Product Description
We are supply the Atlas drive shafts and components, u-joints and prop-shafts and spider and assembly, pleaes contact us if you have any need.
| Atlas PN |
| 5580014149 |
| 5541171300 |
| 6060001268 |
| 5535437300 |
| 5535542400 |
| 3050138000 |
| 3 0571 11000 |
| 3 0571 16000 |
| 3 0571 1571 |
| 3 0571 100 |
| 3 0571 1000 |
| 5728257142 |
| 2657227787 |
| 5535721000 |
| 5535720800 |
| /5541171300 |
| 5535720900 |
| 5535542400 |
| 5728257141 |
| 5541352200 |
| 5112315711 |
| 5540809400 |
| 5112310920 |
| 5112239684 |
| 571704007 |
| 5535720900 |
| 5590018143 |
| 5534200300 |
| 5537673500 |
| 5537597100 |
| 55905712 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | One Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | One Year |
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Natural Color |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Structure: | Single |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are cardan joints suitable for both high-torque and high-speed applications?
Cardan joints can be used in a variety of applications, but their suitability for high-torque and high-speed applications depends on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation of the considerations regarding the use of cardan joints in such scenarios:
1. High-Torque Applications: Cardan joints are generally well-suited for high-torque applications. The design of the joint allows for the transmission of significant torque between misaligned shafts. However, it is important to consider the specific torque requirements and operating conditions. Factors such as the size and type of the joint, the material used, and the application’s torque demands should be taken into account. In extremely high-torque applications, alternative coupling mechanisms such as gear couplings or universal joints may be more appropriate.
2. High-Speed Applications: While cardan joints can operate at relatively high speeds, there are some limitations to consider. At high rotational speeds, cardan joints can experience increased vibration, imbalance, and potential for fatigue failure. The rotating components of the joint can generate centrifugal forces, which can impact the balance and stability of the system. To mitigate these issues, careful design considerations, including balancing and vibration analysis, may be necessary. In some cases, alternative coupling mechanisms like flexible couplings or constant velocity joints may be better suited for high-speed applications.
3. Balancing and Vibration Control: Balancing the rotating components, such as the driveshaft and the joint itself, is essential for minimizing vibration issues in high-torque and high-speed applications. Imbalance can lead to increased vibrations, reduced efficiency, and potential damage to the joint and other system components. Proper balancing techniques, including dynamic balancing during manufacturing or precision balancing during installation, can help achieve smoother operation and minimize vibration problems.
4. Material Selection: The material used in the construction of the cardan joint plays a crucial role in its suitability for high-torque and high-speed applications. High-strength materials, such as alloy steels, are often preferred for their ability to handle increased torque loads. Additionally, materials with good fatigue resistance and high-speed capabilities can help ensure the durability and reliability of the joint in demanding applications.
5. Application-Specific Factors: The suitability of cardan joints for high-torque and high-speed applications also depends on the specific requirements and operating conditions of the application. Factors such as load characteristics, duty cycles, temperature, and environmental conditions should be considered. It is important to consult with the manufacturer or engineering experts to determine the appropriate size, type, and configuration of the cardan joint for a particular high-torque or high-speed application.
In summary, cardan joints can be suitable for both high-torque and high-speed applications, but careful consideration of factors such as torque requirements, speed limitations, balancing, material selection, and application-specific conditions is necessary. Evaluating these factors and consulting with experts can help determine the optimal coupling solution for a given high-torque or high-speed application.

How do you properly maintain and lubricate a cardan joint?
Proper maintenance and lubrication are essential for ensuring the optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of a cardan joint. Regular maintenance helps prevent premature wear, reduce friction, and minimize the risk of component failure. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to properly maintain and lubricate a cardan joint:
- Refer to Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and documentation specific to the cardan joint being used. The manufacturer provides valuable information regarding recommended maintenance intervals, lubrication procedures, and compatible lubricants.
- Cleanliness: Before lubricating a cardan joint, ensure that the joint and its surrounding area are clean and free from dirt, debris, or contaminants. Use appropriate cleaning methods, such as wiping or brushing, to remove any buildup that could hinder proper lubrication.
- Lubrication Points: Identify the lubrication points on the cardan joint. These are typically located at the bearings or bushings where the joint pivots. Refer to the manufacturer’s documentation to determine the specific lubrication points and their recommended lubrication intervals.
- Selection of Lubricant: Select a lubricant that is recommended by the manufacturer and suitable for the operating conditions of the cardan joint. Consider factors such as temperature, load, speed, and environmental conditions when choosing the lubricant. Commonly used lubricants for cardan joints include grease or oil with appropriate viscosity and additives.
- Applying Grease: If using grease, apply a sufficient amount to the lubrication points. Use a grease gun or other suitable lubrication equipment to deliver the grease accurately. Ensure that the grease reaches the bearings or bushings, allowing it to coat the surfaces evenly.
- Applying Oil: If using oil, carefully apply a few drops to each lubrication point. Use a precision oiler or other suitable dispensing method to avoid over-lubrication. The oil should be applied in a controlled manner to prevent excess oil from dripping or spreading to unwanted areas.
- Distribution and Spread: After applying the lubricant, operate the cardan joint through its full range of motion several times. This helps distribute the lubricant evenly and ensures proper coverage of the joint’s surfaces. The motion of the joint helps the lubricant penetrate and adhere to the bearing surfaces, reducing friction and wear.
- Excess Lubricant: Remove any excess lubricant that may have accumulated around the lubrication points or other areas of the joint. Excess lubricant can attract dirt, debris, or contaminants, which can contribute to accelerated wear or hinder the joint’s operation.
- Regular Inspection: Implement a regular inspection schedule for the cardan joint. Periodically check the lubrication points for signs of excessive wear, contamination, or insufficient lubrication. Inspect for leaks, damaged seals, or any other issues that could affect the joint’s performance. Address any problems promptly to prevent further damage or failure.
- Maintenance Records: Maintain proper documentation of the maintenance activities performed on the cardan joint. This includes the dates of lubrication, the type of lubricant used, and any observations or issues noted during inspections. Keeping records helps track maintenance history and facilitates timely maintenance planning and troubleshooting.
It’s important to note that the specific maintenance and lubrication requirements may vary depending on the type, design, and application of the cardan joint. Therefore, always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the particular cardan joint being used, as they provide the most accurate and relevant information for proper maintenance and lubrication.

How do you maintain and service a cardan joint?
Maintaining and servicing a cardan joint is important to ensure its optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. Regular maintenance helps prevent premature wear, address potential issues, and prolong the life of the joint. Here’s a detailed explanation of the maintenance and servicing procedures for a cardan joint:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the cardan joint for any visible signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. Look for cracks, corrosion, loose or missing fasteners, worn bearings, or any abnormalities in the joint components. If any issues are identified, they should be addressed promptly.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation of a cardan joint. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding lubrication type, frequency, quantity, and method. Regularly apply the appropriate lubricant to the designated lubrication points or zerk fittings. Monitor the condition of the lubricant and replenish it as needed to maintain optimal lubrication levels.
- Torque Check: Periodically check the torque of the fasteners that secure the cardan joint and yokes. Over time, vibration and operational stresses can cause fasteners to loosen. Ensure that all fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specified torque values. Be cautious not to overtighten, as it can lead to component damage or failure.
- Alignment Verification: Verify the alignment of the connected shafts that are linked by the cardan joint. Misalignment can cause increased stress and wear on the joint components. Check for any angular misalignment or axial misalignment and make necessary adjustments to minimize misalignment within acceptable tolerances.
- Load and Operating Condition Evaluation: Regularly evaluate the load and operating conditions in which the cardan joint operates. Ensure that the joint is not subjected to excessive loads, speeds, or harsh operating environments beyond its design capabilities. If there are any changes in the operating conditions, consider consulting the manufacturer or an expert to assess the suitability of the cardan joint and make any necessary modifications or replacements.
- Vibration Monitoring: Monitor the vibration levels during operation, as excessive vibration can indicate issues with the cardan joint or the overall system. An increase in vibration may suggest misalignment, worn bearings, or other mechanical problems. If significant vibration is detected, further investigation and corrective actions should be undertaken to address the root cause.
- Periodic Disassembly and Inspection: Depending on the manufacturer’s recommendations and the operating conditions, periodic disassembly and inspection of the cardan joint may be required. This allows for a more thorough assessment of the joint’s condition, including the bearings, seals, and other internal components. Any worn or damaged parts should be replaced with genuine manufacturer-approved replacements.
- Professional Maintenance: In some cases, it may be necessary to engage the services of a professional maintenance technician or a specialized service provider for more comprehensive maintenance or servicing of the cardan joint. They can perform advanced inspections, alignment checks, bearing replacements, or other specialized procedures to ensure the optimal performance of the joint.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance and servicing of the specific cardan joint model. Adhering to proper maintenance practices and promptly addressing any issues that arise will help maximize the service life, reliability, and performance of the cardan joint.


editor by CX 2024-05-15
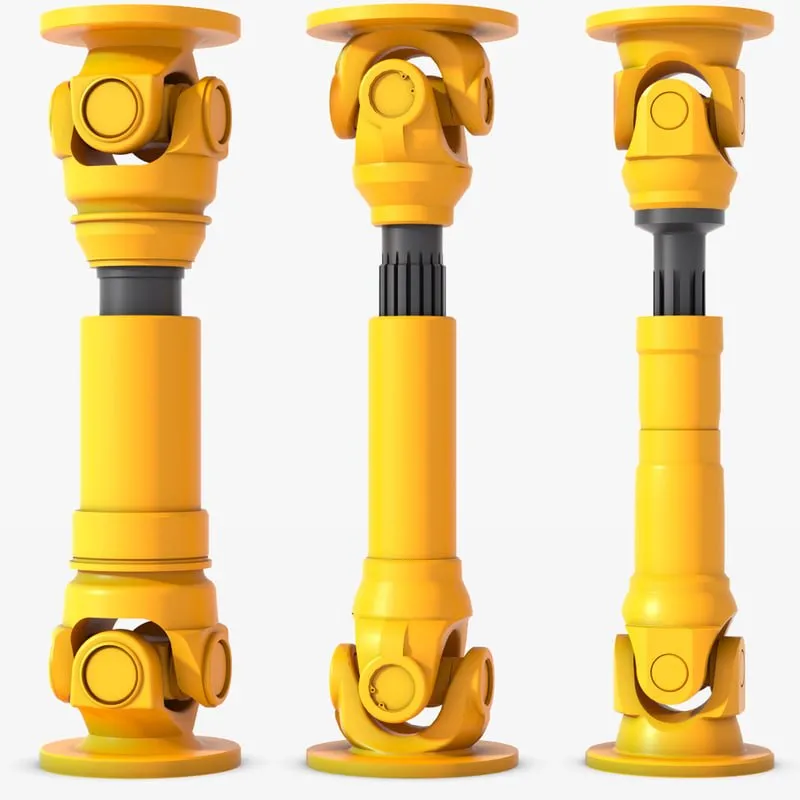
China Custom High Quality Long Nontelescopic Cardan Shaft Swp-D Type Universal Coupling Universal Joints
Product Description
High quality Long Nontelescopic Cardan Shaft SWP-D Type Universal Coupling Universal joints
Description:
The SWP-D long non bending universal joint coupling is a universal joint designed specifically for applications with long distances between 2 shafts. It is a double joint universal joint, which means it can work at an angle of 90 degrees. The “long” CHINAMFG indicates that the main body of the joint is longer than the standard SWP-D universal coupling, which allows it to adapt to more bending in the transmission system. The ‘no flexibility’ CHINAMFG indicates that the joint does not have a flexible coupling, which makes it harder and less susceptible to vibration. SWP-D long flexible universal joint couplings are commonly used in agricultural, construction, and mining equipment. It is also used in some automotive applications, such as transmission shafts and transfer boxes. The following are some characteristics of the SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling: Double joint design, with a working angle of up to 90 degrees Extending the body to make the powertrain system more flexible No flexible coupling, with rigidity and vibration resistance Used in agriculture, construction, mining, and automotive applications
Advantages:
The SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling has many advantages, including: 1. Can adapt to long distances between 2 shafts: The long body of the joint allows SWP-D to be long without flexible universal joint couplings, in order to adapt to more flexibility in the transmission system, which is very important for applications where 2 shafts are far apart. 2. Operable at angles up to 90 degrees: The double joint design of the SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling allows it to operate at angles up to 90%, which is crucial for applications where 2 shafts are misaligned. 3. More rigid and less susceptible to vibration: SWP-D lacks flexible couplings, and the long-term absence of flexible universal joint couplings makes it more rigid and less susceptible to vibration. This is very important for applications where the transmission system is subjected to high vibration loads. 4. Durability and Durability: The SWP-D long non bending universal joint coupling is made of high-quality materials and designed for durability and durability. 5. Reducing noise and vibration: The rigid design of the SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling helps to reduce noise and vibration in the transmission system. 6. Improving efficiency: The SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling helps to improve the efficiency of the transmission system by reducing power loss. 7. Improving safety: The SWP-D long flexible universal joint coupling helps to improve safety by reducing the risk of transmission system failures.
Paramters:
Packing & shipping:
1 Prevent from damage.
2. As customers’ requirements, in perfect condition.
3. Delivery : As per contract delivery on time
4. Shipping : As per client request. We can accept CIF, Door to Door etc. or client authorized agent we supply all the necessary assistant.
FAQ:
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks in PDF or AI format.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 5: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 6: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 19-32 |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 19mm |
| Speed: | 4000r/M |
| Structure: | Rigid |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
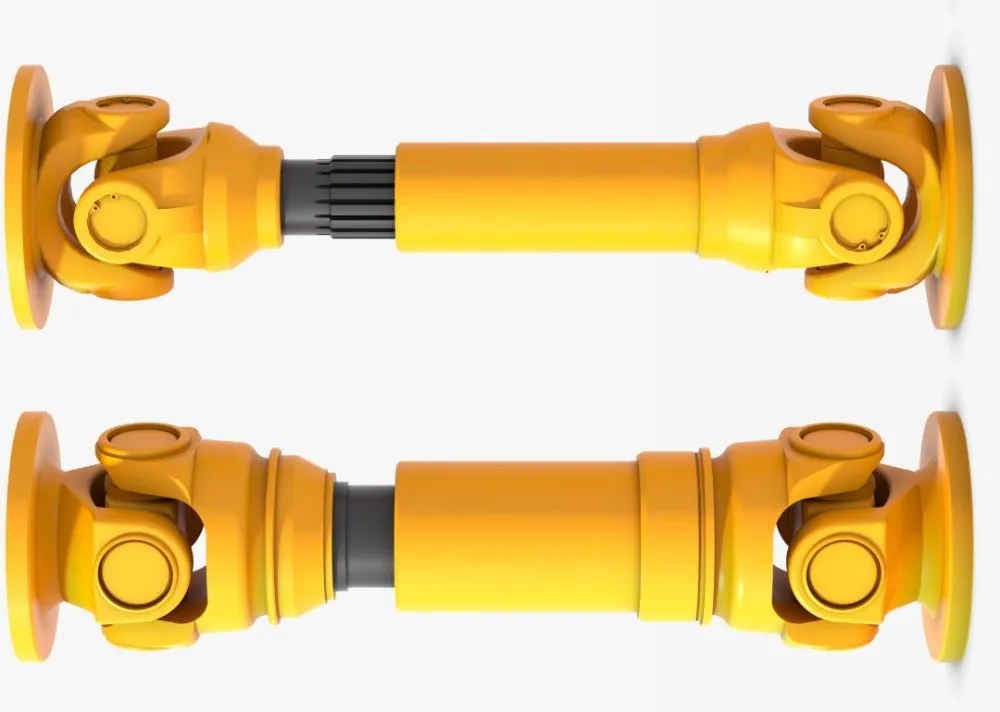
Can cardan joints be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment. Cardan joints, also known as universal joints, are versatile mechanical couplings that transmit torque between misaligned shafts. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of why cardan joints can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment:
- Torque Transmission: Cardan joints are capable of transmitting high levels of torque between misaligned shafts. This makes them well-suited for heavy-duty applications that require the transfer of substantial power. The design of the joint allows for smooth torque transmission, even in cases where the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
- Misalignment Compensation: In heavy-duty machinery and equipment, misalignments between shafts can occur due to factors such as thermal expansion, vibration, or structural flexing. Cardan joints excel at compensating for such misalignments. Their flexible design accommodates angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, allowing for reliable operation in challenging industrial environments.
- Durability and Strength: Heavy-duty machinery and equipment often operate under demanding conditions, subjecting components to high loads and harsh environments. Cardan joints are typically constructed from durable materials such as alloy steels, which provide excellent strength and resistance to fatigue and wear. This durability enables them to withstand the heavy loads and prolonged operation associated with heavy-duty applications.
- Compact Design: Cardan joints have a compact design, which is advantageous in heavy-duty machinery and equipment where space constraints may be present. Their compactness allows for efficient installation and integration within the system, making them suitable for applications where minimizing size and weight is important.
- Versatility: Cardan joints are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different heavy-duty applications. They can be customized to meet specific torque and speed requirements, making them versatile for use in a wide range of machinery and equipment, including industrial machinery, construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and more.
While cardan joints are generally suitable for heavy-duty applications, it is important to consider certain factors to ensure optimal performance. These factors include proper selection of the joint size and type based on the application requirements, adherence to specified torque and speed limits, regular maintenance to prevent wear and ensure proper lubrication, and consideration of any environmental factors that may affect the joint’s performance.
In summary, cardan joints can indeed be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment due to their excellent torque transmission capabilities, ability to compensate for misalignments, durability, compact design, and versatility. By considering the specific requirements of the application and following appropriate maintenance practices, cardan joints can provide reliable and efficient operation in heavy-duty industrial settings.

How do you calculate the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly?
Calculating the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly involves evaluating the power loss in the joint and comparing it to the input power. Efficiency is typically expressed as a percentage and provides an indication of how effectively the cardan joint transfers power from the input shaft to the output shaft. Here’s a detailed explanation:
To calculate the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly, follow these steps:
1. Measure Input Power: Determine the power being supplied to the cardan joint assembly. This can be measured using appropriate instruments such as a dynamometer or by utilizing the known power rating of the input source.
2. Measure Output Power: Measure the power being delivered by the output shaft of the cardan joint assembly. This can be done using a dynamometer or by utilizing the known power rating of the output device or load.
3. Calculate Power Loss: Calculate the power loss in the cardan joint assembly by subtracting the output power from the input power. The power loss represents the amount of power dissipated or wasted within the joint.
Power Loss = Input Power – Output Power
4. Calculate Efficiency: Divide the output power by the input power and multiply the result by 100 to obtain the efficiency as a percentage.
Efficiency = (Output Power / Input Power) * 100
The efficiency of the cardan joint assembly can be interpreted as the percentage of input power that is effectively transmitted to the output shaft. A higher efficiency indicates a more efficient power transfer, while a lower efficiency suggests a higher level of power loss within the joint.
It’s important to note that the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly can be influenced by various factors, including misalignments, lubrication conditions, wear, and operating speeds. Additionally, the efficiency may vary at different operating conditions and under varying loads. Therefore, it is advisable to perform efficiency calculations under representative operating conditions and consider the specific characteristics of the cardan joint assembly being analyzed.
By calculating the efficiency, engineers and designers can assess the performance of the cardan joint assembly, identify potential areas for improvement, and optimize the power transmission system for enhanced efficiency and overall effectiveness.

Are there different types of cardan joints available?
Yes, there are different types of cardan joints available to suit various applications and requirements. The design and configuration of a cardan joint can vary based on factors such as load capacity, torque transmission, operating conditions, and installation constraints. Here’s a detailed explanation of some commonly used types of cardan joints:
- Single Universal Joint: The single universal joint is the most basic and commonly used type of cardan joint. It consists of two yokes connected by a cross, forming a single joint. This type of cardan joint allows for angular misalignment between the input and output shafts. It is often used in applications where misalignment angles are relatively small, and flexibility is required.
- Double Cardan Joint: The double cardan joint, also known as a constant velocity joint (CV joint), is an enhanced version of the single universal joint. It consists of two single universal joints connected by an intermediate shaft. This configuration helps to cancel out the velocity fluctuations and torque variations that can occur with a single joint. Double cardan joints are commonly used in applications where smooth and constant power transmission is required, such as in front-wheel drive vehicles.
- Tractor Joint: A tractor joint is a specialized type of cardan joint used in agricultural machinery, particularly in power take-off (PTO) systems. It consists of three yokes connected by two crosses. The tractor joint allows for higher torque transmission and can accommodate larger misalignment angles. It is designed to handle the demanding conditions and heavy loads often encountered in agricultural applications.
- Ball-and-Socket Joint: The ball-and-socket joint, also known as a Hooke’s joint, is another variant of the cardan joint. It consists of a cross with a spherical ball at each end, which fits into a corresponding socket in the yokes. The ball-and-socket joint provides greater flexibility and can accommodate larger angles of misalignment. It is commonly used in applications where significant angular movement is required, such as steering systems in vehicles.
- Flexible Coupling: While not strictly a cardan joint, flexible couplings serve a similar purpose in accommodating misalignment. Flexible couplings are often used in applications where the misalignment is minimal and torque transmission is a primary concern. They utilize elastomeric or flexible elements to provide flexibility and compensate for small misalignments between shafts.
These are some of the commonly used types of cardan joints. Each type offers specific advantages and is suitable for different applications based on factors such as misalignment requirements, torque transmission, and operating conditions. The selection of the appropriate cardan joint type depends on the specific needs of the application and the desired performance characteristics.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China Custom Standard Steel Ccr or Private Label Cardan Shaft Constant Velocity Joint
Product Description
ABS Ring Included: No
Axle Nut Locking Type: Self Lock
Axle Nut Supplied: Yes
Compressed Length: 21 1/4″
CV Axles Inboard Spline Count: 26
Emission Code : 1
Inboard Joint Type: Female
Input Shaft Connection Style: Spline
Input Shaft Spline Count: 26
Interchange Part Number: , GM-8047, 179047, GM-6120, GM6120, 9456N
Label Description – 80: New Constant Velocity Drive Axle
Length Measurement Method: Compressed
Life Cycle Status Code: 2
Life Cycle Status Description: Available to Order
Maximum Cases per Pallet Layer: 10
MSDS Required Flag: N
National Popularity Code : B
National Popularity Description: Next 20% of Product Group Sales Value
New or Remanufactured: New
Nut Head Size: 36mm Hex Head
Nut Length: OAH 20.8mm
Nut Locking Type: Self Lock
Nut Thread Size: M24 x 2.0
Other Part Number: 815-5270, GM-8232, 80-1507, , 80571
Outboard Joint Type: Male
Outboard Spline Count: 27
Output Shaft Connection Style: Spline
Output Shaft Spline Count: 27
Overall Length: 21 1/4″
Pallet Layer Maximum: 6
Product Condition: New
Product Description – Invoice – 40: CV Drive Axle New
Product Description – Long – 80: CV Drive Axle – Domestic New
Product Description – Short – 20: CV Drive Axle
Remanufactured Part: N
Spindle Nut Hex Head Size: 36mm
Spindle Nut Included: Yes
Spindle Nut Thread Size: M24 x 2.0
Drive Shaft | PATRON : PDS1507
- Fitting Position: Front Axle Right
REF NO.
FactoryNumber
GSP208050
OE Number
MakeNumber
GMC93720063
MakeNumber
GMC
MakeNumber
CHINAMFG
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Available |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Certification: | DIN, ISO, ISO, DIN |
| Type: | C.V. Joint |
| Application Brand: | GM |
| Material: | Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do you address noise issues in a cardan joint?
Noise issues in a cardan joint can arise due to various factors such as misalignment, improper lubrication, wear, or imbalance. Addressing these noise issues requires a systematic approach to identify and rectify the underlying causes. Here’s a detailed explanation of the steps involved in addressing noise issues in a cardan joint:
- Inspection and Diagnosis: The first step is to visually inspect the cardan joint and surrounding components to identify any visible signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Additionally, examining the joint during operation can help pinpoint the source of the noise. Noise can originate from the joint itself, the connected components, or the supporting structure.
- Misalignment Correction: Misalignment is a common cause of noise in cardan joints. If misalignment is detected, it is essential to correct it by adjusting the alignment of the joint and the connected components. This may involve realigning the shafts or adjusting the mounting positions to ensure proper alignment. Precision alignment techniques should be employed to minimize misalignment and reduce noise.
- Lubrication Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction and noise in a cardan joint. Inadequate lubrication or using incorrect lubricants can lead to increased friction, wear, and noise. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding lubrication intervals and use lubricants specifically designed for cardan joints. Regular lubrication maintenance should be carried out to ensure optimal lubrication and minimize noise generation.
- Wear Assessment and Replacement: Wear of the joint components, such as bearings or bushings, can contribute to noise issues. If wear is detected during the inspection, it is necessary to assess the extent of wear and determine if component replacement is required. Worn-out components should be replaced with new ones of appropriate quality and specifications to restore proper functionality and reduce noise.
- Balancing: Imbalance in the rotating components of the cardan joint, such as the driveshaft, can result in noise and vibrations. Balancing the rotating parts can help minimize these issues. Dynamic balancing techniques, either during manufacturing or through precision balancing procedures, can be employed to achieve smoother operation and reduce noise levels.
- Noise Dampening Measures: In some cases, additional noise dampening measures may be necessary to address persistent noise issues. This can involve the use of vibration-dampening materials, such as rubber bushings or vibration isolators, at the connection points of the joint. These measures help absorb and dampen vibrations, reducing noise transmission to the surrounding structure.
By systematically addressing these factors, it is possible to mitigate noise issues in a cardan joint. It is important to consider the specific conditions and requirements of the application and consult with experts or the manufacturer if needed to ensure appropriate corrective actions are taken.
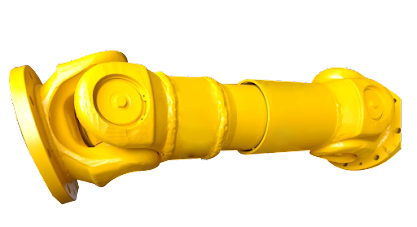
Can cardan joints be used in precision manufacturing equipment?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in precision manufacturing equipment under certain circumstances. However, their suitability depends on the specific requirements of the equipment and the level of precision needed. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Cardan joints are mechanical components that provide torque transmission and compensate for misalignment between rotating shafts. They consist of universal joints that allow for angular movement and accommodate misalignment. While cardan joints offer flexibility and are commonly used in various industrial applications, their use in precision manufacturing equipment may have limitations.
Precision manufacturing equipment typically requires high accuracy, repeatability, and minimal play or backlash in its mechanical components. Cardan joints, due to the nature of their design, introduce some degree of play or backlash, which can impact precision operations. The universal joints in cardan joints have inherent clearance, which can result in angular positioning errors and affect the overall precision of the equipment.
However, in certain applications where the level of precision required is not extremely high, cardan joints can still be utilized effectively. They can provide the necessary torque transmission and compensate for moderate misalignments while maintaining acceptable precision levels. Examples of precision manufacturing equipment where cardan joints may find application include rotary tables, indexing mechanisms, or non-critical assembly systems.
It’s important to note that when considering the use of cardan joints in precision manufacturing equipment, careful evaluation and analysis are necessary. Factors such as the magnitude of misalignment, required accuracy, operating speed, and load conditions should be taken into account. In some cases, additional measures such as incorporating backlash compensation mechanisms or using precision-aligned cardan joints may be necessary to mitigate the inherent play and improve precision.
Ultimately, the decision to use cardan joints in precision manufacturing equipment should be based on a thorough assessment of the specific application requirements, precision tolerances, and potential trade-offs between flexibility and precision. Consulting with engineers or experts specializing in precision mechanical systems can provide valuable insights and guidance in determining the suitability of cardan joints for a particular precision manufacturing application.

How do you choose the right size cardan joint for your application?
Choosing the right size cardan joint for your application is crucial to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. Several factors need to be considered when selecting the appropriate size of a cardan joint. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key considerations:
- Load Capacity: Determine the maximum load that the cardan joint will need to transmit. Consider both the torque (rotational force) and the axial load (thrust) that will be applied to the joint. The load capacity of the cardan joint should exceed the maximum expected loads in your application to ensure safe and reliable operation.
- Operating Speed: Consider the rotational speed at which the cardan joint will be operating. Higher speeds may require specific design considerations, such as balancing, lubrication, and material selection, to ensure smooth operation and avoid premature wear or failure. Verify that the selected cardan joint is rated for the intended operating speed range.
- Shaft Diameter: Measure the diameter of the input and output shafts that will be connected by the cardan joint. The cardan joint should have yokes and bearings that match the shaft diameter to ensure a proper fit and reliable power transmission. It is essential to consider both shaft diameters when selecting a cardan joint.
- Misalignment Angle: Determine the maximum expected misalignment angle between the input and output shafts. Different types of cardan joints have different capabilities to accommodate misalignment. Consider the angular misalignment and choose a cardan joint that can handle the required range of misalignment angles in your application.
- Environmental Factors: Evaluate the operating environment of the cardan joint. Consider factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, chemicals, and vibration. Choose a cardan joint that is suitable for the specific environmental conditions to ensure proper functioning and longevity.
- Service Life and Maintenance: Consider the expected service life of the cardan joint and the maintenance requirements. Some applications may require frequent maintenance or periodic lubrication of the joint. Evaluate the ease of maintenance and factor it into your selection process.
- Standards and Regulations: Depending on your industry or application, there may be specific standards or regulations that dictate the requirements for cardan joints. Ensure that the selected cardan joint complies with the relevant standards and regulations for your application.
It is advisable to consult with a knowledgeable supplier or engineer specializing in power transmission components to assist you in selecting the right size cardan joint for your specific application. They can consider all the relevant factors and provide guidance to ensure optimal performance and reliability of the cardan joint in your application.


editor by CX 2024-05-06
China Custom Full Range of Universal Joint for Cardan Shaft
Product Description
Universal joint description
1) Materials: 20Cr
2) Can develop according to customer’s drawings or samples
3) Full range of part number for the universal joint
4) OEM quality and reasonable price
How customer Saying:
Russia application:
| Item No. |
Part Number |
Weight(kg) |
SIZE |
|
1 |
5320-22 0571 1 |
2.5 |
50X135-1 |
|
2 |
4310-22 0571 1 |
3.2 |
50X155 |
|
3 |
53205-22 0571 1 |
3.2 |
50X155-1 |
|
4 |
53A-2257125 |
0.95 |
35X98 |
|
5 |
53A-2257125 no logo |
0.94 |
35X98 |
|
6 |
0.6 |
30X88(small needle) |
|
|
7 |
no logo |
0.6 |
30X88(small needle) |
|
8 |
0.6 |
30X55X88 |
|
|
9 |
0.25 |
23.8X61.2 |
|
|
10 |
0.42 |
28X71 |
|
|
11 |
5.49 |
62X173 |
|
|
12 |
6520-22 0571 1 |
4.2 |
57X152 |
|
13 |
0.2 |
UJR3302 19X44.6 |
|
|
14 |
2.6 |
50X135-3 |
|
|
15 |
1.43 |
39X118-1 |
|
|
16 |
1.43 |
39X118 |
|
|
17 |
no lubricator |
0.96 |
39X118 |
|
18 |
-01 with circlips |
1.1 |
39X118-1 |
|
19 |
5 |
2.6 |
50X135-2 |
|
20 |
4 |
8.3 |
72X185 |
|
22 |
131-22 0571 1 |
2.5 |
50X135 |
|
23 |
0.24 |
W23X61-1 |
|
|
24 |
0.51 |
UJ412(28X55X83) |
|
|
25 |
0.46 |
UJR5320(28X36X67) |
|
| 26 | -10 | 2.49 | 47.6X135 |
| 27 | 6340/ | 0.13 | 19X56 |
| 28 | 41-015-7205 | 3.3 | In stock now |
| 340–1 | 141-10-14160 | ||
| 144-10-12620 | -1 | 415-20-12620 | |
| 144-15–1 | 418-20-326-1 | 175-20-3-1 | |
| 145-14–1 | |||
| 14X-11-11110 | -1 | ||
| 150-11-00097 | 381-97-6907-1 | ||
| 150-11-12360 | 381-97-6908-1 |
More catalogue, please visit ourweb
Some Packing example:
About us:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Condition: | New |
|---|---|
| Color: | Silver |
| Certification: | ISO, Ts16949 |
| Structure: | Single |
| Material: | 20cr |
| Type: | 20crmnti |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can cardan joints be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment. Cardan joints, also known as universal joints, are versatile mechanical couplings that transmit torque between misaligned shafts. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of why cardan joints can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment:
- Torque Transmission: Cardan joints are capable of transmitting high levels of torque between misaligned shafts. This makes them well-suited for heavy-duty applications that require the transfer of substantial power. The design of the joint allows for smooth torque transmission, even in cases where the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
- Misalignment Compensation: In heavy-duty machinery and equipment, misalignments between shafts can occur due to factors such as thermal expansion, vibration, or structural flexing. Cardan joints excel at compensating for such misalignments. Their flexible design accommodates angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, allowing for reliable operation in challenging industrial environments.
- Durability and Strength: Heavy-duty machinery and equipment often operate under demanding conditions, subjecting components to high loads and harsh environments. Cardan joints are typically constructed from durable materials such as alloy steels, which provide excellent strength and resistance to fatigue and wear. This durability enables them to withstand the heavy loads and prolonged operation associated with heavy-duty applications.
- Compact Design: Cardan joints have a compact design, which is advantageous in heavy-duty machinery and equipment where space constraints may be present. Their compactness allows for efficient installation and integration within the system, making them suitable for applications where minimizing size and weight is important.
- Versatility: Cardan joints are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different heavy-duty applications. They can be customized to meet specific torque and speed requirements, making them versatile for use in a wide range of machinery and equipment, including industrial machinery, construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and more.
While cardan joints are generally suitable for heavy-duty applications, it is important to consider certain factors to ensure optimal performance. These factors include proper selection of the joint size and type based on the application requirements, adherence to specified torque and speed limits, regular maintenance to prevent wear and ensure proper lubrication, and consideration of any environmental factors that may affect the joint’s performance.
In summary, cardan joints can indeed be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment due to their excellent torque transmission capabilities, ability to compensate for misalignments, durability, compact design, and versatility. By considering the specific requirements of the application and following appropriate maintenance practices, cardan joints can provide reliable and efficient operation in heavy-duty industrial settings.

How do you calculate the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly?
Calculating the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly involves evaluating the power loss in the joint and comparing it to the input power. Efficiency is typically expressed as a percentage and provides an indication of how effectively the cardan joint transfers power from the input shaft to the output shaft. Here’s a detailed explanation:
To calculate the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly, follow these steps:
1. Measure Input Power: Determine the power being supplied to the cardan joint assembly. This can be measured using appropriate instruments such as a dynamometer or by utilizing the known power rating of the input source.
2. Measure Output Power: Measure the power being delivered by the output shaft of the cardan joint assembly. This can be done using a dynamometer or by utilizing the known power rating of the output device or load.
3. Calculate Power Loss: Calculate the power loss in the cardan joint assembly by subtracting the output power from the input power. The power loss represents the amount of power dissipated or wasted within the joint.
Power Loss = Input Power – Output Power
4. Calculate Efficiency: Divide the output power by the input power and multiply the result by 100 to obtain the efficiency as a percentage.
Efficiency = (Output Power / Input Power) * 100
The efficiency of the cardan joint assembly can be interpreted as the percentage of input power that is effectively transmitted to the output shaft. A higher efficiency indicates a more efficient power transfer, while a lower efficiency suggests a higher level of power loss within the joint.
It’s important to note that the efficiency of a cardan joint assembly can be influenced by various factors, including misalignments, lubrication conditions, wear, and operating speeds. Additionally, the efficiency may vary at different operating conditions and under varying loads. Therefore, it is advisable to perform efficiency calculations under representative operating conditions and consider the specific characteristics of the cardan joint assembly being analyzed.
By calculating the efficiency, engineers and designers can assess the performance of the cardan joint assembly, identify potential areas for improvement, and optimize the power transmission system for enhanced efficiency and overall effectiveness.

What are the applications of a cardan joint?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, has a wide range of applications across various industries. Its ability to transmit rotational motion and accommodate misalignment between shafts makes it suitable for different systems and machines. Here’s a detailed explanation of the applications of a cardan joint:
- Automotive Drivetrains: One of the primary applications of cardan joints is in automotive drivetrains. They are used in vehicles with rear-wheel drive, all-wheel drive, and four-wheel drive systems. Cardan joints help transmit power from the engine to the driveshaft, allowing the rotational motion to be transferred to the rear axle or all four wheels. They provide flexibility and compensation for misalignment between the engine, transmission, and rear differential.
- Industrial Machinery: Cardan joints find extensive use in various industrial machinery applications. They are commonly employed in power transmission systems, especially when there is a need to transmit rotational motion between non-collinear shafts. Cardan joints are used in conveyor systems, printing presses, machine tools, pumps, mixers, and many other industrial machines that require efficient transmission of rotational power.
- Aerospace and Aviation: Cardan joints have applications in the aerospace and aviation industries. They are used in aircraft control systems, such as the control linkages between the control surfaces (elevator, rudder, ailerons) and the cockpit controls. Cardan joints allow for the transmission of pilot input to the control surfaces while accommodating any misalignment or changes in angles during flight.
- Marine Propulsion: In marine applications, cardan joints are utilized in propulsion systems. They are commonly used in boat drivetrains to transfer rotational motion from the engine to the propeller shaft. Cardan joints enable the engine to be mounted at an angle or in a different position from the propeller shaft, compensating for the misalignment that can arise due to the boat’s hull shape and design.
- Railway Systems: Cardan joints play a role in railway systems, particularly in drivetrains and couplings. They are used in locomotives and train cars to transfer rotational motion between different components, such as the engine, gearbox, and wheel axle. Cardan joints provide flexibility and accommodate misalignment that may occur due to the movement and articulation of train cars on curved tracks.
- Mining and Construction Equipment: Cardan joints are employed in heavy-duty mining and construction equipment. They are used in applications such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and off-highway trucks. Cardan joints help transmit power and motion between different components of these machines, allowing them to operate efficiently and withstand the demanding conditions of mining and construction environments.
- Industrial Robotics: Cardan joints find applications in industrial robotics and automation. They are used in robotic arms and manipulators to transmit rotational motion between different segments or joints of the robotic system. Cardan joints enable precise and flexible movement, allowing robots to perform complex tasks in manufacturing, assembly, and other industrial processes.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of cardan joints. Their ability to handle misalignment, transmit rotational motion at varying angles, and provide flexibility make them a fundamental component in numerous systems and machines across industries.


editor by CX 2024-03-12
China Custom 38X101mm Universal Joint Cross Joint for Cardan Shaft
Product Description
Product Description
The cross joint is a widely utilized component in shafts that are responsible for transmitting rotary motion. It comprises a pair of hinges positioned in close proximity to each other, oriented at a precise 90° angle, and interconnected by means of a cross shaft. As a reputable manufacturer specializing in universal joints, we take pride in offering top-quality u-joints specifically designed for agricultural machinery. We extend a warm invitation to all customers to reach out to us and collaborate in establishing a mutually beneficial partnership.
Product Parameters:
Product Name: Budget-friendly universal joint cross bearing Joint Spider Kit
Keywords: Drive Shaft, Universal Joint Cardan Shaft, Propeller Shaft
Here is our advantages when compare to similar products from China:
1.Forged yokes make PTO shafts strong enough for usage and working;
2.Internal sizes standard to confirm installation smooth;
3.CE and ISO certificates to guarantee to quality of our goods;
4.Strong and professional package to confirm the good situation when you receive the goods.
Product Specifications
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
NingBo Hanon Technology Co.,ltd is a modern enterprise specilizing in the development,production,sales and services of Agricultural Parts like PTO shaft and Gearboxes. We adhere to the principle of ” High Quality, Customers’Satisfaction”, using advanced technology and equipments to ensure all the technical standards of transmission .We follow the principle of people first , trying our best to set up a pleasant surroundings and platform of performance for each employee. So everyone can be self-consciously active to join Hanon Machinery.
FAQ
1.WHAT’S THE PAYMENT TERM?
When we quote for you,we will confirm with you the way of transaction,FOB,CIFetc.<br> For mass production goods, you need to pay 30% deposit before producing and70% balance against copy of documents.The most common way is by T/T.
2.HOW TO DELIVER THE GOODS TO US?
Usually we will ship the goods to you by sea.
3.How long is your delivery time and shipment?
30-45days
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Cross Joint |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Pto Shaft |
| Material: | 20crmn /20crmnti |
| Power Source: | Pto Dirven Shaft |
| Weight: | 1.1-2.4kg |
| After-sales Service: | Online Support |
| Samples: |
US$ 20/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
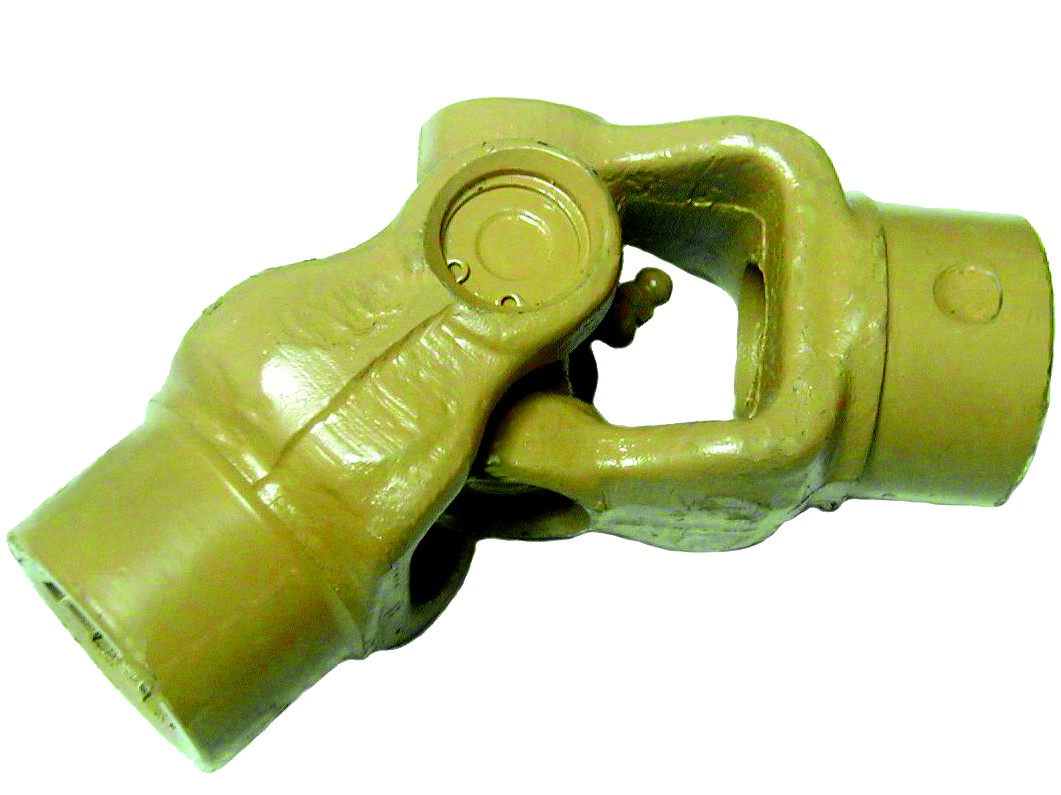

What are the potential limitations or drawbacks of using cardan joints?
While cardan joints offer numerous advantages in transmitting rotational motion between misaligned shafts, they also have certain limitations and drawbacks to consider. Here are some potential limitations associated with the use of cardan joints:
- Angular Limitations: Cardan joints have limited angularity or operating angles. They are designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and exceeding these angles can cause accelerated wear, increased vibration, and potential joint failure. Extreme operating angles can lead to binding, decreased efficiency, and reduced power transmission capacity. In applications where large operating angles are required, alternative flexible coupling mechanisms or constant velocity joints may be more suitable.
- Backlash and Torsional Stiffness: Cardan joints inherently exhibit some degree of backlash, which is the clearance or free play between the mating components. This can result in a slight delay in power transmission and can affect the precision of motion in certain applications. Additionally, cardan joints may have higher torsional stiffness compared to other coupling mechanisms, which can transmit higher vibrations and shocks to the connected components.
- Maintenance Requirements: Cardan joints require regular maintenance to ensure proper lubrication, alignment, and performance. The lubricant needs to be regularly replenished or replaced, and the joint should be inspected for wear, misalignment, or other issues. Failure to perform adequate maintenance can result in premature wear, reduced efficiency, and potential joint failure. Maintenance procedures may require specialized tools and expertise.
- Space and Weight: Cardan joints can occupy a significant amount of space due to their design and the need for perpendicular shafts. In applications with limited space constraints, finding suitable locations for cardan joints can be challenging. Additionally, the weight of cardan joints, especially in heavy-duty applications, can add to the overall weight of the system, which may have implications for fuel efficiency, payload capacity, or overall performance.
- Cost: Cardan joints, particularly high-quality and precision-engineered ones, can be relatively expensive compared to other coupling mechanisms. The complex design, manufacturing tolerances, and specialized materials involved contribute to their higher cost. In cost-sensitive applications, alternative coupling solutions may be considered if the angular limitations and other drawbacks of cardan joints are not critical.
- High-Speed Limitations: At high rotational speeds, cardan joints can experience increased vibration, imbalance, and potential for fatigue failure. The rotating components of the joint can generate centrifugal forces that impact the balance and stability of the system. In high-speed applications, careful design considerations, including balancing and vibration analysis, may be necessary to mitigate these issues.
It is important to evaluate the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and limitations when considering the use of cardan joints. While they offer versatility and flexibility in many scenarios, alternative coupling mechanisms may be more suitable in cases where the limitations and drawbacks of cardan joints pose significant challenges.

What are the key design considerations for optimizing cardan joint performance?
Optimizing the performance of a cardan joint requires careful design considerations that take into account various factors influencing its functionality, durability, and efficiency. By addressing these key design considerations, the performance of the cardan joint can be enhanced. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Mechanical Load and Torque Requirements: Understand the mechanical load and torque requirements of the application in which the cardan joint will be used. This includes analyzing the magnitude, direction, and variability of the loads and torques that the joint will experience. Properly selecting the cardan joint’s size, material, and configuration based on these requirements is crucial for optimizing its performance.
2. Operating Speed and Angular Misalignment: Consider the operating speed and the expected angular misalignment between the input and output shafts. The design of the cardan joint should accommodate the required speed range and angular movements while maintaining smooth operation and torque transmission. Balancing the joint’s ability to handle misalignments with its rotational capabilities is essential for optimizing performance.
3. Material Selection: Choose appropriate materials for the cardan joint components based on factors such as strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Consider the specific operating conditions, including temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals or contaminants. Selecting high-quality materials that can withstand the application’s demands is crucial for optimizing performance and longevity.
4. Critical Dimensions and Clearances: Pay attention to critical dimensions and clearances within the cardan joint design. These include the size and geometry of the joint’s components, as well as the clearances between them. Properly dimensioning these aspects ensures sufficient strength, flexibility, and clearance for smooth operation and efficient torque transmission.
5. Lubrication and Sealing: Implement effective lubrication and sealing mechanisms to minimize friction, wear, and the ingress of contaminants. Proper lubrication ensures smooth operation and reduces power losses due to friction. Sealing the joint against dust, moisture, and other environmental factors helps maintain its performance and extend its lifespan.
6. Bearing and Bushing Design: Consider the design and selection of bearings or bushings used within the cardan joint. These components play a crucial role in supporting the joint’s rotational movement and transferring torque. Proper bearing or bushing selection, based on load capacity, lubrication requirements, and expected lifespan, is essential for optimizing the joint’s performance and reducing wear.
7. Structural Integrity and Rigidity: Ensure that the cardan joint assembly is structurally sound and rigid. Adequate stiffness and strength prevent excessive deflection and deformation during operation, leading to improved torque transmission efficiency and reduced wear on the joint and connected components.
8. Manufacturability and Quality Control: Consider manufacturability aspects during the design phase to ensure that the cardan joint can be produced consistently and cost-effectively. Implement quality control measures to verify dimensional accuracy, material quality, and functional performance of the manufactured joints, ensuring that they meet the required specifications and performance criteria.
9. Environmental Factors: Take into account environmental factors such as temperature variations, humidity, presence of corrosive agents, or exposure to vibrations. Design the cardan joint to withstand these conditions and incorporate appropriate protective measures or materials to ensure long-term performance and reliability.
10. Maintenance and Serviceability: Consider ease of maintenance and serviceability when designing the cardan joint. Provide access to lubrication points, inspection areas, and potential wear points for efficient maintenance activities. Designing for easy disassembly and replacement of worn components can minimize downtime and extend the joint’s lifespan.
By carefully addressing these key design considerations, the performance of a cardan joint can be optimized, resulting in improved torque transmission, durability, and overall efficiency. It is important to evaluate the specific requirements of the application and consult with experienced engineers or designers specializing in drivetrain systems to ensure the best design practices are followed.

Can you explain the purpose of a cardan joint in a drive shaft?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, serves a crucial purpose in a drive shaft. The drive shaft is responsible for transmitting rotational motion and torque from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here’s a detailed explanation of the purpose of a cardan joint in a drive shaft:
A drive shaft is a mechanical component that connects the output of the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components of a vehicle or machinery. It is typically a tubular shaft that rotates at high speeds and transmits the torque generated by the engine to propel the vehicle or operate the machinery. The drive shaft needs to accommodate various factors, including changes in distance, misalignment, and different angles between the engine and the wheels or driven components.
This is where the cardan joint comes into play. The cardan joint is located at each end of the drive shaft, connecting it to the engine or power source and the wheels or driven components. The purpose of the cardan joint is to allow the drive shaft to transmit rotational motion and torque while accommodating the misalignment and changes in angles that occur between these components.
When the engine or power source rotates, it generates rotational motion and torque. The cardan joint at the engine end of the drive shaft receives this rotational motion and torque and transfers it to the drive shaft. As the drive shaft rotates, the cardan joint allows for the changes in angle and misalignment between the engine and the wheels or driven components. This flexibility of the cardan joint ensures that the drive shaft can operate smoothly and transmit power effectively, even when the components are not perfectly aligned or when there are variations in the angles.
At the other end of the drive shaft, another cardan joint is present to connect the drive shaft to the wheels or driven components. This cardan joint receives the rotational motion and torque from the drive shaft and transfers it to the wheels or driven components, allowing them to rotate and perform their intended functions.
The cardan joint in the drive shaft effectively compensates for misalignment, changes in angles, and variations in distance between the engine and the wheels or driven components. It ensures that the rotational motion and torque generated by the engine can be transmitted smoothly and efficiently to propel the vehicle or operate the machinery.
Overall, the purpose of the cardan joint in a drive shaft is to provide flexibility and accommodate misalignment, allowing for the effective transmission of rotational motion and torque between the engine or power source and the wheels or driven components.


editor by CX 2024-03-04
China Custom 20cr Material Automobile Cardan Cross Shaft Universal Joint Gun-48
Product Description
Product Deascription
Specification
| Brand | CSZBTR |
| Model No | GUN-48 |
| Material | stainless steel |
Other Models
| PARTA NO. | Dmm | Omm | Lmm |
| 19 | 44.6 | ||
| -06 | 23.84 | 61.3 | |
| 28 | 52.2 | 83 | |
| 28 | 37.2 | 68 | |
| -01 | 28 | 70.95 | |
| 28 | 70.95 | ||
| 28 | 42.5 | 73 | |
| 28 | 70.95 | ||
| 3 | 30 | 88 | |
| 53A-2257125-10 | 35 | 98 | |
| A | 39 | 118 | |
| 39 | 118 | ||
| A-1 | 39 | 118 | |
| 50 | 135 | ||
| 255B-2257125 | 50 | 155 | |
| 50 | 155 | ||
| 53205-22 0571 1 | 50 | 155 | |
| 5 | 50 | 135 | |
| 33541 | 62 | 173 | |
| 62 | 173 | ||
| 65641 | 72 | 185 |
| Part No. | D mm | L mm | Spicer |
| 5-263X | 34.9 | 126.2 | 5-263X |
| 5-275X | 34.9 | 126.2 | 5-275X |
| 5-2X | 23.8 | 61.2 | 5-2X |
| 5-31000X | 22 | 55 | 5-31000X |
| 5-310X | 27 | 61.9 | 5-310X |
| 5-316X | 65.1 | 144.4 | 5-316X |
| 5-32000X | 23.82 | 61.2 | 5-32000X |
| 5-33000X | 27 | 74.6 | 5-33000X |
| 5-3400X | 32 | 76 | 5-3400X |
| 5-35000X | 36 | 89 | 5-35000X |
| 5-431X | 33.3 | 67.4 | 5-431X |
| 5-443X | 27 | 61.9 | 5-443X |
| 5-4X | 27.01 | 74.6 | 5-4X |
| GU1000 | 27 | 81.7 | 5-153X |
| GU1100 | 27 | 74.6 | 5-4X |
| PARTA NO. | Dmm | Omm | Lmm |
| GUN-25 | 32 | 64 | |
| GUN-26 | 23. 82 | 64 | 61.3 |
| GUN-27 | 25 | 40 | |
| GUN-28 | 20. 01 | 35 | 57 |
| GUN-29 | 28 | 53 | |
| GUN-30 | 30. 188 | 92.08 | |
| GUN-31 | 32 | 107 | |
| GUN-32 | 35.5 | 119.2 | |
| GUN-33 | 43 | 128 | |
| GUN-34 | 25 | 52 | |
| GUN-36 | 25 | 77.6 | |
| GUN-38 | 26 | 45.6 | |
| GUN-41 | 43 | 136 | |
| GUN-43 | 55.1 | 163.8 | |
| GUN-44 | 20.5 | 56.6 | |
| GUN-45 | 20.7 | 52.4 | |
| GUN-46 | 27 | 46 | |
| GUN-47 | 27 | 71.75 | |
| GUN-48 | 27 | 81.75 |
Application
Company Profile
HangZhou Terry Machinery Co.Ltd is a leading supplier of bearings, linear motion
system for CNC,ball transfer unit and transmission component. The growing industrial and
favorable policy of HangZhoubenefit the development of Terry Machinery.Our products are
utilized in industrial, motorcycle, vehicleand Automation applications. Now we are exporting
to 46 countries includingUSA, GBR, Germany, Spain,Poland, Turkey ect. The goal of Terry
Machinery to provide out customers with widest range of productsatcompetitive prices, backed
with the best Service.
Packing & Deliverey
Custome Praise
FAQ
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 24 Hours Online Answering |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Condition: | New |
| Samples: |
US$ 2/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you prevent premature wear in a universal joint?
Preventing premature wear in a universal joint is crucial for maintaining its performance, longevity, and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Several measures can be taken to prevent premature wear in a universal joint:
- Proper Lubrication: Adequate lubrication is essential for reducing friction, dissipating heat, and preventing premature wear in a universal joint. Regularly lubricating the joint with the recommended lubricant, such as grease or oil, helps to create a protective film between the moving parts, minimizing frictional losses and preventing metal-to-metal contact.
- Correct Alignment: Misalignment is a common cause of premature wear in a universal joint. Ensuring proper alignment between the shafts connected by the joint is crucial to distribute the load evenly and prevent excessive stress on the joint’s components. Misalignment can be minimized by using precision alignment techniques and checking the operating angles specified by the manufacturer.
- Appropriate Operating Angles: Universal joints have specified operating angles within which they can operate optimally. Operating the joint beyond these recommended angles can lead to increased wear and reduced lifespan. It is important to adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding the maximum allowable operating angles to prevent premature wear.
- Regular Maintenance: Implementing a regular maintenance schedule can help identify and address potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. Routine inspections of the universal joint, including checking for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage, can help detect any issues early on and allow for timely repairs or replacements.
- Proper Torque Capacity: Selecting a universal joint with an appropriate torque capacity for the specific application is essential for preventing premature wear. If the joint is subjected to torque levels exceeding its capacity, it can lead to excessive stress, deformation, and wear on the components. Ensuring that the selected joint can handle the expected loads and operating conditions is crucial.
- Quality Components: Using high-quality universal joint components, such as yokes, cross bearings, and needle bearings, can significantly contribute to preventing premature wear. Components made from durable materials with excellent strength and wear resistance properties are more likely to withstand the demanding conditions and provide longer service life.
- Avoiding Overloading: Overloading a universal joint beyond its rated capacity can lead to accelerated wear and failure. It is important to operate the joint within its specified load limits and avoid subjecting it to excessive torque or radial loads. Understanding the application requirements and ensuring that the joint is appropriately sized and rated for the intended load is crucial.
By following these preventive measures, it is possible to minimize premature wear in a universal joint, enhance its durability, and prolong its operational life. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, correct alignment, and adherence to operating guidelines are key to ensuring optimal performance and preventing premature wear in universal joints.
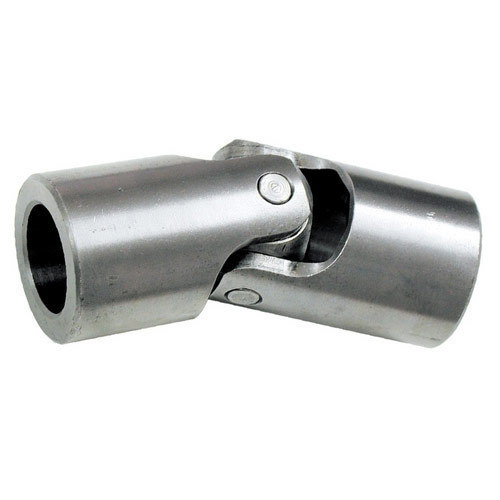

Can universal joints be used in agricultural equipment?
Yes, universal joints can be used in agricultural equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Universal joints are commonly employed in various types of agricultural equipment and machinery. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for agricultural applications. Here are some key points to consider:
- Torque Transmission: Agricultural equipment often requires the transmission of high torque levels to perform tasks such as plowing, tilling, harvesting, or powering other implements. Universal joints are capable of transmitting significant amounts of torque, making them suitable for handling the power requirements of agricultural machinery.
- Flexibility: Agricultural equipment frequently operates in uneven terrain or encounters obstacles that can cause angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. Universal joints can accommodate such misalignment and transmit torque even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned. This flexibility allows agricultural machinery to navigate uneven surfaces and maintain power transfer.
- Durability: Universal joints can be constructed from materials that provide high strength and durability, such as alloy steels. Agricultural equipment often operates in demanding conditions, including exposure to dust, moisture, and vibrations. Robust universal joints can withstand these harsh environments and repetitive motions, ensuring reliable performance and longevity.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Universal joints offer a cost-effective solution for torque transmission in agricultural equipment. Compared to alternative power transmission methods, such as complex gear systems or hydraulic drives, universal joints can provide a more economical option while still delivering adequate performance and reliability.
- Wide Application Range: Universal joints can be used in various agricultural equipment, including tractors, combine harvesters, balers, seeders, sprayers, and more. They are versatile components that can be integrated into different systems and configurations, allowing for efficient power transmission in a wide range of agricultural applications.
It’s important to note that the specific design and selection of universal joints for agricultural equipment should consider factors such as the torque requirements, operating conditions, maintenance practices, and safety considerations. Proper sizing, lubrication, and regular inspections are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and preventing premature wear or failure.
In summary, universal joints can indeed be used in agricultural equipment. Their torque transmission capabilities, flexibility, durability, cost-effectiveness, and versatility make them a suitable choice for power transmission in various agricultural machinery and equipment.

Can you provide examples of vehicles that use universal joints?
Universal joints are commonly used in various types of vehicles for transmitting torque between shafts that are not in a straight line or are at an angle to each other. Here are some examples of vehicles that use universal joints:
- Automobiles: Universal joints are widely used in automobiles for transmitting torque from the engine to the rear wheels in rear-wheel drive vehicles. They are commonly found in the driveline, connecting the transmission or gearbox to the driveshaft, and in the driveshaft itself. Universal joints are also used in front-wheel drive vehicles for transmitting torque from the transaxle to the front wheels.
- Trucks and commercial vehicles: Universal joints are utilized in trucks and commercial vehicles for transmitting torque between various components of the drivetrain. They can be found in the driveshaft, connecting the transmission or gearbox to the rear differential or axle assembly.
- Off-road vehicles and SUVs: Universal joints are extensively used in off-road vehicles and SUVs that have four-wheel drive or all-wheel drive systems. They are employed in the driveline to transmit torque from the transmission or transfer case to the front and rear differentials or axle assemblies.
- Military vehicles: Universal joints are utilized in military vehicles for transmitting torque between different components of the drivetrain, similar to their use in trucks and off-road vehicles. They provide reliable torque transfer in demanding off-road and rugged environments.
- Agricultural and construction machinery: Universal joints are commonly found in agricultural and construction machinery, such as tractors, combines, excavators, loaders, and other heavy equipment. They are used in the drivelines and power take-off (PTO) shafts to transmit torque from the engine or motor to various components, attachments, or implements.
- Marine vessels: Universal joints are employed in marine vessels for transmitting torque between the engine and the propeller shaft. They are used in various types of watercraft, including boats, yachts, ships, and other marine vessels.
- Aircraft: Universal joints are utilized in certain aircraft applications, such as helicopters, to transmit torque between the engine and the rotor assembly. They allow for angular displacement and smooth transmission of power in the complex rotor systems of helicopters.
- Industrial machinery: Universal joints find applications in various types of industrial machinery, including manufacturing equipment, conveyors, pumps, and other power transmission systems. They enable torque transmission between non-aligned or angularly displaced shafts in industrial settings.
Please note that the specific usage of universal joints may vary depending on the vehicle design, drivetrain configuration, and application requirements. Different types of universal joints, such as single joint, double joint, constant velocity (CV) joint, or Cardan joint, may be employed based on the specific needs of the vehicle or machinery.


editor by CX 2024-02-18
China Custom Cardan Shaft Universal Joint for Agricultural Tractor Pto
Product Description
Cardan Shaft Universal Joint for Agricultural Tractor pto
Product Description
The cross joint is a widely utilized component in shafts that are responsible for transmitting rotary motion. It comprises a pair of hinges positioned in close proximity to each other, oriented at a precise 90° angle, and interconnected by means of a cross shaft. As a reputable manufacturer specializing in universal joints, we take pride in offering top-quality u-joints specifically designed for agricultural machinery. We extend a warm invitation to all customers to reach out to us and collaborate in establishing a mutually beneficial partnership.
Product Parameters:
Product Name: Economical universal joint cross bearing Joint Spider Kit
Keywords: Drive Shaft, Universal Joint Cardan Shaft, Propeller Shaft
Here is our advantages when compare to similar products from China:
| 1.Forged yokes make PTO shafts strong enough for usage and working; |
| 2.Internal sizes standard to confirm installation smooth; |
| 3.CE and ISO certificates to guarantee to quality of our goods; |
| 4.Strong and professional package to confirm the good situation when you receive the goods. |
Product Specifications
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
NingBo Hanon Technology Co.,ltd is a modern enterprise specilizing in the development,production,sales and services of Agricultural Parts like PTO shaft and Gearboxes. We adhere to the principle of ” High Quality, Customers’Satisfaction”, using advanced technology and equipments to ensure all the technical standards of transmission .We follow the principle of people first , trying our best to set up a pleasant surroundings and platform of performance for each employee. So everyone can be self-consciously active to join Hanon Machinery.
FAQ
1.WHAT’S THE PAYMENT TERM?
When we quote for you,we will confirm with you the way of transaction,FOB,CIFetc.<br> For mass production goods, you need to pay 30% deposit before producing and70% balance against copy of documents.The most common way is by T/T.
2.HOW TO DELIVER THE GOODS TO US?
Usually we will ship the goods to you by sea.
3.HOW LONG IS YPUR DELIVERY TOME AND SHIPMENT?
30-45days.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Cross Joint |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Agricultural Products Processing, Farmland Infrastructure, Tillage, Harvester, Planting and Fertilization, Grain Threshing, Cleaning and Drying, Pto Shaft |
| Material: | 20crmn /20crmnti |
| Power Source: | Pto Dirven Shaft |
| Weight: | 1.1-2.4kg |
| After-sales Service: | Online Support |
| Samples: |
US$ 20/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do you calculate the operating angles of a cardan joint?
The operating angles of a cardan joint can be calculated based on the angular misalignment between the input and output shafts. The operating angles are crucial for determining the joint’s performance and ensuring its proper functioning. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to calculate the operating angles of a cardan joint:
- Identify the Shaft Axes: Begin by identifying the axes of the input and output shafts connected by the cardan joint. These axes represent the rotational axes of the shafts.
- Measure the Angular Misalignments: Measure the angular misalignments between the shaft axes. The misalignments are typically measured in terms of angles, such as angular displacement in degrees or radians. There are three types of misalignments to consider:
- Angular Misalignment (α): This refers to the angular difference between the two shaft axes in the horizontal plane (X-Y plane).
- Parallel Misalignment (β): Parallel misalignment represents the offset or displacement between the two shaft axes in the vertical plane (Z-axis).
- Axial Misalignment (γ): Axial misalignment refers to the shift or displacement of one shaft along its axis with respect to the other shaft.
- Calculate the Operating Angles: Once the misalignments are measured, the operating angles can be calculated using trigonometric functions. The operating angles are:
- Operating Angle (θ): The operating angle is the total angular misalignment between the input and output shafts. It is calculated as the square root of the sum of the squares of the individual misalignments:
These calculated operating angles provide valuable information about the misalignment and geometry of the cardan joint. They help in selecting the appropriate joint size, determining the joint’s torque capacity, assessing potential operating issues, and ensuring proper installation and alignment of the joint within the system.
It is important to note that these calculations assume small operating angles and neglect any elastic deformation or non-linearities that may occur in the joint. In cases where larger operating angles or more precise calculations are required, advanced engineering techniques or software tools specific to cardan joint analysis may be employed.

How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint?
When retrofitting an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint, careful planning and consideration of various factors are necessary to ensure a successful integration. The retrofitting process involves modifying the system to accommodate the cardan joint’s requirements for torque transmission and misalignment compensation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to retrofit an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint:
- Evaluate the Existing System: Begin by thoroughly evaluating the existing mechanical system to understand its design, components, and operational requirements. Identify the areas where a cardan joint can be integrated effectively and assess the feasibility of retrofitting.
- Identify the Integration Points: Determine the specific locations within the system where the cardan joint will be installed. This could include areas where torque transmission or misalignment compensation is required, such as connections between shafts, pulleys, or other rotating components.
- Measurements and Compatibility: Take accurate measurements of the existing components and spaces where the cardan joint will be installed. Ensure that the dimensions and specifications of the cardan joint are compatible with the available space and the system’s requirements. Consider factors such as shaft sizes, torque ratings, misalignment angles, and operating conditions.
- Design Modifications: Based on the evaluation and measurements, make necessary design modifications to accommodate the cardan joint. This may involve modifying shaft ends, adding or removing components, or adjusting mounting positions. Ensure that the modifications do not compromise the structural integrity or functionality of the system.
- Installation and Alignment: Install the cardan joint at the identified integration points according to the manufacturer’s guidelines and engineering best practices. Pay attention to proper alignment, ensuring that the joint aligns with the shafts and other connected components. Precise alignment is crucial for efficient torque transmission and to prevent excessive wear or failure.
- Secure Mounting: Properly secure the cardan joint to the system, ensuring that it is firmly and securely mounted. Use appropriate fasteners, couplings, or brackets to hold the joint in place and prevent any movement or vibration that could affect its performance.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication and maintenance of the cardan joint. Proper lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the joint. Establish a maintenance schedule to regularly inspect and maintain the retrofit components to prevent any potential issues.
- Testing and Validation: After the retrofitting is complete, perform thorough testing to validate the functionality and performance of the retrofitted system. Test for torque transmission, misalignment compensation, and overall system operation. Monitor the system during operation to ensure that the cardan joint performs as expected and does not introduce any adverse effects.
It is essential to consult with experienced engineers or professionals specializing in retrofitting and cardan joint applications during the process. They can provide valuable guidance, expertise, and assistance in selecting the appropriate cardan joint, making design modifications, and ensuring a successful retrofit of the existing mechanical system.

How is a cardan joint different from other types of universal joints?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, is a specific type of universal joint design. While there are different variations of universal joints, the cardan joint has distinct characteristics that set it apart from other types. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a cardan joint differs from other universal joints:
1. Design and Structure: The cardan joint consists of two yokes and a cross-shaped member called the cross or spider. The yokes are typically fork-shaped and attached to the shafts, while the cross sits in the center, connecting the yokes. In contrast, other types of universal joints, such as the constant-velocity (CV) joint or Rzeppa joint, have different designs and structures. CV joints often use a combination of bearings and balls to transmit motion and maintain constant velocity, making them suitable for applications requiring smooth rotation without speed fluctuations.
2. Misalignment Compensation: One of the primary functions of a cardan joint is to accommodate misalignment between shafts. It can handle angular misalignment, axial misalignment, or a combination of both. The design of the cardan joint allows for the tilting of the cross as the input and output shafts rotate at different speeds. This tilting action compensates for misalignment and allows the joint to transmit motion. Other types of universal joints, such as the Oldham coupling or Hooke’s joint, have different mechanisms for compensating misalignment. For example, the Oldham coupling uses sliding slots and intermediate disks to accommodate misalignment, while Hooke’s joint uses a combination of rotating links and flexible connections.
3. Operating Range: Cardan joints are commonly used in applications where a wide range of operating angles is required. They can effectively transmit motion and torque at various angles, making them suitable for applications with non-collinear shafts. Other types of universal joints may have specific limitations or operating ranges. For instance, some types of CV joints are designed for constant velocity applications and are optimized for specific operating angles or speed ranges.
4. Applications: Cardan joints find applications in various industries, including automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, and more. They are commonly used in drivetrain systems, power transmission systems, and applications that require flexibility, misalignment compensation, and reliable motion transmission. Other types of universal joints have their own specific applications. For example, CV joints are commonly used in automotive applications, particularly in front-wheel drive systems, where they provide smooth and constant power transmission while accommodating suspension movements.
5. Limitations: While cardan joints offer flexibility and misalignment compensation, they also have certain limitations. At extreme operating angles, cardan joints can introduce non-uniform motion, increased vibration, backlash, and potential loss of efficiency. Other types of universal joints may have their own limitations and considerations depending on their specific design and application requirements.
In summary, a cardan joint, or universal joint, is a specific type of universal joint design that can accommodate misalignment between shafts and transmit motion at various angles. Its structure, misalignment compensation mechanism, operating range, and applications differentiate it from other types of universal joints. Understanding these distinctions is crucial when selecting the appropriate joint for a specific application.


editor by CX 2023-12-29
China Custom 20 Years High Quality Universal-Joint for Cardan Shaft
Product Description
Universal joint description
1>it is FOB HangZhou price . (also can send free to HangZhou HangZhou /ning bo ZheJiang and so on. warehouse .)
2>the material is 20cr good material , must not any complain from your customers. (also have 20Mn . 20cr Mn Ti )
3>our delivery time is 40days (with 20Gp container ) . very in time .
4> Can develop according to customer’s drawings or samples
5> OEM is available
6> Full range for the universal joint
7> Good quality and resonable price
Packaging & Delivery
the packing . Standard netural packing with carton.
Delivery detail: 30-45 working days,depend on the actual produce condition
FAQ
Q1: What is the location of your company?
A1: Our company is located in the CHINAMFG Zhou(Jin jiang) City ,Fu jian province,China.Welcome to visit our factory at anytime!
Q2: How does your factory do regarding quality control?
A2: Our standard QC system to control quality(TS16949 2016).
Q3: What is your delivery time?
A3: Usually within 30-40 days after the receipt of payment.Delivery time must depend on the actual produce condition.
Q4: What are your strengths?
A4: 1.We are the manufacturer,having competitive advantage in price.
2.A large part of money is put into advancing CNC equipments and product
R&D department annual,the performance of universal joint can be guaranteed.
3.About quality issues or follow-up after-sales service,we report directly to the boss.
Specification
There is no uniform standard for the specifications of cross assemblies. Please contact us directly for confirmation.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Condition: | New |
|---|---|
| Color: | Natural Color |
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
| Structure: | Single |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
| Type: | 20mn 20cr 20crmnti |
| Samples: |
US$ 49.7/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are cardan joints suitable for both high-torque and high-speed applications?
Cardan joints can be used in a variety of applications, but their suitability for high-torque and high-speed applications depends on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation of the considerations regarding the use of cardan joints in such scenarios:
1. High-Torque Applications: Cardan joints are generally well-suited for high-torque applications. The design of the joint allows for the transmission of significant torque between misaligned shafts. However, it is important to consider the specific torque requirements and operating conditions. Factors such as the size and type of the joint, the material used, and the application’s torque demands should be taken into account. In extremely high-torque applications, alternative coupling mechanisms such as gear couplings or universal joints may be more appropriate.
2. High-Speed Applications: While cardan joints can operate at relatively high speeds, there are some limitations to consider. At high rotational speeds, cardan joints can experience increased vibration, imbalance, and potential for fatigue failure. The rotating components of the joint can generate centrifugal forces, which can impact the balance and stability of the system. To mitigate these issues, careful design considerations, including balancing and vibration analysis, may be necessary. In some cases, alternative coupling mechanisms like flexible couplings or constant velocity joints may be better suited for high-speed applications.
3. Balancing and Vibration Control: Balancing the rotating components, such as the driveshaft and the joint itself, is essential for minimizing vibration issues in high-torque and high-speed applications. Imbalance can lead to increased vibrations, reduced efficiency, and potential damage to the joint and other system components. Proper balancing techniques, including dynamic balancing during manufacturing or precision balancing during installation, can help achieve smoother operation and minimize vibration problems.
4. Material Selection: The material used in the construction of the cardan joint plays a crucial role in its suitability for high-torque and high-speed applications. High-strength materials, such as alloy steels, are often preferred for their ability to handle increased torque loads. Additionally, materials with good fatigue resistance and high-speed capabilities can help ensure the durability and reliability of the joint in demanding applications.
5. Application-Specific Factors: The suitability of cardan joints for high-torque and high-speed applications also depends on the specific requirements and operating conditions of the application. Factors such as load characteristics, duty cycles, temperature, and environmental conditions should be considered. It is important to consult with the manufacturer or engineering experts to determine the appropriate size, type, and configuration of the cardan joint for a particular high-torque or high-speed application.
In summary, cardan joints can be suitable for both high-torque and high-speed applications, but careful consideration of factors such as torque requirements, speed limitations, balancing, material selection, and application-specific conditions is necessary. Evaluating these factors and consulting with experts can help determine the optimal coupling solution for a given high-torque or high-speed application.

What are the safety considerations when working with cardan joints?
Working with cardan joints requires careful attention to safety to prevent accidents, injuries, and equipment damage. Cardan joints are mechanical components used for torque transmission and misalignment compensation, and they operate under various loads and conditions. Here are important safety considerations to keep in mind when working with cardan joints:
- Proper Training and Knowledge: Ensure that individuals working with cardan joints have proper training and understanding of their operation, installation, and maintenance. Adequate knowledge of safe working practices, procedures, and potential hazards associated with cardan joints is crucial.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing, when handling cardan joints. PPE protects against potential hazards like flying debris, sharp edges, or accidental contact with rotating components.
- Lockout/Tagout: Before performing any maintenance or repair work involving cardan joints, follow lockout/tagout procedures to isolate and de-energize the system. This prevents accidental startup or movement of machinery, ensuring the safety of personnel working on or near the cardan joints.
- Secure Mounting and Fastening: Ensure that cardan joints are securely mounted and properly fastened to prevent unexpected movement or dislodgment during operation. Loose joints or fasteners can lead to component failure, sudden movements, or damage to other parts of the system.
- Torque and Load Limits: Adhere to the recommended torque and load limits specified by the manufacturer for the cardan joints. Exceeding these limits can result in premature wear, deformation, or failure of the joints, posing safety risks and compromising the overall system’s functionality.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Implement a regular inspection and maintenance program for the cardan joints. Inspect for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment, and address any issues promptly. Lubricate the joints according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure smooth operation and prevent excessive friction or overheating.
- Safe Handling and Lifting: When handling or lifting cardan joints, use appropriate lifting equipment and techniques. Cardan joints can be heavy, and improper lifting can lead to strain or injuries. Ensure that lifting devices have the capacity to handle the weight of the joints safely.
- Avoid Contact with Rotating Components: Never reach into or make contact with rotating components of a system that incorporates cardan joints while the system is in operation. Keep loose clothing, jewelry, and other items away from moving parts to prevent entanglement or injury.
- Proper Disposal of Used or Damaged Joints: Follow proper disposal procedures for used or damaged cardan joints. Consult local regulations and guidelines for the disposal of mechanical components to minimize environmental impact and ensure compliance with safety and waste management standards.
- Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Always refer to and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and warnings specific to the cardan joints being used. Manufacturers provide important safety information, installation procedures, and maintenance recommendations specific to their products.
By addressing these safety considerations, individuals can mitigate potential risks associated with working with cardan joints, promote a safe working environment, and ensure the reliable and efficient operation of the systems they are integrated into.

How does a cardan joint accommodate misalignment between shafts?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, is designed to accommodate misalignment between shafts. Its unique structure and mechanism allow for flexibility and compensation when there are angular or axial deviations between the input and output shafts. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a cardan joint accommodates misalignment:
The cardan joint consists of two yokes, typically fork-shaped, and a cross-shaped member called the cross or spider. The yokes are attached to the input and output shafts, while the cross sits in the center, connecting the yokes. The cross has four arms, and each arm has a bearing cap that holds a bearing. The bearings allow the cross to rotate within the yokes.
When the input and output shafts are perfectly aligned, the cardan joint operates in a straight configuration, and the cross remains in a centered position. However, when misalignment occurs, such as angular misalignment or axial misalignment, the cardan joint can flex and adjust to accommodate the deviation.
Angular Misalignment: When the input and output shafts are at an angle to each other, the cardan joint can accommodate the angular misalignment. As the input shaft rotates, it causes the yoke attached to it to rotate. This rotation is transmitted to the cross through the bearing cap and bearing. As the cross rotates, it causes the other yoke attached to the output shaft to rotate. The angular misalignment is compensated by the ability of the cross to tilt and follow the changing angles of the shafts. The bearings and bearing caps allow the cross to pivot and adjust its position, ensuring that the rotational motion is smoothly transmitted despite the misalignment.
Axial Misalignment: In cases of axial misalignment, where there is a difference in the axial position of the input and output shafts, the cardan joint can also accommodate the misalignment. The axial misalignment can cause the yokes to be slightly offset along the axis. However, the flexibility of the cardan joint allows the cross to adjust its position and maintain the connection between the yokes. The bearings and bearing caps within the cross allow it to move slightly along the axis, compensating for the axial misalignment and ensuring that the rotational motion can still be transmitted.
By allowing the cross to tilt and adjust its position, the cardan joint effectively accommodates misalignment between shafts. It provides the flexibility needed to transmit rotational motion and torque even when the input and output shafts are not perfectly aligned. The ability of the cardan joint to compensate for misalignment makes it a versatile component in various applications where flexibility and misalignment tolerance are required.


editor by CX 2023-12-28
China Good quality Top Quality Custom Mini Cardan Joint High Quality Double Cardan Joint Shaft Cross Bearing
Product Description
| Product Name | U joint | Place of origin | China |
| Brand | Mighty | Model | PB,PR,NB,CN |
PR-HS universal joint coupling
1.Application to all kinds of general mechanical situation, maximum rotate speed may reach1000~1500r/min.
Our Universal Joint widely used in multiaxle drilling machine ,construction machine,packaging machine,automobile.parking facility and paper machine,medical machine,farm machine
2.Have single -jointed type and bimodal type
3.Each point of the largest rotation angle can be 45o
4.Needle roller bearing,maintenance-free
5.The hole on the finshed product tolerance is H7 according to spline , hexagonal and square hole are available as long as you request.
Advantages:
• Many sizes available
• Max. angle 45 degree
• Max. speed 1000 rpm
• Available in various materials
• All subcomponents very precisely machined from bar: No cheap castings or powdered metal parts, resulting in better overall and more consistent performance
• Several subtle design innovations that optimize performance and reduce cost
• Could manufacture products according to your drawing
Variations offered:
• Materials for midsection(Cube and Pin): 20Cr,40Cr
• Materials for hub: 40Cr,45#steel
• Materials for spline: 45#steel
Quick-Change universal joint(Nature color )
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Video Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1years |
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | Natural Color, Silver, Black |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Structure: | Single |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the potential challenges in designing and manufacturing cardan joints?
Designing and manufacturing cardan joints can present several challenges that need to be carefully addressed to ensure the functionality, durability, and performance of the joint. Here’s a detailed explanation of the potential challenges in designing and manufacturing cardan joints:
- Misalignment Compensation: One of the primary challenges is designing the joint to effectively compensate for misalignments between the input and output shafts. The joint must accommodate angular, parallel, and axial misalignments while maintaining smooth torque transmission and minimizing stress concentrations.
- Load Capacity and Torque Transmission: Cardan joints are often used in applications that require the transmission of high torque and handling substantial loads. Designing the joint to withstand these loads while ensuring efficient torque transmission can be a challenge. It involves selecting appropriate materials, optimizing the joint’s geometry, and considering factors like bearing capacity and fatigue resistance.
- Bearing Arrangement: Proper bearing arrangement is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of the cardan joint. Ensuring adequate support and load distribution on the bearings can be challenging, especially in applications with high speeds, heavy loads, or extreme operating conditions. The design must consider factors such as bearing type, size, lubrication, and alignment to optimize performance.
- Compact Design: Cardan joints are often used in systems with limited space, requiring a compact design. Designing a compact joint while maintaining its mechanical properties, load capacity, and misalignment compensation capabilities can be challenging. It involves optimizing the joint’s dimensions, yoke or flange design, and component arrangement to fit within the given space constraints.
- Torsional Rigidity and Vibration: Cardan joints introduce some level of torsional compliance due to their flexible nature. Excessive torsional compliance can lead to vibrations, power loss, and reduced system performance. Designing the joint to provide adequate torsional rigidity while still accommodating misalignments is a challenge that requires careful consideration of the joint’s materials, cross-sectional geometry, and manufacturing processes.
- Manufacturability and Precision: Manufacturing cardan joints with the required precision and quality can be challenging. The joint’s components, such as yokes, cross members, and bearings, need to be manufactured to close tolerances and assembled accurately. Specialized manufacturing techniques, such as forging, machining, and heat treatment, may be required to achieve the desired mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy.
- Material Selection: Selecting the appropriate materials for cardan joints is critical for their performance and durability. The materials must possess high strength, fatigue resistance, and wear resistance to withstand the operating conditions and loads. Balancing material properties, cost considerations, and manufacturability can be challenging during the design process.
- Quality Control and Testing: Ensuring the quality and reliability of cardan joints requires comprehensive testing and quality control measures. Conducting tests to evaluate factors such as torque capacity, misalignment compensation, fatigue life, and dimensional accuracy can be challenging. Implementing effective quality control procedures throughout the manufacturing process is essential to identify and rectify any potential issues.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving engineering expertise in areas such as mechanical design, materials science, manufacturing processes, and quality assurance. Collaboration between design engineers, manufacturing engineers, and quality control personnel is crucial to overcome these challenges and produce high-quality cardan joints.
It is important to note that the specific challenges may vary depending on the application requirements, industry standards, and operating conditions. Continuous research, development, and advancements in design and manufacturing techniques contribute to overcoming these challenges and improving the performance and reliability of cardan joints.

How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint?
When retrofitting an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint, careful planning and consideration of various factors are necessary to ensure a successful integration. The retrofitting process involves modifying the system to accommodate the cardan joint’s requirements for torque transmission and misalignment compensation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to retrofit an existing mechanical system with a cardan joint:
- Evaluate the Existing System: Begin by thoroughly evaluating the existing mechanical system to understand its design, components, and operational requirements. Identify the areas where a cardan joint can be integrated effectively and assess the feasibility of retrofitting.
- Identify the Integration Points: Determine the specific locations within the system where the cardan joint will be installed. This could include areas where torque transmission or misalignment compensation is required, such as connections between shafts, pulleys, or other rotating components.
- Measurements and Compatibility: Take accurate measurements of the existing components and spaces where the cardan joint will be installed. Ensure that the dimensions and specifications of the cardan joint are compatible with the available space and the system’s requirements. Consider factors such as shaft sizes, torque ratings, misalignment angles, and operating conditions.
- Design Modifications: Based on the evaluation and measurements, make necessary design modifications to accommodate the cardan joint. This may involve modifying shaft ends, adding or removing components, or adjusting mounting positions. Ensure that the modifications do not compromise the structural integrity or functionality of the system.
- Installation and Alignment: Install the cardan joint at the identified integration points according to the manufacturer’s guidelines and engineering best practices. Pay attention to proper alignment, ensuring that the joint aligns with the shafts and other connected components. Precise alignment is crucial for efficient torque transmission and to prevent excessive wear or failure.
- Secure Mounting: Properly secure the cardan joint to the system, ensuring that it is firmly and securely mounted. Use appropriate fasteners, couplings, or brackets to hold the joint in place and prevent any movement or vibration that could affect its performance.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication and maintenance of the cardan joint. Proper lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and heat generation, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the joint. Establish a maintenance schedule to regularly inspect and maintain the retrofit components to prevent any potential issues.
- Testing and Validation: After the retrofitting is complete, perform thorough testing to validate the functionality and performance of the retrofitted system. Test for torque transmission, misalignment compensation, and overall system operation. Monitor the system during operation to ensure that the cardan joint performs as expected and does not introduce any adverse effects.
It is essential to consult with experienced engineers or professionals specializing in retrofitting and cardan joint applications during the process. They can provide valuable guidance, expertise, and assistance in selecting the appropriate cardan joint, making design modifications, and ensuring a successful retrofit of the existing mechanical system.

What is a cardan joint and how does it work?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, is a mechanical coupling used to transmit rotational motion between two shafts that are not collinear or have a constant angular relationship. It provides flexibility and accommodates misalignment between the shafts. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a cardan joint works:
A cardan joint consists of three main components: two yokes and a cross-shaped member called the cross or spider. The yokes are attached to the ends of the shafts that need to be connected, while the cross sits in the center, connecting the yokes.
The cross has four arms that intersect at a central point, forming a cross shape. Each arm has a bearing surface or trunnion on which the yoke of the corresponding shaft is mounted. The yokes are typically fork-shaped and have holes or bearings to accommodate the trunnions of the cross.
When the input shaft rotates, it transfers the rotational motion to one of the yokes. The cross, being connected to both yokes, transmits this motion to the other yoke and subsequently to the output shaft.
The key feature of a cardan joint is its ability to accommodate misalignment between the input and output shafts. This misalignment can be angular, axial, or both. As the input and output shafts are not collinear, the angles between the shafts cause the yokes to rotate at different speeds during operation.
The universal joint’s design allows the cross to rotate freely within the yokes, while still transferring motion from one shaft to the other. When the input shaft rotates, the yoke connected to it rotates with the shaft. This rotation causes the cross to tilt, as the other yoke is fixed to the output shaft. As a result, the angle between the arms of the cross changes, allowing for the compensation of misalignment.
As the cross tilts, the relative speeds of the yokes change, but the rotational motion is still transferred to the output shaft. The cardan joint effectively converts the input shaft’s rotation into a modified rotation at the output shaft, accommodating the misalignment between the two shafts.
It’s important to note that while cardan joints provide flexibility and can handle misalignment, they introduce certain limitations. These include non-uniform motion, increased vibration, backlash, and potential loss of efficiency at extreme operating angles. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of cardan joints.


editor by CX 2023-12-19
China supplier Made in China OEM Custom Stainless Steel Adjustable Shaft Coupling Double Cardan Universal Joint
Product Description
Product Description
|
Company Profile
HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Machinery Manufacture Co., Ltd., located in HangZhou, “China’s ancient copper capital”, is a “national high-tech enterprise”. At the beginning of its establishment, the company adhering to the “to provide clients with high quality products, to provide timely service” concept, adhere to the “everything for the customer, make customer excellent supplier” for the mission.
Certifications
Q: Where is your company located ?
A: HangZhou ZheJiang .
Q: How could l get a sample?
A: Before we received the first order, please afford the sample cost and express fee. we will return the sample cost back
to you within your first order.
Q: Sample time?
A: Existing items: within 20-60 days.
Q: Whether you could make our brand on your products?
A: Yes. We can print your Logo on both the products and the packages if you can meet our MOQ.
Q: How to guarantee the quality of your products?
A: 1) stict detection during production. 2) Strict completely inspecion on products before shipment and intact product
packaging ensured.
Q: lf my drawings are safe?
A: Yes ,we can CHINAMFG NDA.
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Nonstandard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 8-24 |
| Torque: | OEM/ODM/Customized |
| Bore Diameter: | OEM/ODM/Customized |
| Speed: | OEM/ODM/Customized |
| Structure: | Flexible |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the potential limitations or drawbacks of using cardan joints?
While cardan joints offer numerous advantages in transmitting rotational motion between misaligned shafts, they also have certain limitations and drawbacks to consider. Here are some potential limitations associated with the use of cardan joints:
- Angular Limitations: Cardan joints have limited angularity or operating angles. They are designed to operate within specific angular ranges, and exceeding these angles can cause accelerated wear, increased vibration, and potential joint failure. Extreme operating angles can lead to binding, decreased efficiency, and reduced power transmission capacity. In applications where large operating angles are required, alternative flexible coupling mechanisms or constant velocity joints may be more suitable.
- Backlash and Torsional Stiffness: Cardan joints inherently exhibit some degree of backlash, which is the clearance or free play between the mating components. This can result in a slight delay in power transmission and can affect the precision of motion in certain applications. Additionally, cardan joints may have higher torsional stiffness compared to other coupling mechanisms, which can transmit higher vibrations and shocks to the connected components.
- Maintenance Requirements: Cardan joints require regular maintenance to ensure proper lubrication, alignment, and performance. The lubricant needs to be regularly replenished or replaced, and the joint should be inspected for wear, misalignment, or other issues. Failure to perform adequate maintenance can result in premature wear, reduced efficiency, and potential joint failure. Maintenance procedures may require specialized tools and expertise.
- Space and Weight: Cardan joints can occupy a significant amount of space due to their design and the need for perpendicular shafts. In applications with limited space constraints, finding suitable locations for cardan joints can be challenging. Additionally, the weight of cardan joints, especially in heavy-duty applications, can add to the overall weight of the system, which may have implications for fuel efficiency, payload capacity, or overall performance.
- Cost: Cardan joints, particularly high-quality and precision-engineered ones, can be relatively expensive compared to other coupling mechanisms. The complex design, manufacturing tolerances, and specialized materials involved contribute to their higher cost. In cost-sensitive applications, alternative coupling solutions may be considered if the angular limitations and other drawbacks of cardan joints are not critical.
- High-Speed Limitations: At high rotational speeds, cardan joints can experience increased vibration, imbalance, and potential for fatigue failure. The rotating components of the joint can generate centrifugal forces that impact the balance and stability of the system. In high-speed applications, careful design considerations, including balancing and vibration analysis, may be necessary to mitigate these issues.
It is important to evaluate the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and limitations when considering the use of cardan joints. While they offer versatility and flexibility in many scenarios, alternative coupling mechanisms may be more suitable in cases where the limitations and drawbacks of cardan joints pose significant challenges.

Can cardan joints be used in pumps and compressors?
Yes, cardan joints can be used in pumps and compressors to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between the driving and driven shafts. They offer several advantages that make them suitable for these applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Torque Transmission: Pumps and compressors often require the transmission of torque from the driving motor or engine to the rotating shaft that operates the pump or compressor. Cardan joints excel at transmitting torque efficiently, even at significant angles and misalignments. They can handle the high torque loads typically encountered in pump and compressor applications.
2. Misalignment Compensation: Cardan joints are designed to accommodate misalignments between the driving and driven shafts. In pumps and compressors, misalignments can occur due to factors such as thermal expansion, structural deflection, or assembly tolerances. Cardan joints can compensate for these misalignments, ensuring smooth and reliable torque transmission without excessive stress or wear on the connected components.
3. Angular Flexibility: Pumps and compressors often require flexibility in their drivetrain to adapt to different installation configurations or accommodate dynamic movements. Cardan joints provide rotational freedom and allow for angular movement, enabling the pump or compressor to adjust to changing requirements. Their universal joint design allows for smooth rotation and accommodates the required range of motion.
4. Shock and Vibration Absorption: Pumps and compressors can generate significant vibrations and shocks during operation. Cardan joints help absorb these vibrations and shocks, reducing their transmission to the rest of the drivetrain. This feature helps protect other components, such as bearings and seals, from excessive stress and wear, enhancing the overall reliability and lifespan of the pump or compressor.
5. Compact Design: Cardan joints have a relatively compact design, making them suitable for integration into pump and compressor systems where space is often limited. Their compact size allows for efficient packaging within the equipment, optimizing overall design and minimizing footprint. This is especially beneficial in applications where multiple joints are required within a confined space.
6. Durability and Strength: Pumps and compressors operate under demanding conditions, including high pressures, heavy loads, and continuous operation. Cardan joints are often constructed using durable materials such as alloy steels or high-strength alloys, providing the necessary strength and resilience to withstand these conditions. They are designed to handle the demanding loads and forces encountered in pump and compressor applications.
7. Easy Maintenance and Serviceability: Cardan joints are generally low-maintenance components. They require periodic inspection, lubrication, and replacement of worn parts, but their design often allows for easy access and replacement if needed. This facilitates maintenance activities and minimizes downtime in pump and compressor systems.
8. Cost-Effectiveness: Cardan joints offer a cost-effective solution for torque transmission in pump and compressor applications. Their durability, reliability, and long service life contribute to reduced maintenance and replacement costs. Additionally, their ability to accommodate misalignments helps minimize wear on other drivetrain components, further reducing overall maintenance expenses.
When integrating cardan joints into pump and compressor systems, it is important to consider the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and load characteristics. Proper design, selection, and installation practices should be followed to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Consulting with engineers or experts specializing in drivetrain systems and pump/compressor design can provide valuable insights and guidance on the selection, integration, and maintenance of cardan joints for these applications.

What are the benefits of using a cardan joint in a mechanical system?
A cardan joint, also known as a universal joint or U-joint, offers several benefits when used in a mechanical system. These benefits contribute to efficient power transmission, flexibility, and the ability to accommodate misalignment. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using a cardan joint:
- Misalignment Compensation: One of the primary advantages of a cardan joint is its ability to accommodate misalignment between the input and output shafts. The flexible design of the joint allows for angular misalignment, axial misalignment, or a combination of both. This capability is particularly useful in applications where the shafts are not perfectly aligned, or where movement and flexibility are required.
- Power Transmission: Cardan joints are efficient in transmitting rotational motion and torque between non-collinear shafts. They maintain a constant velocity ratio between the input and output shafts, ensuring smooth power transmission. This feature is especially beneficial in applications where a consistent and uninterrupted transfer of power is essential, such as drivetrain systems in vehicles and industrial machinery.
- Flexibility and Articulation: The flexible nature of a cardan joint allows for articulation and movement between the connected shafts. It enables the mechanical system to adapt to changing angles, positions, or misalignment during operation. This flexibility is particularly advantageous in applications that involve variable operating conditions, such as vehicles navigating uneven terrain or machinery with moving components.
- Torsional Vibration Damping: Cardan joints can help dampen torsional vibrations that may occur in a mechanical system. The cross-shaped design of the joint, combined with the flexibility of the bearings, can absorb and mitigate torsional vibrations, reducing stress on the components and improving overall system performance and durability.
- Compact Design: Cardan joints have a relatively compact design, allowing them to be easily integrated into various mechanical systems. They occupy less space compared to other types of power transmission components, making them suitable for applications with limited installation space or where weight reduction is a concern.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cardan joints are generally cost-effective compared to alternative power transmission solutions. Their simple design, ease of manufacturing, and wide availability contribute to their affordability. Additionally, their durability and ability to handle misalignment can reduce the need for frequent maintenance or replacement, leading to cost savings in the long run.
These benefits make cardan joints a versatile and valuable component in numerous mechanical systems across industries such as automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, marine, and more. Their ability to transmit power efficiently, accommodate misalignment, and provide flexibility contribute to improved performance, reliability, and operational efficiency of the overall mechanical system.


editor by CX 2023-12-01