication practices will help optimize the performance, reduce wear, and extend the lifespan of the universal joint.


editor by CX 2024-04-15
China Good quality Cardan Shaft High Quality Long Flex Welding Type Cross Shaft Universal Coupling Universal Joint
Product Description
Cardan Shaft High Quality Long Flex Welding Type Cross Shaft Universal Coupling Universal Joint
Description:
The SWC-CH long flexible welded universal joint is a Universal joint designed to transmit power between 2 misaligned shafts. It is a flexible coupling, which means it can compensate for misalignment up to 25 degrees. The SWC-CH long bend welded universal coupling is made of 35CrMo material and comes in various sizes to meet the needs of different applications. SWC-CH long bend welded universal couplings are widely used in mechanical applications such as rolling mills, punches, straighteners, crushers, ship transmissions, papermaking equipment, ordinary machinery, water pump equipment, test benches, etc.
SWC-CH Long Flexible Welded Universal Coupling Features:
1. Possess the ability to compensate for large angles.
2. The structure is compact and reasonable. The SWC-CH universal coupling is equipped with an integrated fork, making it more reliable in carrying capacity.
3. Carrying capacity. Compared to other types of rotating joint shafts with the same diameter, it provides more torque, limits the turning diameter of mechanical equipment, and has a wider range.
4. High transmission efficiency. Its transmission efficiency is 98-99.8%, suitable for high-power transmission and has energy-saving effect.
5. Smooth carrying, low noise, easy disassembly and maintenance.
SWC-CH Long Flexible Welded Universal Coupling Application:
The SWC-CH long flexible welded universal coupling is a universal and reliable coupling that is very suitable for various applications. Some of the most common applications include:
(1) Construction machinery: SWC-CH long flexible welded universal couplings are used in various construction machinery, such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes. It helps to ensure smooth and efficient operation of the machine, even when the shafts are not fully aligned.
(2) Mining machinery: SWC-CH long flexible welded universal couplings are also used in mining machinery, such as loaders, conveyors, and drilling rigs. It helps to transfer power from the engine to the working components of the machine, even if the shaft is affected by high loads and vibrations.
(3) Agricultural machinery: SWC-CH long flexible welded universal coupling is used for tractors, harvesters, Combine harvester and other agricultural machinery. It helps to ensure smooth and efficient operation of the machine, even when the shafts are not fully aligned.
(4) Marine machinery: SWC-CH long flexible welded universal coupling is used for marine machinery such as ships. It helps to transfer power from the engine to the propeller, even if the shaft is affected by high loads and vibrations.
(5) Power generation equipment: SWC-CH long flexible welded universal coupling is used for power generation equipment, such as turbines and generators. It helps to transfer power from the prime mover to the generator, even if the shafts are not fully aligned.
Packing & shipping:
1 Prevent from damage.
2. As customers’ requirements, in perfect condition.
3. Delivery : As per contract delivery on time
4. Shipping : As per client request. We can accept CIF, Door to Door etc. or client authorized agent we supply all the necessary assistant.
FAQ:
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks in PDF or AI format.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 5: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 6: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 19mm |
| Speed: | 4000r/M |
| Structure: | Flexible |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do you address noise issues in a cardan joint?
Noise issues in a cardan joint can arise due to various factors such as misalignment, improper lubrication, wear, or imbalance. Addressing these noise issues requires a systematic approach to identify and rectify the underlying causes. Here’s a detailed explanation of the steps involved in addressing noise issues in a cardan joint:
- Inspection and Diagnosis: The first step is to visually inspect the cardan joint and surrounding components to identify any visible signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Additionally, examining the joint during operation can help pinpoint the source of the noise. Noise can originate from the joint itself, the connected components, or the supporting structure.
- Misalignment Correction: Misalignment is a common cause of noise in cardan joints. If misalignment is detected, it is essential to correct it by adjusting the alignment of the joint and the connected components. This may involve realigning the shafts or adjusting the mounting positions to ensure proper alignment. Precision alignment techniques should be employed to minimize misalignment and reduce noise.
- Lubrication Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction and noise in a cardan joint. Inadequate lubrication or using incorrect lubricants can lead to increased friction, wear, and noise. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding lubrication intervals and use lubricants specifically designed for cardan joints. Regular lubrication maintenance should be carried out to ensure optimal lubrication and minimize noise generation.
- Wear Assessment and Replacement: Wear of the joint components, such as bearings or bushings, can contribute to noise issues. If wear is detected during the inspection, it is necessary to assess the extent of wear and determine if component replacement is required. Worn-out components should be replaced with new ones of appropriate quality and specifications to restore proper functionality and reduce noise.
- Balancing: Imbalance in the rotating components of the cardan joint, such as the driveshaft, can result in noise and vibrations. Balancing the rotating parts can help minimize these issues. Dynamic balancing techniques, either during manufacturing or through precision balancing procedures, can be employed to achieve smoother operation and reduce noise levels.
- Noise Dampening Measures: In some cases, additional noise dampening measures may be necessary to address persistent noise issues. This can involve the use of vibration-dampening materials, such as rubber bushings or vibration isolators, at the connection points of the joint. These measures help absorb and dampen vibrations, reducing noise transmission to the surrounding structure.
By systematically addressing these factors, it is possible to mitigate noise issues in a cardan joint. It is important to consider the specific conditions and requirements of the application and consult with experts or the manufacturer if needed to ensure appropriate corrective actions are taken.

Can cardan joints be used in pumps and compressors?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in pumps and compressors to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between the driving and driven shafts. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for these applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Torque Transmission: Pumps and compressors often require the transmission of torque from the driving motor or engine to the rotating shaft that operates the pump or compressor. Cardan joints excel at transmitting torque efficiently, even at significant angles and misalignments. They can handle the high torque loads typically encountered in pump and compressor applications.
2. Misalignment Compensation: Cardan joints are designed to accommodate misalignments between the driving and driven shafts. In pumps and compressors, misalignments can occur due to factors such as thermal expansion, structural deflection, or assembly tolerances. Cardan joints can compensate for these misalignments, ensuring smooth and reliable torque transmission without excessive stress or wear on the connected components.
3. Angular Flexibility: Pumps and compressors often require flexibility in their drivetrain to adapt to different installation configurations or accommodate dynamic movements. Cardan joints provide rotational freedom and allow for angular movement, enabling the pump or compressor to adjust to changing requirements. Their universal joint design allows for smooth rotation and accommodates the required range of motion.
4. Shock and Vibration Absorption: Pumps and compressors can generate significant vibrations and shocks during operation. Cardan joints help absorb these vibrations and shocks, reducing their transmission to the rest of the drivetrain. This feature helps protect other components, such as bearings and seals, from excessive stress and wear, enhancing the overall reliability and lifespan of the pump or compressor.
5. Compact Design: Cardan joints have a relatively compact design, making them suitable for integration into pump and compressor systems where space is often limited. Their compact size allows for efficient packaging within the equipment, optimizing overall design and minimizing footprint. This is especially beneficial in applications where multiple joints are required within a confined space.
6. Durability and Strength: Pumps and compressors operate under demanding conditions, including high pressures, heavy loads, and continuous operation. Cardan joints are often constructed using durable materials such as alloy steels or high-strength alloys, providing the necessary strength and resilience to withstand these conditions. They are designed to handle the demanding loads and forces encountered in pump and compressor applications.
7. Easy Maintenance and Serviceability: Cardan joints are generally low-maintenance components. They require periodic inspection, lubrication, and replacement of worn parts, but their design often allows for easy access and replacement if needed. This facilitates maintenance activities and minimizes downtime in pump and compressor systems.
8. Cost-Effectiveness: Cardan joints offer a cost-effective solution for torque transmission in pump and compressor applications. Their durability, reliability, and long service life contribute to reduced maintenance and replacement costs. Additionally, their ability to accommodate misalignments helps minimize wear on other drivetrain components, further reducing overall maintenance expenses.
When integrating cardan joints into pump and compressor systems, it is important to consider the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and load characteristics. Proper design, selection, and installation practices should be followed to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Consulting with engineers or experts specializing in drivetrain systems and pump/compressor design can provide valuable insights and guidance on the selection, integration, and maintenance of cardan joints for these applications.

How is a cardan joint different from other types of universal joints?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, is a specific type of universal joint design. While there are different variations of universal joints, the cardan joint has distinct characteristics that set it apart from other types. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a cardan joint differs from other universal joints:
1. Design and Structure: The cardan joint consists of two yokes and a cross-shaped member called the cross or spider. The yokes are typically fork-shaped and attached to the shafts, while the cross sits in the center, connecting the yokes. In contrast, other types of universal joints, such as the constant-velocity (CV) joint or Rzeppa joint, have different designs and structures. CV joints often use a combination of bearings and balls to transmit motion and maintain constant velocity, making them suitable for applications requiring smooth rotation without speed fluctuations.
2. Misalignment Compensation: One of the primary functions of a cardan joint is to accommodate misalignment between shafts. It can handle angular misalignment, axial misalignment, or a combination of both. The design of the cardan joint allows for the tilting of the cross as the input and output shafts rotate at different speeds. This tilting action compensates for misalignment and allows the joint to transmit motion. Other types of universal joints, such as the Oldham coupling or Hooke’s joint, have different mechanisms for compensating misalignment. For example, the Oldham coupling uses sliding slots and intermediate disks to accommodate misalignment, while Hooke’s joint uses a combination of rotating links and flexible connections.
3. Operating Range: Cardan joints are commonly used in applications where a wide range of operating angles is required. They can effectively transmit motion and torque at various angles, making them suitable for applications with non-collinear shafts. Other types of universal joints may have specific limitations or operating ranges. For instance, some types of CV joints are designed for constant velocity applications and are optimized for specific operating angles or speed ranges.
4. Applications: Cardan joints find applications in various industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, and more. They are commonly used in drivetrain systems, power transmission systems, and applications that require flexibility, misalignment compensation, and reliable motion transmission. Other types of universal joints have their own specific applications. For example, CV joints are commonly used in automotive applications, particularly in front-wheel drive systems, where they provide smooth and constant power transmission while accommodating suspension movements.
5. Limitations: While cardan joints offer flexibility and misalignment compensation, they also have certain limitations. At extreme operating angles, cardan joints can introduce non-uniform motion, increased vibration, backlash, and potential loss of efficiency. Other types of universal joints may have their own limitations and considerations depending on their specific design and application requirements.
In summary, a cardan joint, or universal joint, is a specific type of universal joint design that can accommodate misalignment between shafts and transmit motion at various angles. Its structure, misalignment compensation mechanism, operating range, and applications differentiate it from other types of universal joints. Understanding these distinctions is crucial when selecting the appropriate joint for a specific application.


editor by CX 2024-04-15